|
Size: 56871
Comment:
|
Size: 58516
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 6: | Line 6: |
| Line 9: | Line 10: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 58: | Line 59: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 100: | Line 101: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 116: | Line 117: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 136: | Line 137: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 164: | Line 165: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 237: | Line 238: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 250: | Line 251: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 348: | Line 349: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 454: | Line 455: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 456: | Line 457: |
| # polar coordinates #(x,y)=(u*cos(v),u*sin(v)); (u_range,v_range)=([0..6],[0..2*pi,step=pi/12]) # weird example (x,y)=(u^2-v^2,u*v+cos(u*v)); (u_range,v_range)=([-5..5],[-5..5]) thickness=4 square_length=.05 |
|
| Line 459: | Line 469: |
| def trans(x=input_box(u^2-v^2, label="x=",type=SR), \ y=input_box(u*v+cos(u*v), label="y=",type=SR), \ t_val=slider(0,10,0.2,6, label="Length of curves"), \ |
def trans(x=input_box(x, label="x",type=SR), y=input_box(y, label="y",type=SR), |
| Line 464: | Line 473: |
| u_range=input_box(range(-5,5,1), label="u lines"), v_range=input_box(range(-5,5,1), label="v lines")): thickness=4 u_val = min(u_range)+(max(u_range)-min(u_range))*u_percent v_val = min(v_range)+(max(v_range)-min(v_range))*v_percent t_min = -t_val t_max = t_val g1=sum([parametric_plot((i,v), (v,t_min,t_max), rgbcolor=(1,0,0)) for i in u_range]) g2=sum([parametric_plot((u,i), (u,t_min,t_max), rgbcolor=(0,0,1)) for i in v_range]) vline_straight=parametric_plot((u,v_val), (u,t_min,t_max), rgbcolor=(0,0,1), linestyle='-',thickness=thickness) uline_straight=parametric_plot((u_val, v), (v,t_min,t_max),rgbcolor=(1,0,0), linestyle='-',thickness=thickness) (g1+g2+vline_straight+uline_straight).save("uv_coord.png",aspect_ratio=1, figsize=[5,5], axes_labels=['$u$','$v$']) xuv = fast_float(x,'u','v') yuv = fast_float(y,'u','v') xvu = fast_float(x,'v','u') yvu = fast_float(y,'v','u') g3=sum([parametric_plot((partial(xuv,i),partial(yuv,i)), (v,t_min,t_max), rgbcolor=(1,0,0)) for i in u_range]) g4=sum([parametric_plot((partial(xvu,i),partial(yvu,i)), (u,t_min,t_max), rgbcolor=(0,0,1)) for i in v_range]) uline=parametric_plot((partial(xuv,u_val),partial(yuv,u_val)),(v,t_min,t_max),rgbcolor=(1,0,0), linestyle='-',thickness=thickness) vline=parametric_plot((partial(xvu,v_val),partial(yvu,v_val)), (u,t_min,t_max), rgbcolor=(0,0,1), linestyle='-',thickness=thickness) (g3+g4+vline+uline).save("xy_coord.png", aspect_ratio=1, figsize=[5,5], axes_labels=['$x$','$y$']) print jsmath("x=%s, \: y=%s"%(latex(x), latex(y))) print "<html><table><tr><td><img src='cell://uv_coord.png'/></td><td><img src='cell://xy_coord.png'/></td></tr></table></html>" }}} |
t_val=slider(0,10,0.2,6, label="Length"), u_range=input_box(u_range, label="u lines"), v_range=input_box(v_range, label="v lines")): x(u,v)=x y(u,v)=y u_val = min(u_range)+(max(u_range)-min(u_range))*u_percent v_val = min(v_range)+(max(v_range)-min(v_range))*v_percent t_min = -t_val t_max = t_val uvplot=sum([parametric_plot((i,v), (v,t_min,t_max), color='red',axes_labels=['u','v'],figsize=[5,5]) for i in u_range]) uvplot+=sum([parametric_plot((u,i), (u,t_min,t_max), color='blue',axes_labels=['u','v']) for i in v_range]) uvplot+=parametric_plot((u,v_val), (u,t_min,t_max), rgbcolor=(0,0,1), linestyle='-',thickness=thickness) uvplot+=parametric_plot((u_val, v), (v,t_min,t_max),rgbcolor=(1,0,0), linestyle='-',thickness=thickness) pt=vector([u_val,v_val]) du=vector([(t_max-t_min)*square_length,0]) dv=vector([0,(t_max-t_min)*square_length]) uvplot+=polygon([pt,pt+dv,pt+du+dv,pt+du],color='purple',alpha=0.7) uvplot+=line([pt,pt+dv,pt+du+dv,pt+du],color='green') T(u,v)=(x,y) xuv = fast_float(x,'u','v') yuv = fast_float(y,'u','v') xvu = fast_float(x,'v','u') yvu = fast_float(y,'v','u') xyplot=sum([parametric_plot((partial(xuv,i),partial(yuv,i)), (v,t_min,t_max), color='red', axes_labels=['x','y'],figsize=[5,5]) for i in u_range]) xyplot+=sum([parametric_plot((partial(xvu,i),partial(yvu,i)), (u,t_min,t_max), color='blue') for i in v_range]) xyplot+=parametric_plot((partial(xuv,u_val),partial(yuv,u_val)),(v,t_min,t_max),color='red', linestyle='-',thickness=thickness) xyplot+=parametric_plot((partial(xvu,v_val),partial(yvu,v_val)), (u,t_min,t_max), color='blue', linestyle='-',thickness=thickness) jacobian=abs(T.diff().det()).simplify_full() t_vals=[0..1,step=t_val*.01] vertices=[(x(*c),y(*c)) for c in [pt+t*dv for t in t_vals]] vertices+=[(x(*c),y(*c)) for c in [pt+dv+t*du for t in t_vals]] vertices+=[(x(*c),y(*c)) for c in [pt+(1-t)*dv+du for t in t_vals]] vertices+=[(x(*c),y(*c)) for c in [pt+(1-t)*du for t in t_vals]] xyplot+=polygon(vertices,color='purple',alpha=0.7) xyplot+=line(vertices,color='green') html("$T(u,v)=%s$"%(latex(T(u,v)))) html("Jacobian: $%s$"%latex(jacobian(u,v))) html("A very small region in $xy$ plane is approximately %0.4g times the size of the corresponding region in the $uv$ plane"%jacobian(u_val,v_val).n()) html.table([[uvplot,xyplot]])}}} |
| Line 496: | Line 521: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 519: | Line 544: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 546: | Line 571: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 572: | Line 597: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 587: | Line 612: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 633: | Line 658: |
| {{{ from scipy.special.orthogonal import p_roots |
{{{#!sagecell import scipy import numpy from scipy.special.orthogonal import p_roots, t_roots, u_roots |
| Line 643: | Line 670: |
| 'Chebyshev': {'w': 1/sqrt(1-x**2), 'xmin': -1, 'xmax': 1, 'func': t_roots}, 'Chebyshev2': {'w': sqrt(1-x**2), 'xmin': -1, 'xmax': 1, 'func': u_roots}, 'Trapezoid': {'w': 1, 'xmin': -1, 'xmax': 1, 'func': lambda n: (linspace(-1r,1,n), numpy.array([1.0r]+[2.0r]*(n-2)+[1.0r])*1.0r/n)}, 'Simpson': {'w': 1, 'xmin': -1, 'xmax': 1, 'func': lambda n: (linspace(-1r,1,n), numpy.array([1.0r]+[4.0r,2.0r]*int((n-3.0r)/2.0r)+[4.0r,1.0r])*2.0r/(3.0r*n))}} |
'Chebyshev': {'w': 1/sqrt(1-x**2), 'xmin': -1, 'xmax': 1, 'func': t_roots}, 'Chebyshev2': {'w': sqrt(1-x**2), 'xmin': -1, 'xmax': 1, 'func': u_roots}, 'Trapezoid': {'w': 1, 'xmin': -1, 'xmax': 1, 'func': lambda n: (linspace(-1r,1,n), numpy.array([1.0r]+[2.0r]*(n-2)+[1.0r])*1.0r/n)}, 'Simpson': {'w': 1, 'xmin': -1, 'xmax': 1, 'func': lambda n: (linspace(-1r,1,n), numpy.array([1.0r]+[4.0r,2.0r]*int((n-3.0r)/2.0r)+[4.0r,1.0r])*2.0r/(3.0r*n))}} |
| Line 650: | Line 680: |
| return polygon([(center-width2,0),(center+width2,0),(center+width2,height),(center-width2,height)],**kwds) | return polygon([(center-width2,0), (center+width2,0),(center+width2,height),(center-width2,height)],**kwds) |
| Line 654: | Line 685: |
| def weights(n=slider(1,30,1,default=10),f=input_box(default=3*x+cos(10*x)),show_method=["Legendre", "Chebyshev", "Chebyshev2", "Trapezoid","Simpson"]): | def weights(n=slider(1,30,1,default=10),f=input_box(default=3*x+cos(10*x),type=SR), show_method=["Legendre", "Chebyshev", "Chebyshev2", "Trapezoid","Simpson"]): |
| Line 663: | Line 695: |
| scaled_ff = fast_float(scaled_func) | scaled_ff = fast_float(scaled_func, 'x') |
| Line 671: | Line 703: |
| stems = sum(line([(x,0),(x,scaled_ff(x))],rgbcolor=(1-y,1-y,1-y),thickness=2,markersize=6,alpha=y) for x,y in coords_scaled) points = sum([point([(x,0),(x,scaled_ff(x))],rgbcolor='black',pointsize=30) for x,_ in coords]) |
stems = sum(line([(x,0),(x,scaled_ff(x))],rgbcolor=(1-y,1-y,1-y), thickness=2,markersize=6,alpha=y) for x,y in coords_scaled) points = sum([point([(x,0), (x,scaled_ff(x))],rgbcolor='black',pointsize=30) for x,_ in coords]) |
| Line 677: | Line 711: |
| show(graph,xmin=plot_min,xmax=plot_max) | show(graph,xmin=plot_min,xmax=plot_max,aspect_ratio="auto") |
| Line 685: | Line 719: |
| html("$$\sum_{i=1}^{i=%s}w_i\left(%s\\right)= %s\\approx %s =\int_{-1}^{1}%s \,dx$$"%(n,latex(f.subs(x="x_i")), approximation, integral, latex(scaled_func))) | html("$$\sum_{i=1}^{i=%s}w_i\left(%s\\right)= %s\\approx %s =\int_{-1}^{1}%s \,dx$$"%(n, latex(f), approximation, integral, latex(scaled_func))) |
| Line 698: | Line 733: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 810: | Line 845: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 847: | Line 882: |
| velocity = derivative( position(t) ) acceleration = derivative(velocity(t)) |
velocity = derivative( position(t), t) acceleration = derivative(velocity(t), t) |
| Line 850: | Line 885: |
| speed_deriv = derivative(speed) | speed_deriv = derivative(speed, t) |
| Line 852: | Line 887: |
| dT = derivative(tangent(t)) | dT = derivative(tangent(t), t) |
| Line 855: | Line 890: |
| ## dB = derivative(binormal(t)) | ## dB = derivative(binormal(t), t) |
| Line 936: | Line 971: |
| {{{ | http://www.sagenb.org/home/pub/2828/ {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 944: | Line 981: |
| ## An updated version of this worksheet may be available at http://sagenb.mc.edu | |
| Line 970: | Line 1008: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 1007: | Line 1045: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 1060: | Line 1098: |
| {{{ %hide %auto |
{{{#!sagecell |
| Line 1121: | Line 1157: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 1159: | Line 1195: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 1197: | Line 1233: |
| {{{ | http://www.sagenb.org/home/pub/2829/ {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 1201: | Line 1239: |
| ## ## ## An updated version of this worksheet may be available at http://sagenb.mc.edu |
|
| Line 1299: | Line 1340: |
| {{{ | http://www.sagenb.org/home/pub/2826/ {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 1356: | Line 1399: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 1375: | Line 1418: |
| {{{ | http://www.sagenb.org/home/pub/2827/ {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 1382: | Line 1427: |
| ## ## An updated version of this worksheet may be available at http://sagenb.mc.edu |
Sage Interactions - Calculus
goto interact main page
Contents
-
Sage Interactions - Calculus
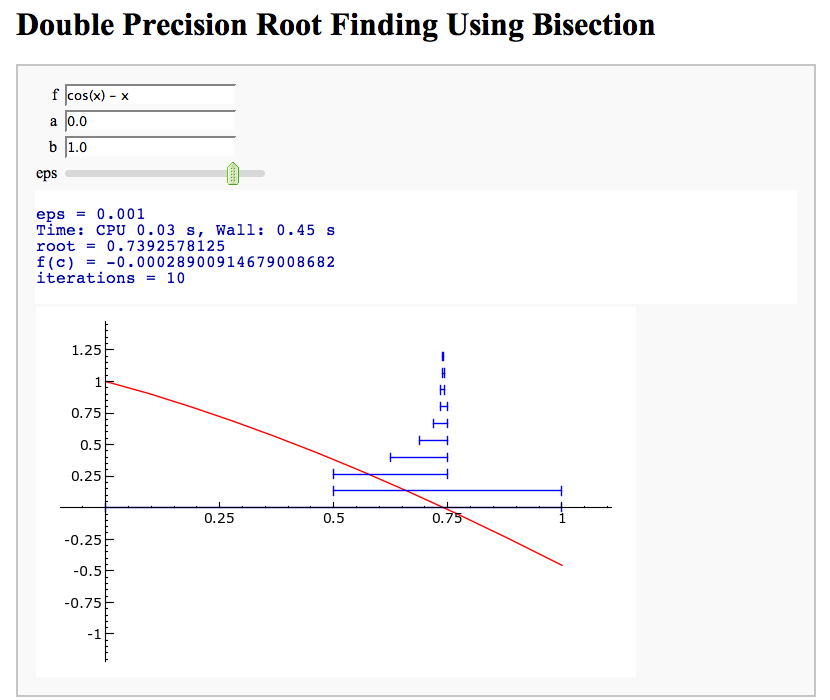
- Root Finding Using Bisection
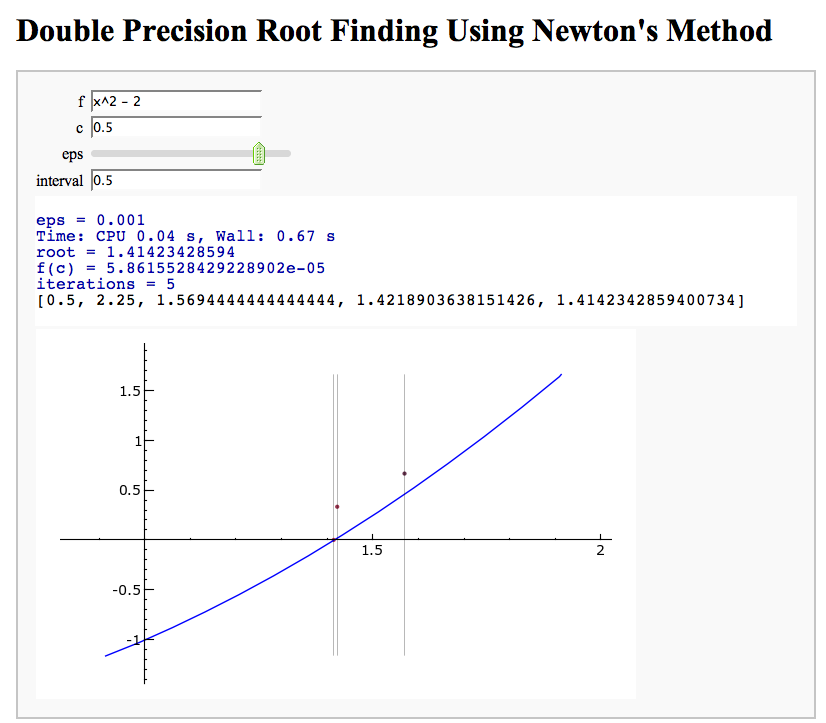
- Newton's Method
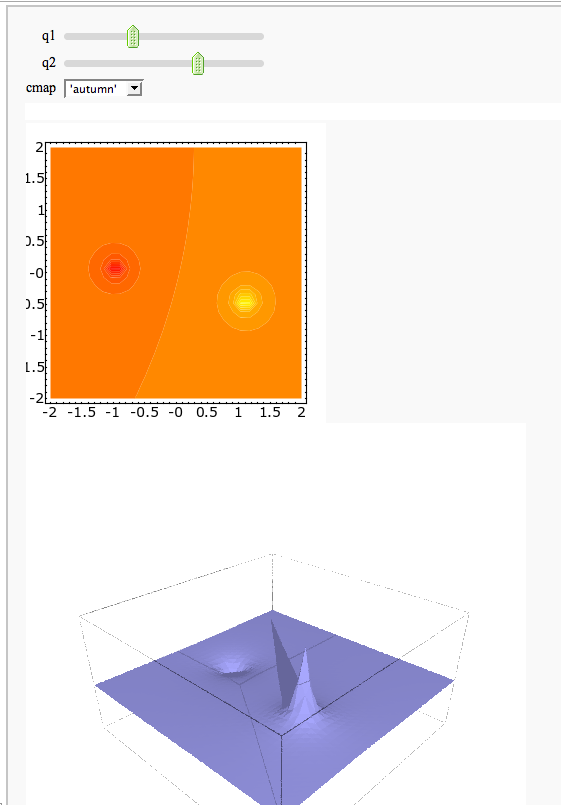
- A contour map and 3d plot of two inverse distance functions
- A simple tangent line grapher
- Numerical integrals with the midpoint rule
- Numerical integrals with various rules
- Some polar parametric curves
- Function tool
- Newton-Raphson Root Finding
- Coordinate Transformations
- Taylor Series
- Illustration of the precise definition of a limit
- A graphical illustration of sin(x)/x -> 1 as x-> 0
- Quadric Surface Plotter
- The midpoint rule for numerically integrating a function of two variables
- Gaussian (Legendre) quadrature
- Vector Calculus, 2-D Motion
- Vector Calculus, 3-D Motion
- Multivariate Limits by Definition
- Directional Derivatives
- 3D graph with points and curves
- Approximating function in two variables by differential
- Taylor approximations in two variables
- Volumes over non-rectangular domains
- Lateral Surface Area
- Parametric surface example
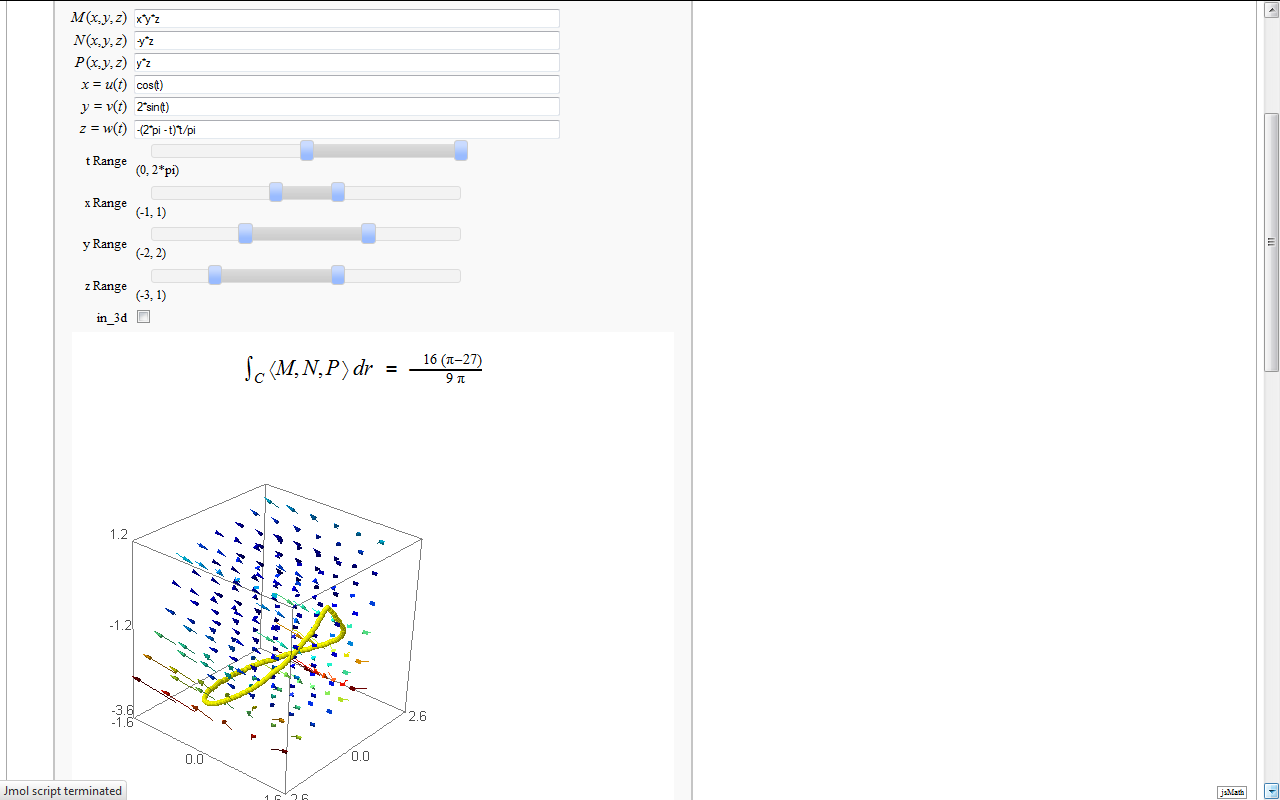
- Line Integrals in 3D Vector Field
Root Finding Using Bisection
by William Stein
Newton's Method
Note that there is a more complicated Newton's method below.
by William Stein
http://sagenb.org/home/pub/2824/
A contour map and 3d plot of two inverse distance functions
by William Stein
http://sagenb.org/home/pub/2823/
A simple tangent line grapher
by Marshall Hampton
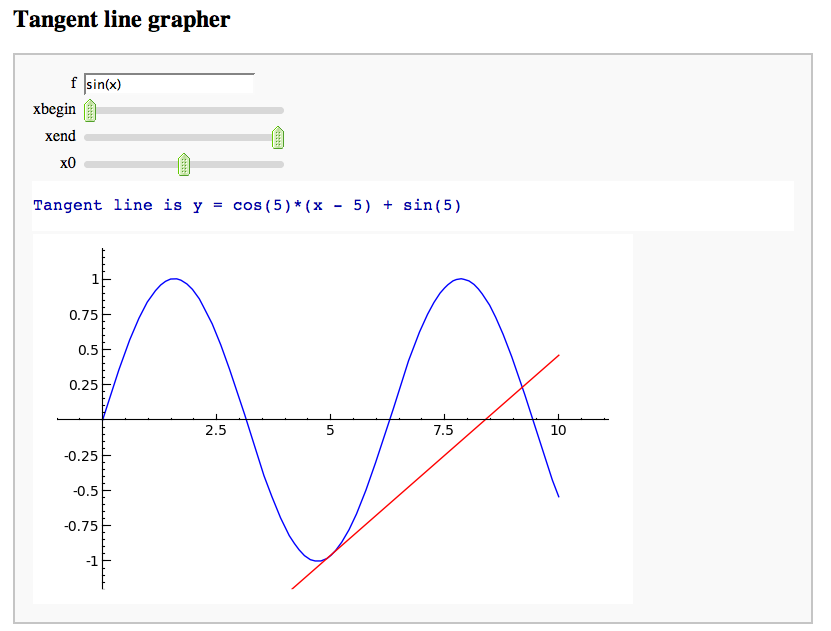
Numerical integrals with the midpoint rule
by Marshall Hampton

Numerical integrals with various rules
by Nick Alexander (based on the work of Marshall Hampton)
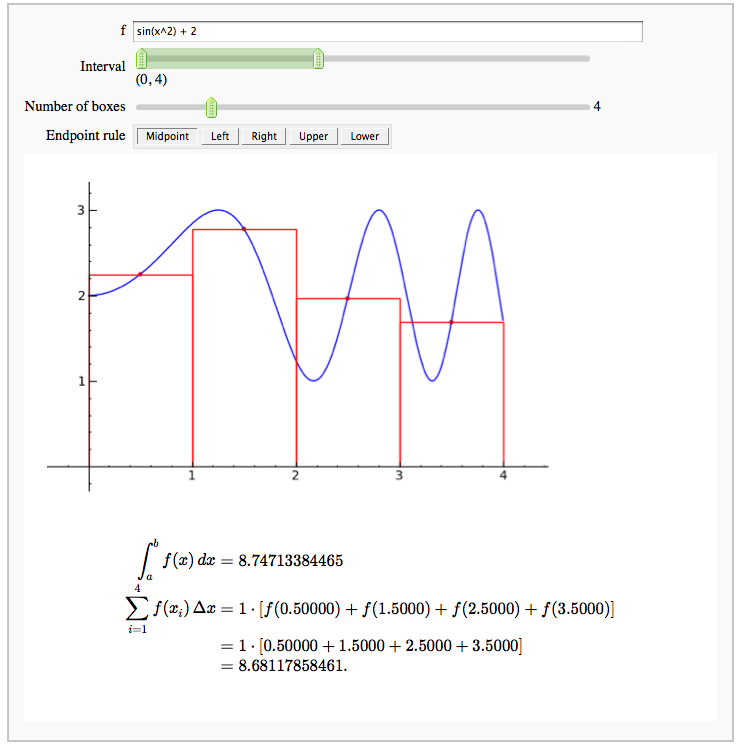
Some polar parametric curves
by Marshall Hampton. This is not very general, but could be modified to show other families of polar curves.
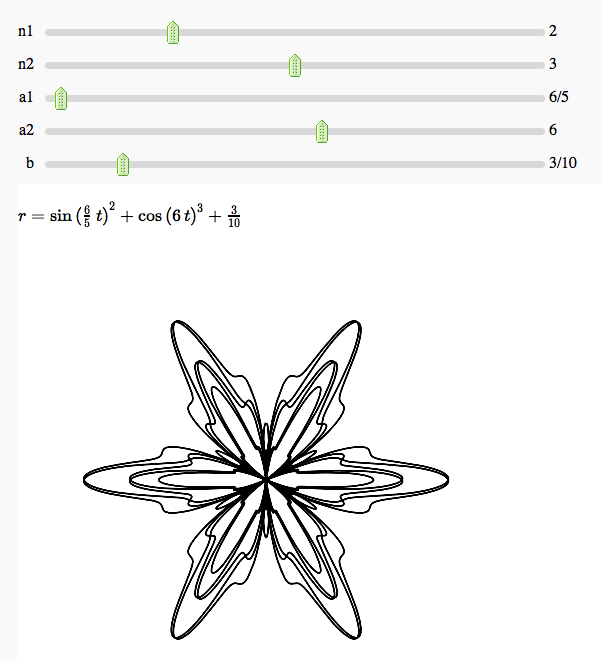
Function tool
Enter symbolic functions f, g, and a, a range, then click the appropriate button to compute and plot some combination of f, g, and a along with f and g. This is inspired by the Matlab funtool GUI.
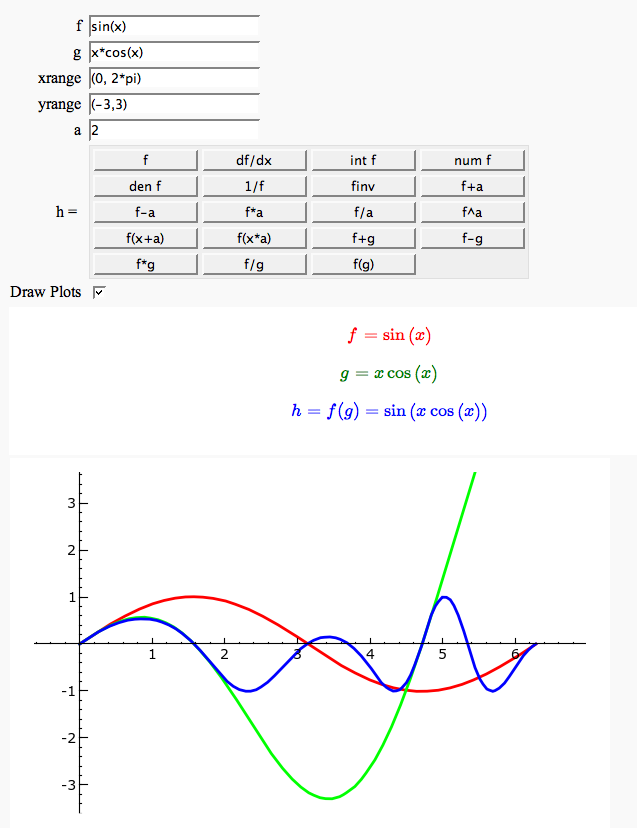
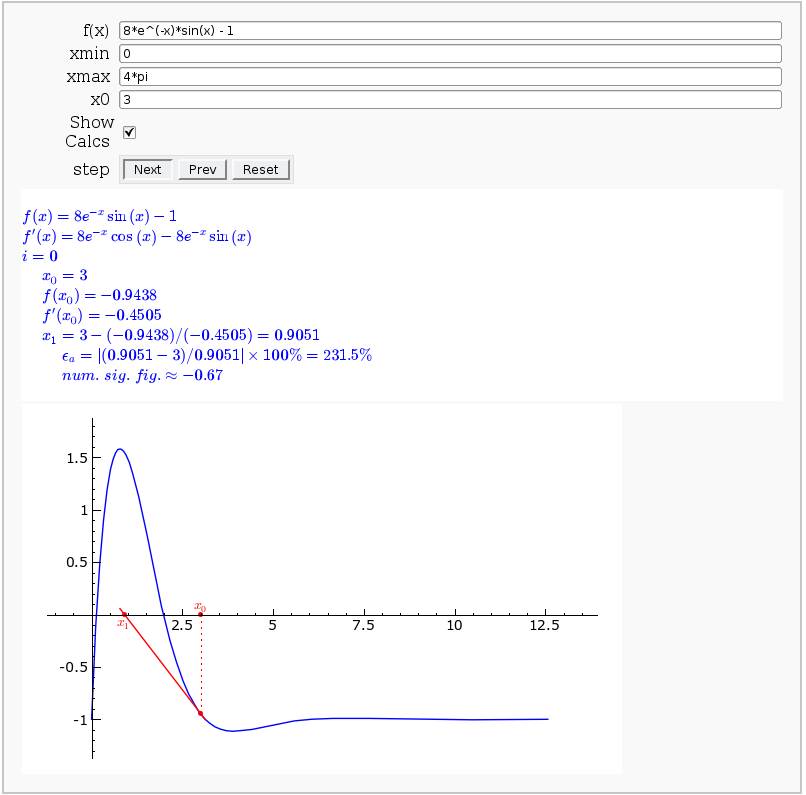
Newton-Raphson Root Finding
by Neal Holtz
This allows user to display the Newton-Raphson procedure one step at a time. It uses the heuristic that, if any of the values of the controls change, then the procedure should be re-started, else it should be continued.
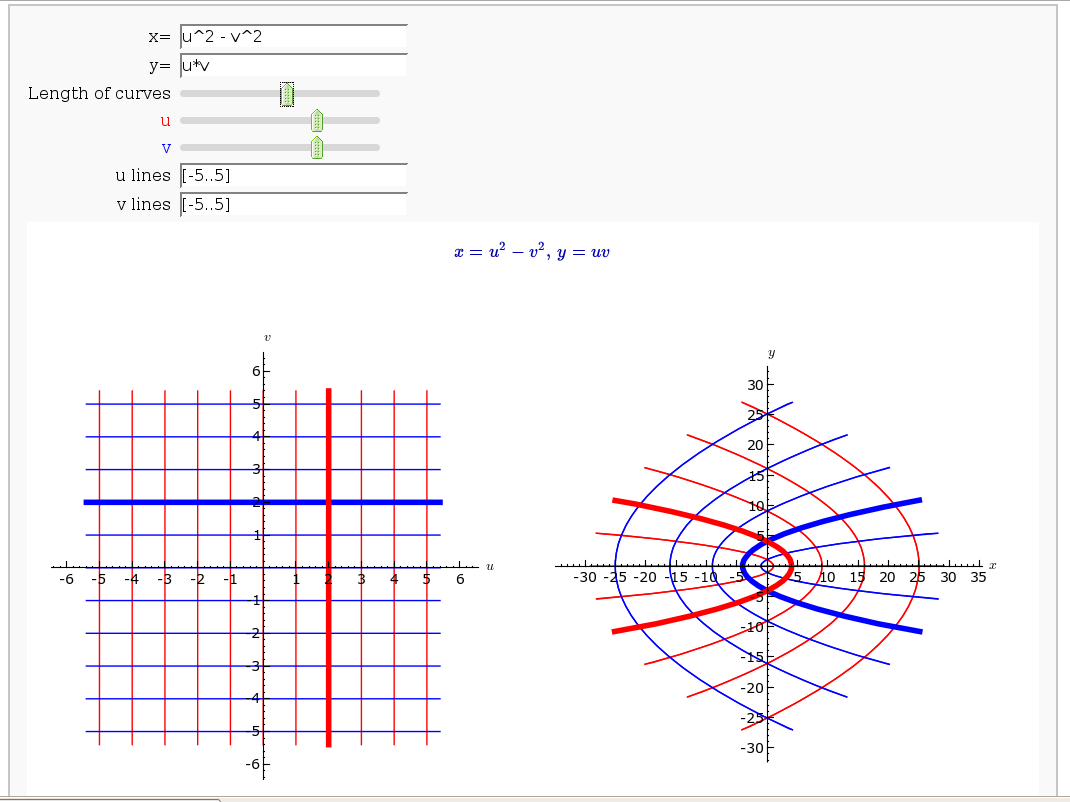
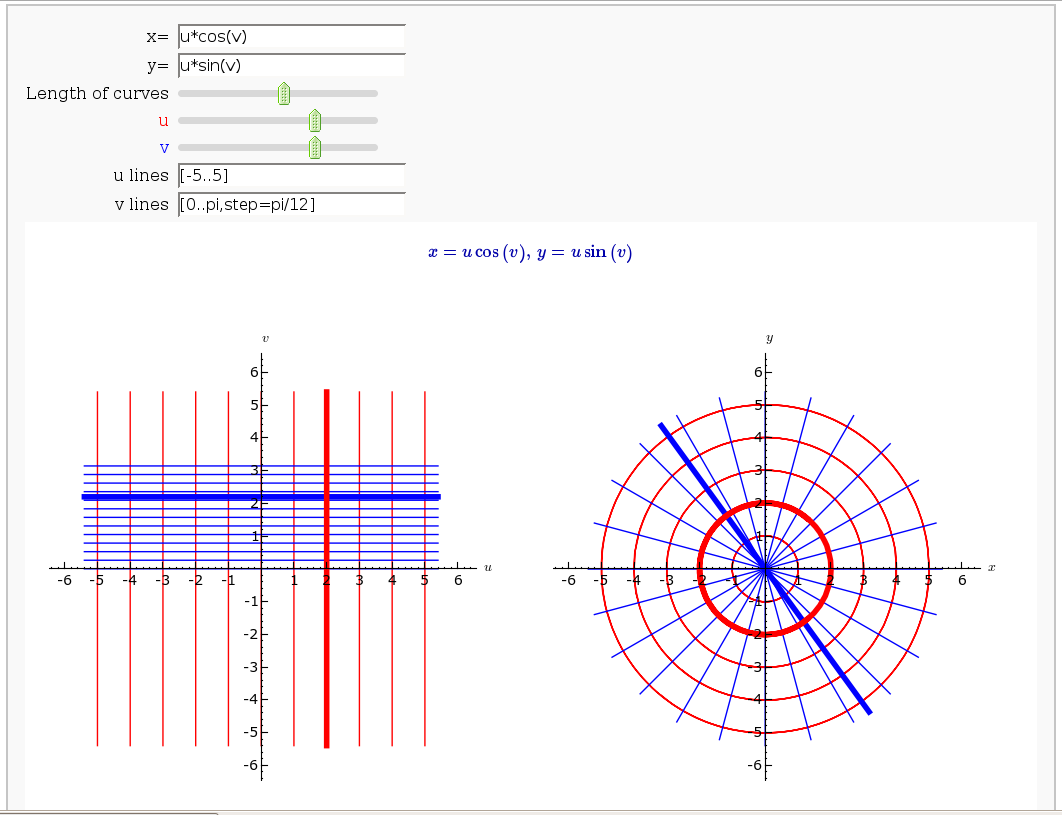
Coordinate Transformations
by Jason Grout
Taylor Series
by Harald Schilly
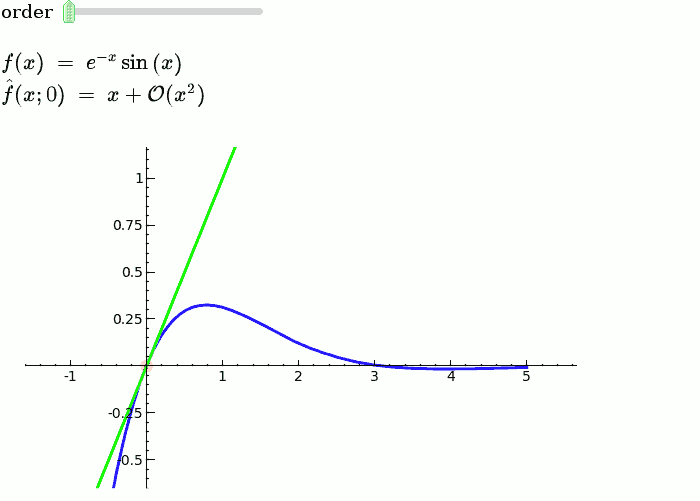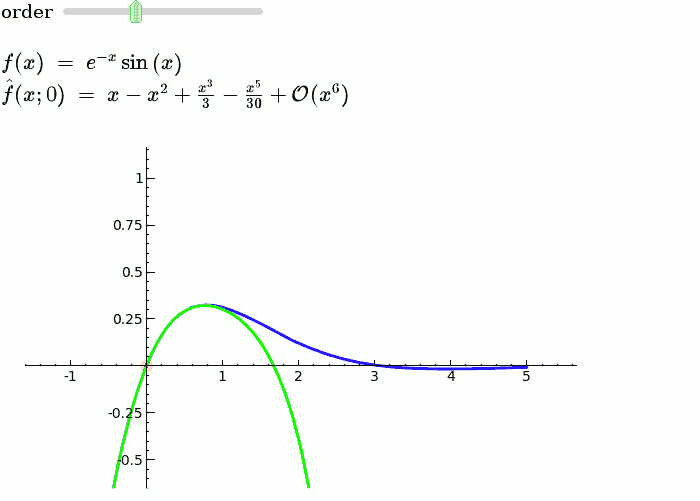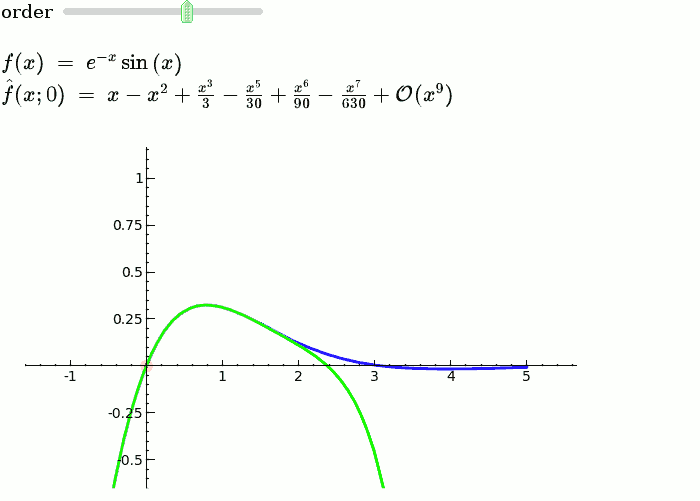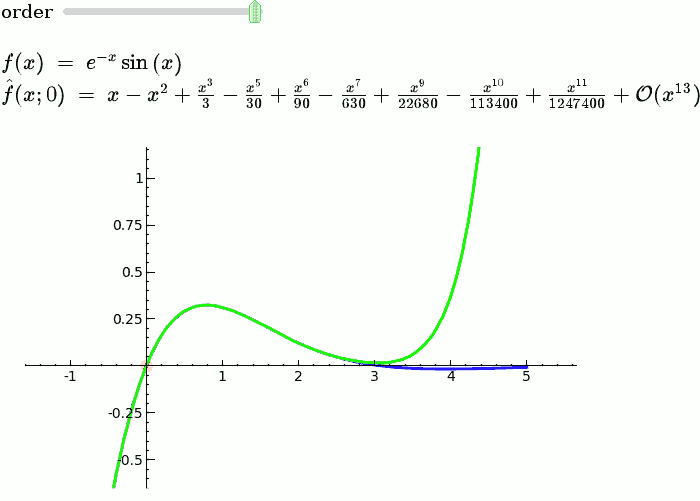
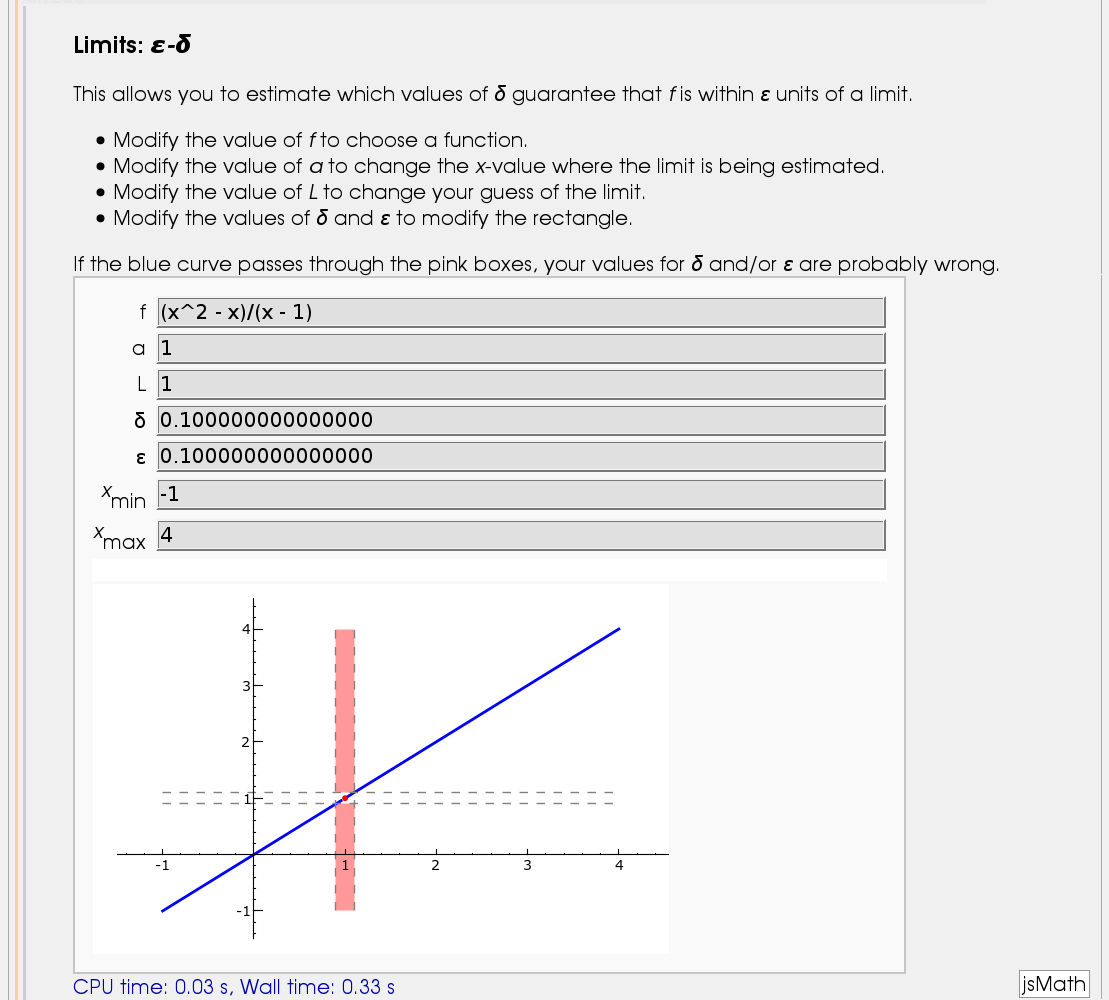
Illustration of the precise definition of a limit
by John Perry
I'll break tradition and put the image first. Apologies if this is Not A Good Thing.
A graphical illustration of sin(x)/x -> 1 as x-> 0
by Wai Yan Pong
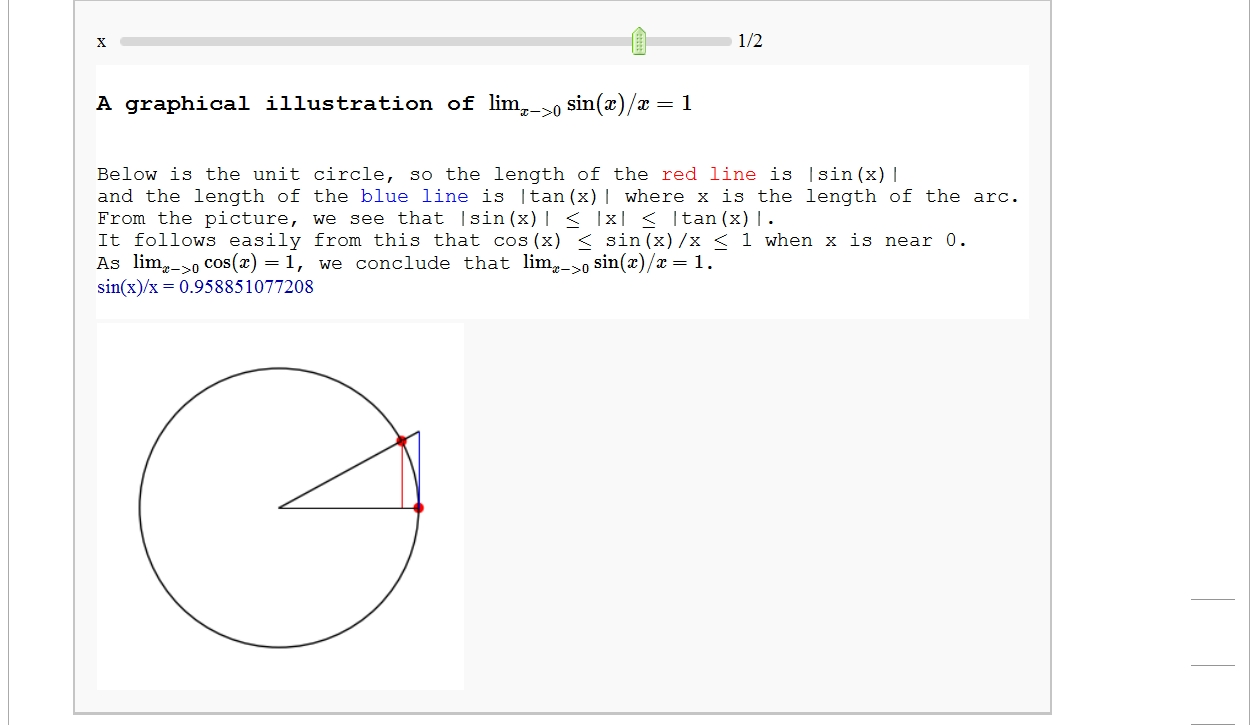
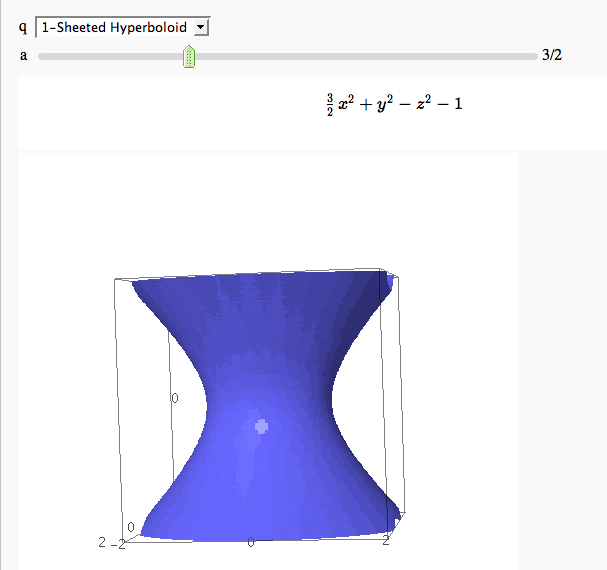
Quadric Surface Plotter
by Marshall Hampton. This is pretty simple, so I encourage people to spruce it up. In particular, it isn't set up to show all possible types of quadrics.
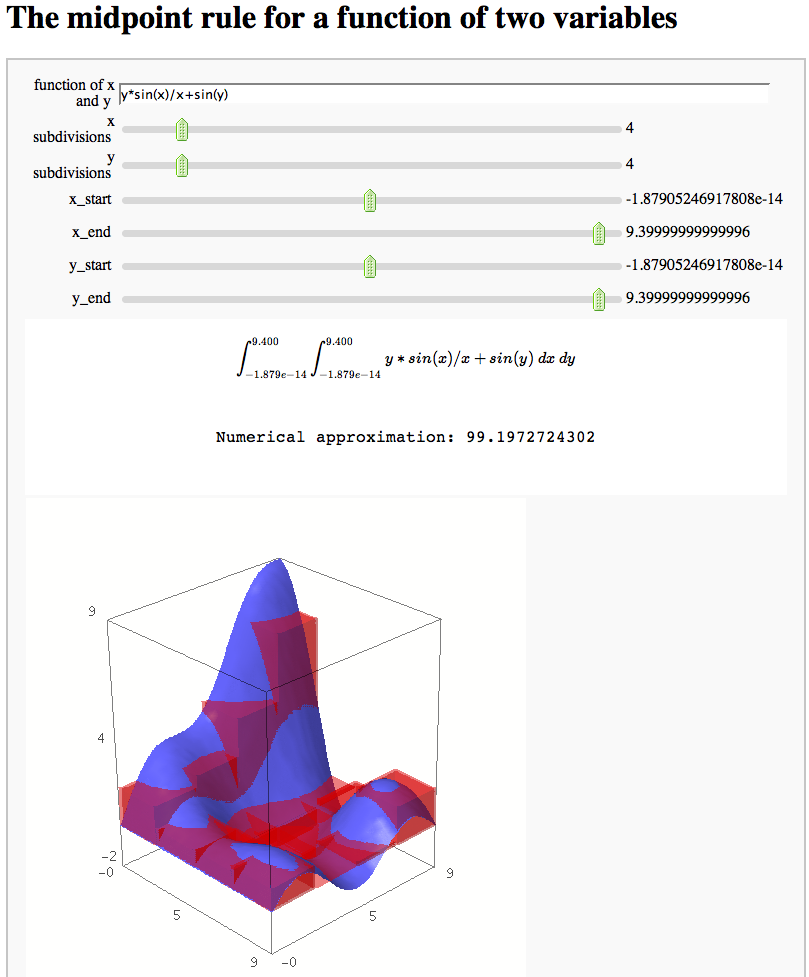
The midpoint rule for numerically integrating a function of two variables
by Marshall Hampton
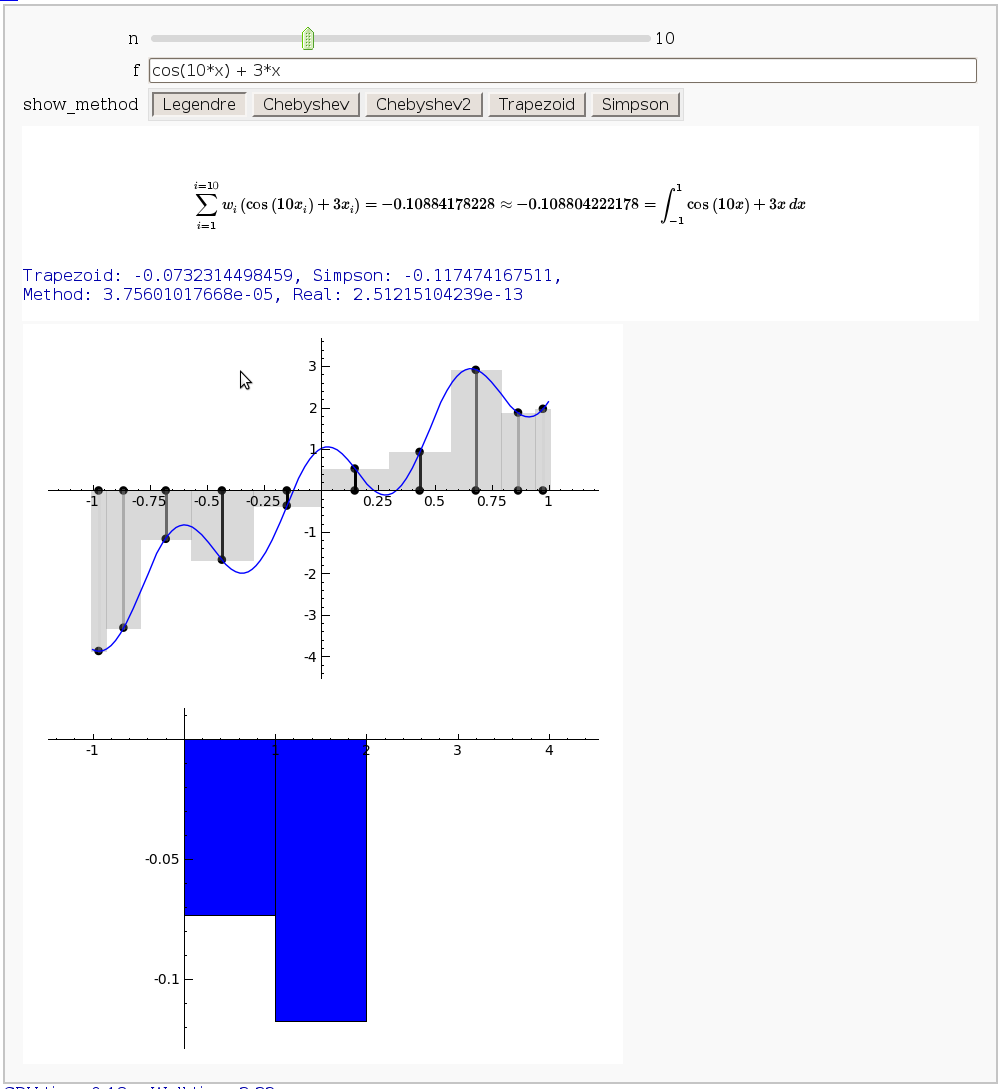
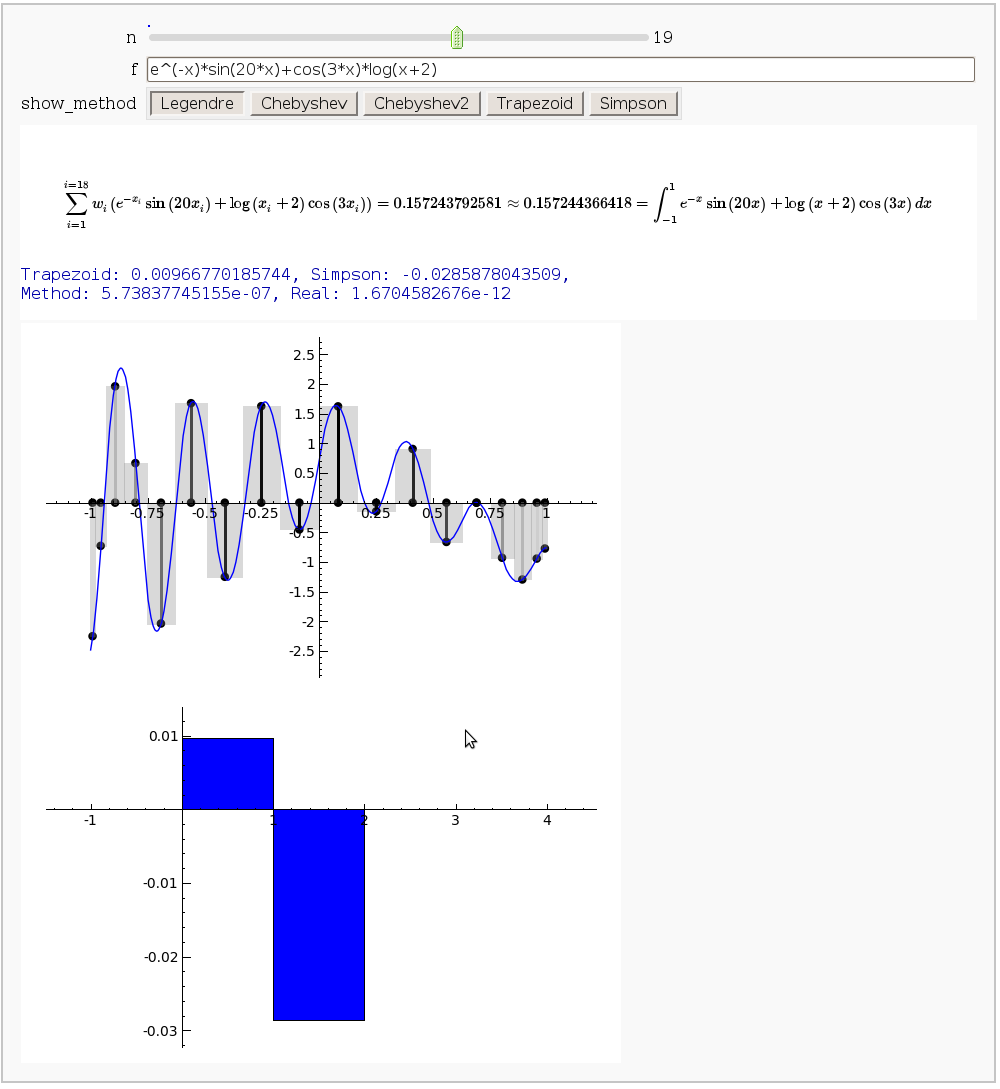
Gaussian (Legendre) quadrature
by Jason Grout
The output shows the points evaluated using Gaussian quadrature (using a weight of 1, so using Legendre polynomials). The vertical bars are shaded to represent the relative weights of the points (darker = more weight). The error in the trapezoid, Simpson, and quadrature methods is both printed out and compared through a bar graph. The "Real" error is the error returned from scipy on the definite integral.
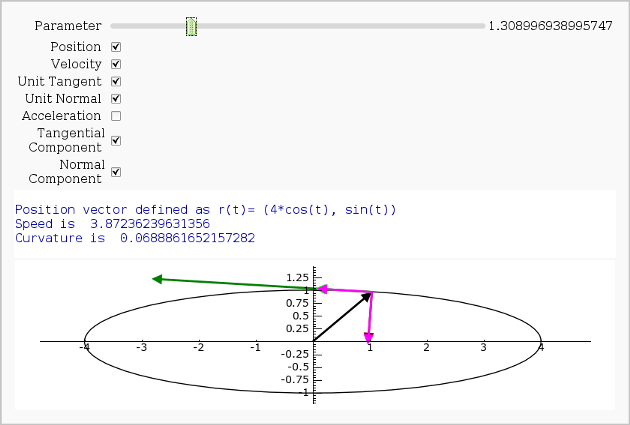
Vector Calculus, 2-D Motion
By Rob Beezer
A fast_float() version is available in a worksheet
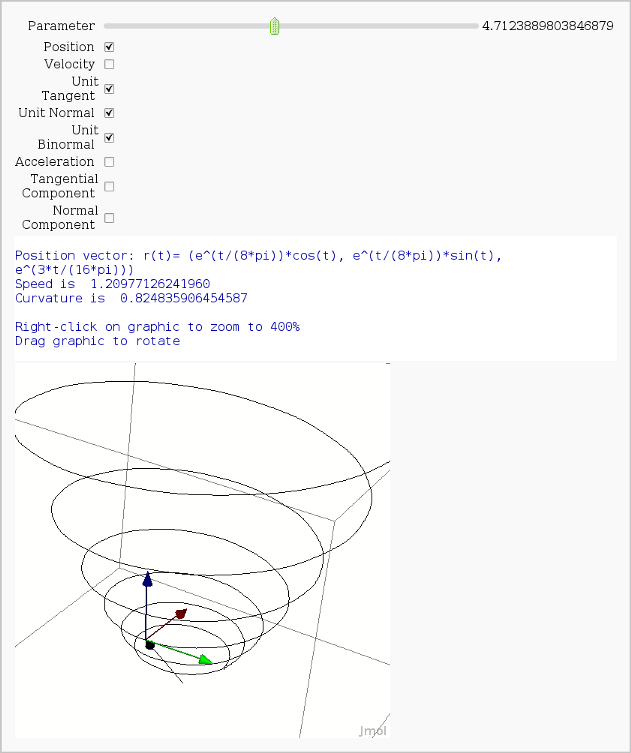
Vector Calculus, 3-D Motion
by Rob Beezer
Available as a worksheet
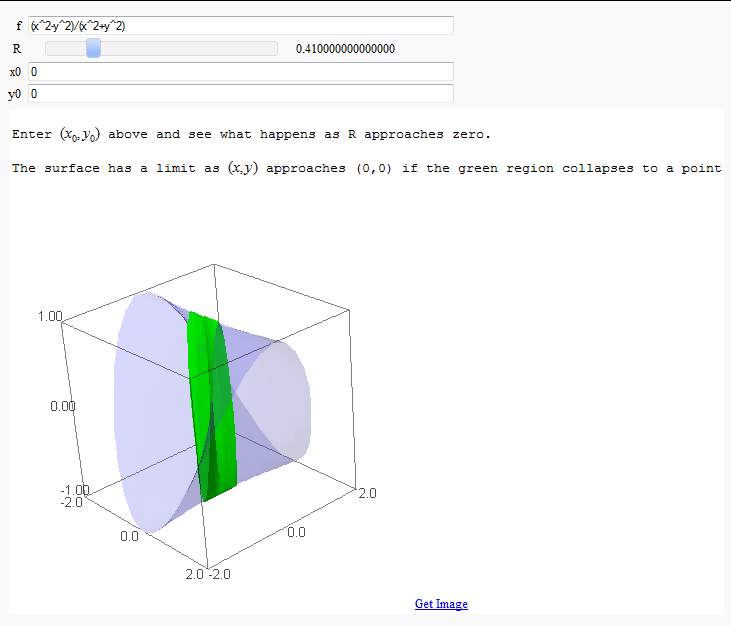
Multivariate Limits by Definition
by John Travis
http://www.sagenb.org/home/pub/2828/
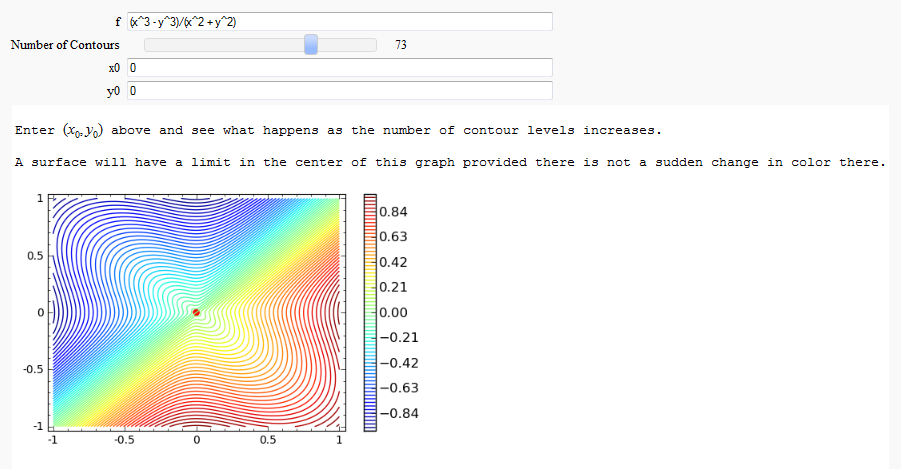
Directional Derivatives
This interact displays graphically a tangent line to a function, illustrating a directional derivative (the slope of the tangent line).
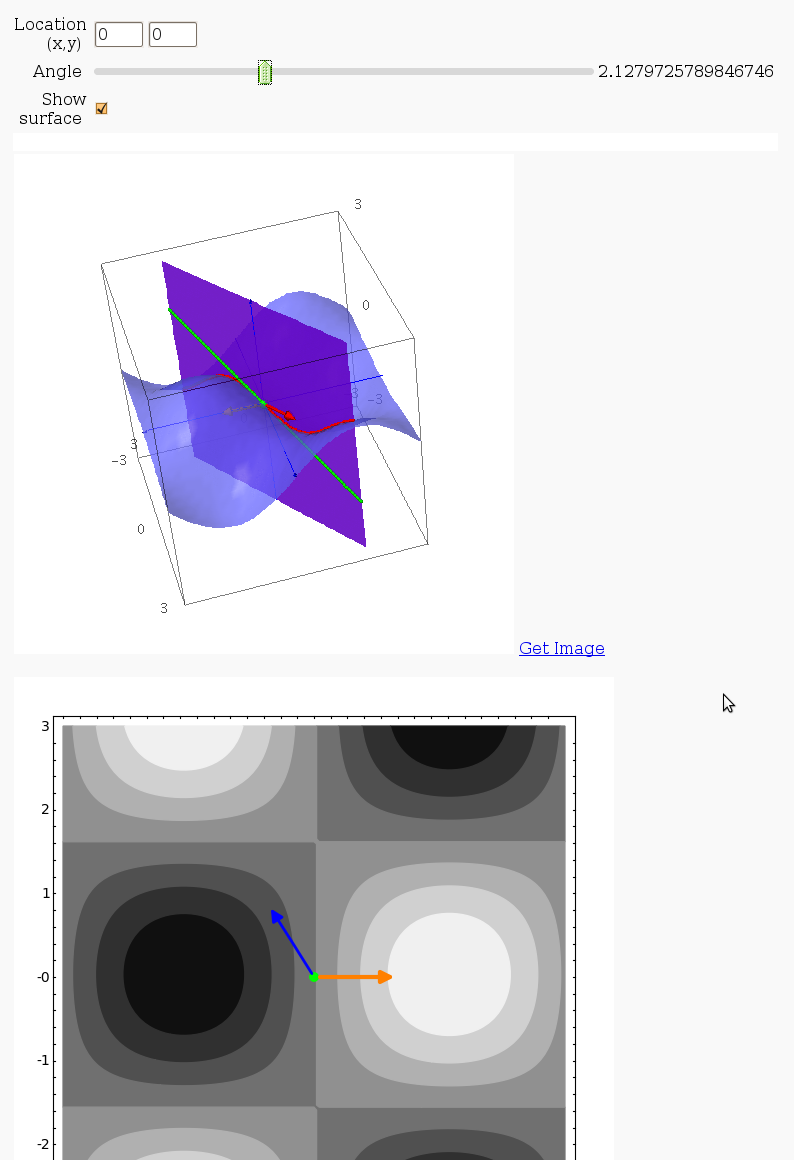
3D graph with points and curves
By Robert Marik
This sagelet is handy when showing local, constrained and absolute maxima and minima in two variables. Available as a worksheet
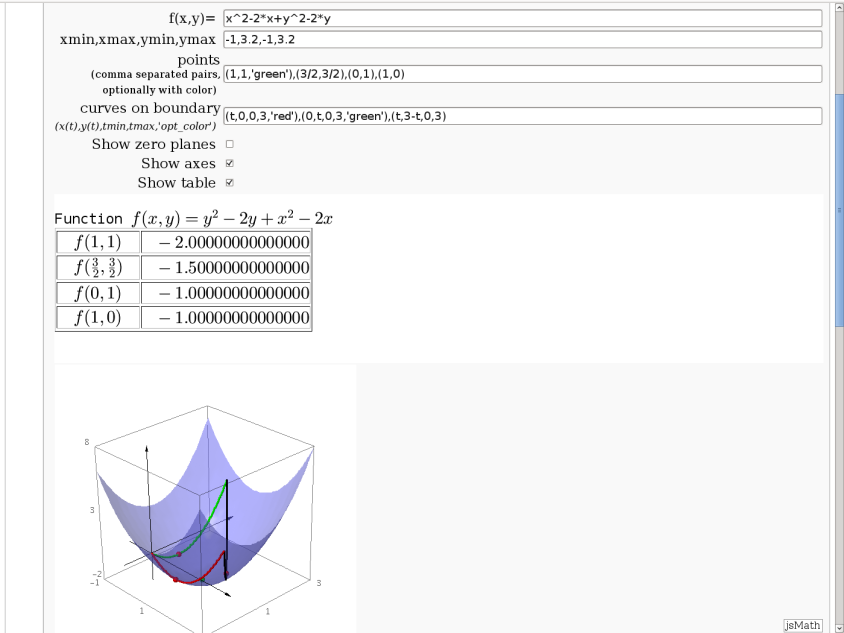
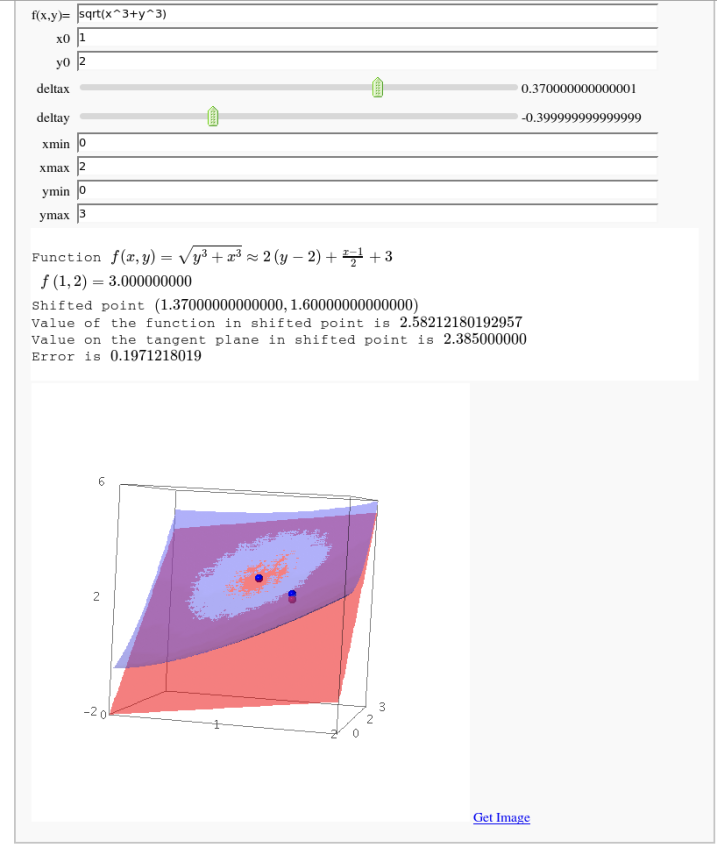
Approximating function in two variables by differential
by Robert Marik
Taylor approximations in two variables
by John Palmieri
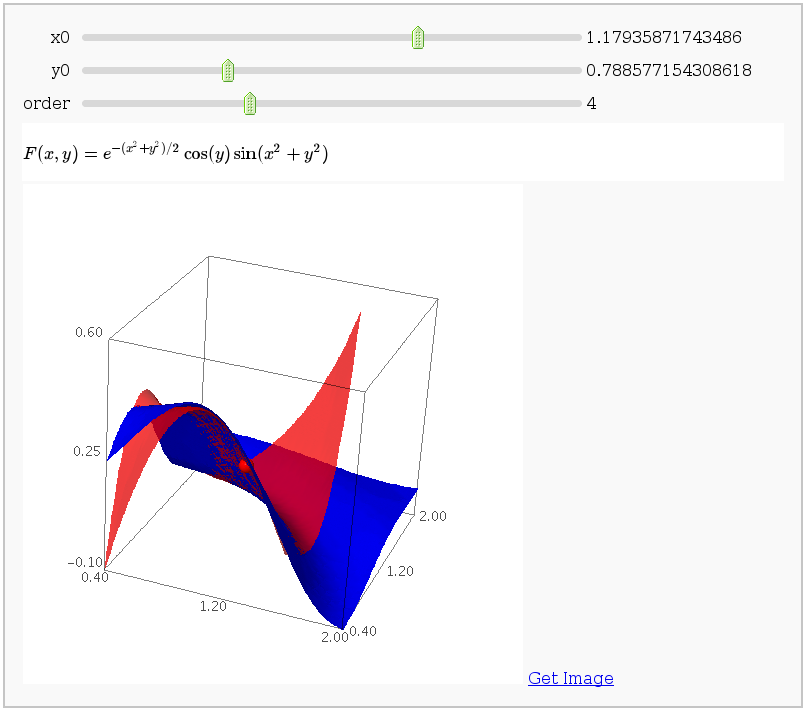
This displays the nth order Taylor approximation, for n from 1 to 10, of the function sin(x2 + y2) cos(y) exp(-(x2+y2)/2).
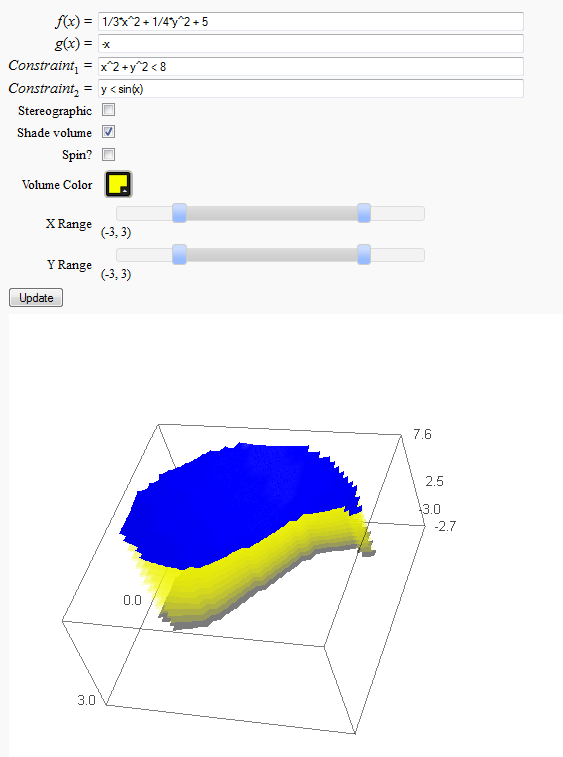
Volumes over non-rectangular domains
by John Travis
http://www.sagenb.org/home/pub/2829/
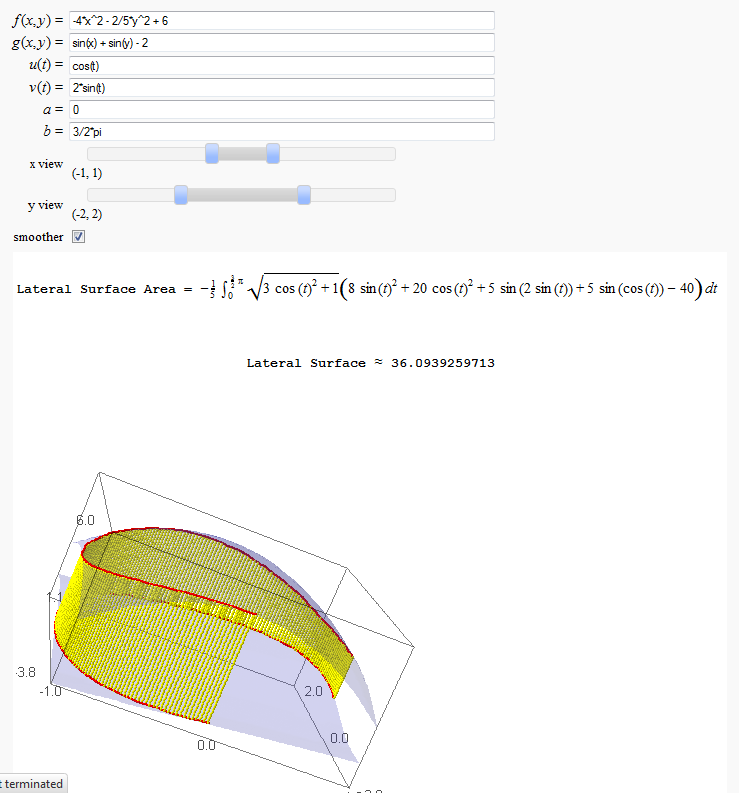
Lateral Surface Area
by John Travis
http://www.sagenb.org/home/pub/2826/
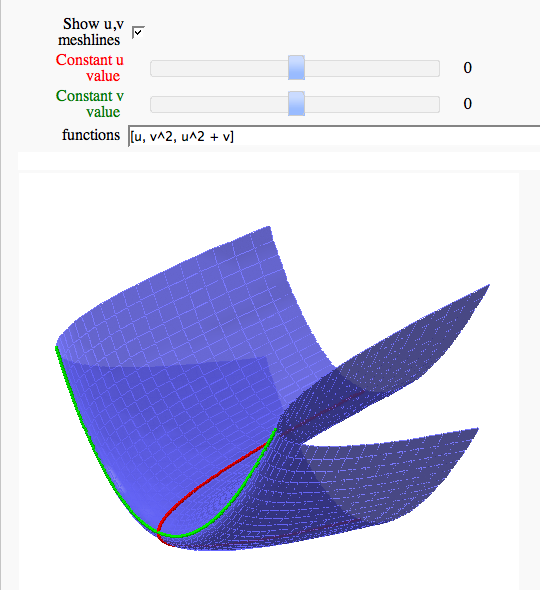
Parametric surface example
by Marshall Hampton
Line Integrals in 3D Vector Field
by John Travis
http://www.sagenb.org/home/pub/2827/