|
Size: 63134
Comment: fix DeprecationWarning and an AttributeError in Numerical integrals with the midpoint rule
|
Size: 62941
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 27: | Line 27: |
| raise ValueError, "f must have a sign change in the interval (%s,%s)"%(a,b) | raise ValueError("f must have a sign change in the interval (%s,%s)"%(a,b)) |
| Line 33: | Line 33: |
| print "eps = %s"%float(eps) | print("eps = %s" % float(eps)) |
| Line 37: | Line 37: |
| print "f must have opposite sign at the endpoints of the interval" | print("f must have opposite sign at the endpoints of the interval") |
| Line 40: | Line 40: |
| print "root =", c print "f(c) = %r"%f(x=c) print "iterations =", len(intervals) |
print("root =", c) print("f(c) = %r" % f(x=c)) print("iterations =", len(intervals)) |
| Line 69: | Line 69: |
| for i in xrange(maxiter): | for i in range(maxiter): |
| Line 81: | Line 81: |
| print "eps = %s"%float(eps) | print("eps = %s"%float(eps)) |
| Line 83: | Line 83: |
| print "root =", z print "f(c) = %r"%f(x=z) |
print("root = {}".format(z)) print("f(c) = %r" % f(x=z)) |
| Line 86: | Line 86: |
| print "iterations =", n | print("iterations = {}".format(n)) |
| Line 127: | Line 127: |
| print 'Tangent line is y = ' + tanf._repr_() | print('Tangent line is y = ' + tanf._repr_()) |
| Line 155: | Line 155: |
| pretty_print(html('$\int_{a}^{b}{f(x) dx} {\\approx} \sum_i{f(x_i) \Delta x}$')) print "\n\nSage numerical answer: " + str(integral_numerical(func,a,b,max_points = 200)[0]) print "Midpoint estimated answer: " + str(RDF(dx*sum([midys[q] for q in range(n)]))) |
pretty_print(html(r'$\int_{a}^{b}{f(x) dx} {\approx} \sum_i{f(x_i) \Delta x}$')) print("\n\nSage numerical answer: " + str(integral_numerical(func,a,b,max_points = 200)[0])) print("Midpoint estimated answer: " + str(RDF(dx*sum([midys[q] for q in range(n)])))) |
| Line 166: | Line 166: |
| # by Nick Alexander (based on the work of Marshall Hampton) #find_maximum_on_interval and find_minimum_on_interval are deprecated #use find_local_maximum find_local_minimum instead #see http://trac.sagemath.org/2607 for details -RRubalcaba |
|
| Line 179: | Line 174: |
| t = sage.calculus.calculus.var('t') | t = var('t') |
| Line 224: | Line 219: |
| html(r''' <div class="math"> \begin{align*} \int_{a}^{b} {f(x) \, dx} & = %s \\\ \sum_{i=1}^{%s} {f(x_i) \, \Delta x} & = %s \\\ & = %s \\\ & = %s . \end{align*} </div> ''' % (numerical_answer, number_of_subdivisions, sum_html, num_html, estimated_answer)) |
pretty_print(html(r''' <div class="math"> \begin{align*} \int_{a}^{b} {f(x) \, dx} & = %s \\\ \sum_{i=1}^{%s} {f(x_i) \, \Delta x} & = %s \\\ & = %s \\\ & = %s . \end{align*} </div>''' % (numerical_answer, number_of_subdivisions, sum_html, num_html, estimated_answer))) |
| Line 265: | Line 257: |
| except TypeError, msg: print msg[-200:] print "Unable to make sense of f,g, or a as symbolic expressions." |
except TypeError as msg: print(msg[-200:]) print("Unable to make sense of f,g, or a as symbolic expressions.") |
| Line 382: | Line 374: |
| vertical_alignment="bottom" if f(x0) < 0 else "top" ) | vertical_alignment="bottom" if f(x=x0) < 0 else "top" ) |
| Line 398: | Line 390: |
| fi = RR(f(xi)) fpi = RR(df(xi)) |
fi = RR(f(x=xi)) fpi = RR(df(x=xi)) |
| Line 434: | Line 426: |
| vertical_alignment="bottom" if f(xip1) < 0 else "top" ) | vertical_alignment="bottom" if f(x=xip1) < 0 else "top" ) |
| Line 450: | Line 442: |
| html( t ) | pretty_print(html( t )) |
| Line 454: | Line 446: |
| == Coordinate Transformations (FIXME in Jupyter) == | == Coordinate Transformations == |
| Line 474: | Line 466: |
| u_percent=slider(0,1,0.05,label="<font color='red'>u</font>", default=.7), v_percent=slider(0,1,0.05,label="<font color='blue'>v</font>", default=.7), |
u_percent=slider(0,1,0.05,label="u", default=.7), v_percent=slider(0,1,0.05,label="v", default=.7), |
| Line 505: | Line 497: |
| jacobian=abs(T.diff().det()).simplify_full() | jacobian(u,v)=abs(T.diff().det()).simplify_full() |
| Line 516: | Line 508: |
| pretty_print(table([[uvplot,xyplot]])) | show(graphics_array([uvplot,xyplot])) |
| Line 530: | Line 522: |
| dot = point((x0,f(x0)),pointsize=80,rgbcolor=(1,0,0)) @interact def _(order=(1..12)): |
dot = point((x0,f(x=x0)),pointsize=80,rgbcolor=(1,0,0)) @interact def _(order=[1..12]): |
| Line 535: | Line 527: |
| pretty_print(html('$f(x)\;=\;%s$'%latex(f))) pretty_print(html('$\hat{f}(x;%s)\;=\;%s+\mathcal{O}(x^{%s})$'%(x0,latex(ft),order+1))) |
pretty_print(html(r'$f(x)\;=\;%s$'%latex(f))) pretty_print(html(r'$\hat{f}(x;%s)\;=\;%s+\mathcal{O}(x^{%s})$'%(x0,latex(ft),order+1))) |
| Line 557: | Line 549: |
| def delta_epsilon(f = input_box(default=(x^2-x)/(x-1)), a=input_box(default=1), L = input_box(default=1), delta=input_box(label="δ",default=0.1), epsilon=input_box(label="ε",default=0.1), xm=input_box(label="<i>x</i><sub>min</sub>",default=-1), xM=input_box(label="<i>x</i><sub>max</sub>",default=4)): | def delta_epsilon(f = input_box(default=(x^2-x)/(x-1), label="$f$"), a=input_box(default=1, label="$a$"), L = input_box(default=1, label="$L$"), delta=input_box(label=r"$\delta$",default=0.1), epsilon=input_box(label=r"$\varepsilon$",default=0.1), xm=input_box(label=r"$x_{min}$",default=-1), xM=input_box(label=r"$x_{max}$",default=4)): |
| Line 605: | Line 597: |
| def quads(q = selector(quadrics.keys()), a = slider(0,5,1/2,default = 1)): | def quads(q = selector(list(quadrics)), a = slider(0,5,1/2,default = 1)): |
| Line 607: | Line 599: |
| if a==0 or q=='Cone': html('<center>$'+latex(f)+' \ $'+ '(degenerate)</center>') else: html('<center>$'+latex(f)+'$ </center>') |
if a==0 or q=='Cone': pretty_print(latex(f), " (degenerate)") else: pretty_print(latex(f)) |
| Line 726: | Line 718: |
| print "Trapezoid: %s, Simpson: %s, \nMethod: %s, Real: %s"%tuple(error_data) | print("Trapezoid: %s, Simpson: %s, \nMethod: %s, Real: %s" % tuple(error_data)) |
| Line 764: | Line 756: |
| path = parametric_plot( position(t).list(), (t, start, stop), color = "black" ) | path = parametric_plot( position.list(), (t, start, stop), color = "black" ) |
| Line 768: | Line 760: |
| velocity = derivative(position(t), t) acceleration = derivative(velocity(t), t) |
velocity = derivative(position, t) acceleration = derivative(velocity, t) |
| Line 773: | Line 765: |
| dT = derivative(tangent(t), t) | dT = derivative(tangent, t) |
| Line 794: | Line 786: |
| pos_tzero = position(t0) | pos_tzero = position(t=t0) |
| Line 798: | Line 790: |
| speed_component = speed(t0) tangent_component = speed_deriv(t0) normal_component = sqrt( acceleration(t0).norm()^2 - tangent_component^2 ) |
speed_component = speed(t=t0) tangent_component = speed_deriv(t=t0) normal_component = sqrt( acceleration(t=t0).norm()^2 - tangent_component^2 ) |
| Line 806: | Line 798: |
| tan = arrow(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + tangent(t0), rgbcolor=(0,1,0) ) vel = arrow(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + velocity(t0), rgbcolor=(0,0.5,0)) nor = arrow(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + normal(t0), rgbcolor=(0.5,0,0)) acc = arrow(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + acceleration(t0), rgbcolor=(1,0,1)) tancomp = arrow(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + tangent_component*tangent(t0), rgbcolor=(1,0,1) ) norcomp = arrow(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + normal_component*normal(t0), rgbcolor=(1,0,1)) |
tan = arrow(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + tangent(t=t0), rgbcolor=(0,1,0) ) vel = arrow(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + velocity(t=t0), rgbcolor=(0,0.5,0)) nor = arrow(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + normal(t=t0), rgbcolor=(0.5,0,0)) acc = arrow(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + acceleration(t=t0), rgbcolor=(1,0,1)) tancomp = arrow(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + tangent_component*tangent(t=t0), rgbcolor=(1,0,1) ) norcomp = arrow(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + normal_component*normal(t=t0), rgbcolor=(1,0,1)) |
| Line 833: | Line 825: |
| print "Position vector defined as r(t)=", position(t) print "Speed is ", N(speed(t0)) print "Curvature is ", N(curvature) |
print("Position vector defined as r(t)={}".format(position)) print("Speed is {}".format(N(speed(t=t0)))) print("Curvature is {}".format(N(curvature))) |
| Line 844: | Line 836: |
| == Vector Calculus, 3-D Motion (FIXME) == | == Vector Calculus, 3-D Motion == |
| Line 865: | Line 857: |
| assume(t, 'real') | |
| Line 882: | Line 875: |
| path = parametric_plot3d( position(t).list(), (t, start, stop), color = "black" ) | path = parametric_plot3d( position.list(), (t, start, stop), color = "black" ) |
| Line 886: | Line 879: |
| velocity = derivative( position(t), t) acceleration = derivative(velocity(t), t) |
velocity = derivative( position, t) acceleration = derivative(velocity, t) |
| Line 891: | Line 884: |
| dT = derivative(tangent(t), t) | dT = derivative(tangent, t) |
| Line 894: | Line 887: |
| ## dB = derivative(binormal(t), t) | ## dB = derivative(binormal, t) |
| Line 915: | Line 908: |
| pos_tzero = position(t0) | pos_tzero = position(t=t0) |
| Line 919: | Line 912: |
| speed_component = speed(t0) tangent_component = speed_deriv(t0) normal_component = sqrt( acceleration(t0).norm()^2 - tangent_component^2 ) |
speed_component = speed(t=t0) tangent_component = speed_deriv(t=t0) normal_component = sqrt( acceleration(t=t0).norm()^2 - tangent_component^2 ) |
| Line 928: | Line 921: |
| tan = arrow3d(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + tangent(t0), rgbcolor=(0,1,0) ) vel = arrow3d(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + velocity(t0), rgbcolor=(0,0.5,0)) nor = arrow3d(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + normal(t0), rgbcolor=(0.5,0,0)) bin = arrow3d(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + binormal(t0), rgbcolor=(0,0,0.5)) acc = arrow3d(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + acceleration(t0), rgbcolor=(1,0,1)) tancomp = arrow3d(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + tangent_component*tangent(t0), rgbcolor=(1,0,1) ) norcomp = arrow3d(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + normal_component*normal(t0), rgbcolor=(1,0,1)) |
tan = arrow3d(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + tangent(t=t0), rgbcolor=(0,1,0) ) vel = arrow3d(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + velocity(t=t0), rgbcolor=(0,0.5,0)) nor = arrow3d(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + normal(t=t0), rgbcolor=(0.5,0,0)) bin = arrow3d(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + binormal(t=t0), rgbcolor=(0,0,0.5)) acc = arrow3d(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + acceleration(t=t0), rgbcolor=(1,0,1)) tancomp = arrow3d(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + tangent_component*tangent(t=t0), rgbcolor=(1,0,1) ) norcomp = arrow3d(pos_tzero, pos_tzero + normal_component*normal(t=t0), rgbcolor=(1,0,1)) |
| Line 958: | Line 951: |
| print "Position vector: r(t)=", position(t) print "Speed is ", N(speed(t0)) print "Curvature is ", N(curvature) ## print "Torsion is ", N(torsion) print "Right-click on graphic to zoom to 400%" print "Drag graphic to rotate" |
print("Position vector: r(t)=", position) print("Speed is ", N(speed(t=t0))) print("Curvature is ", N(curvature)) ## print("Torsion is ", N(torsion)) print() print("Right-click on graphic to zoom to 400%") print("Drag graphic to rotate") |
| Line 1259: | Line 1252: |
| order=(1..10)): | order=[1..10]): |
Sage Interactions - Calculus
goto interact main page
Contents
-
Sage Interactions - Calculus
- Root Finding Using Bisection
- Newton's Method
- A contour map and 3d plot of two inverse distance functions
- A simple tangent line grapher
- Numerical integrals with the midpoint rule
- Numerical integrals with various rules
- Some polar parametric curves
- Function tool
- Newton-Raphson Root Finding
- Coordinate Transformations
- Taylor Series
- Illustration of the precise definition of a limit
- A graphical illustration of sin(x)/x -> 1 as x-> 0
- Quadric Surface Plotter
- The midpoint rule for numerically integrating a function of two variables
- Gaussian (Legendre) quadrature
- Vector Calculus, 2-D Motion
- Vector Calculus, 3-D Motion
- Multivariate Limits by Definition
- Directional Derivatives
- 3D graph with points and curves
- Approximating function in two variables by differential
- Taylor approximations in two variables
- Volumes over non-rectangular domains
- Lateral Surface Area (FIXME in Jupyter)
- Parametric surface example (FIXME in Jupyter)
- Line Integrals in 3D Vector Field
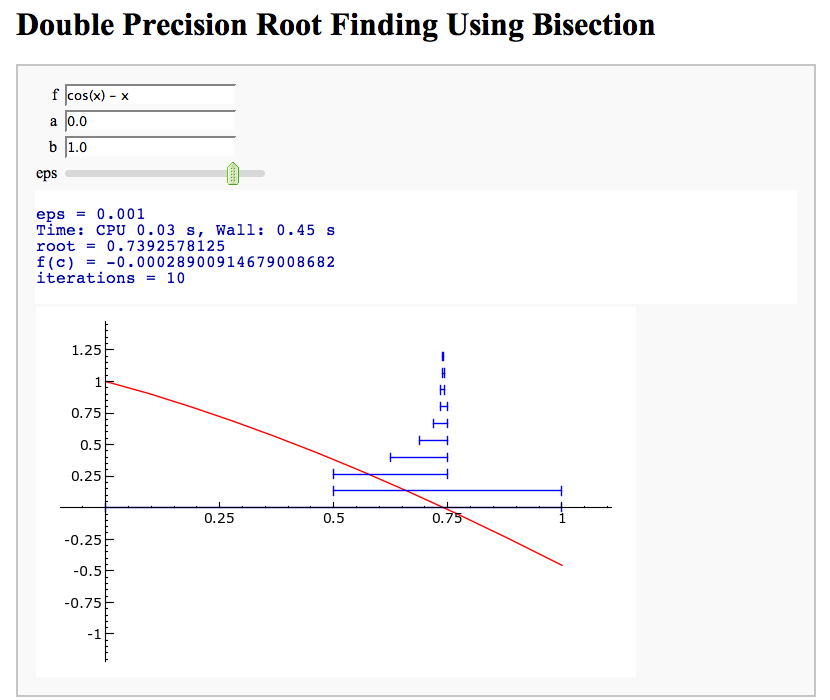
Root Finding Using Bisection
by William Stein
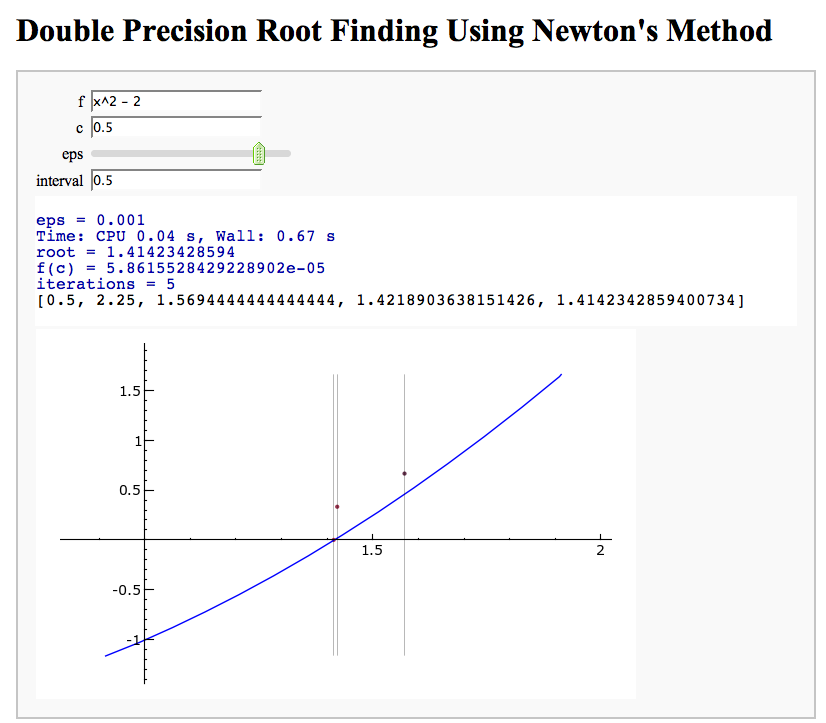
Newton's Method
Note that there is a more complicated Newton's method below.
by William Stein
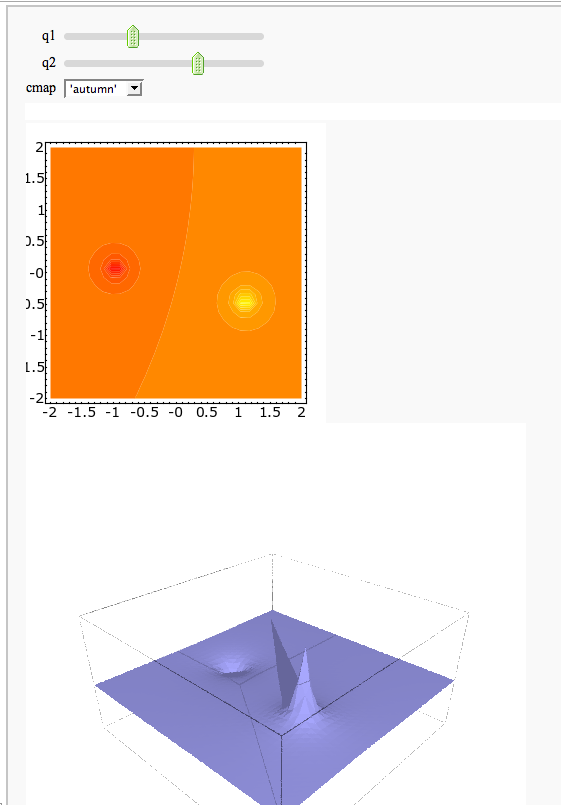
A contour map and 3d plot of two inverse distance functions
by William Stein
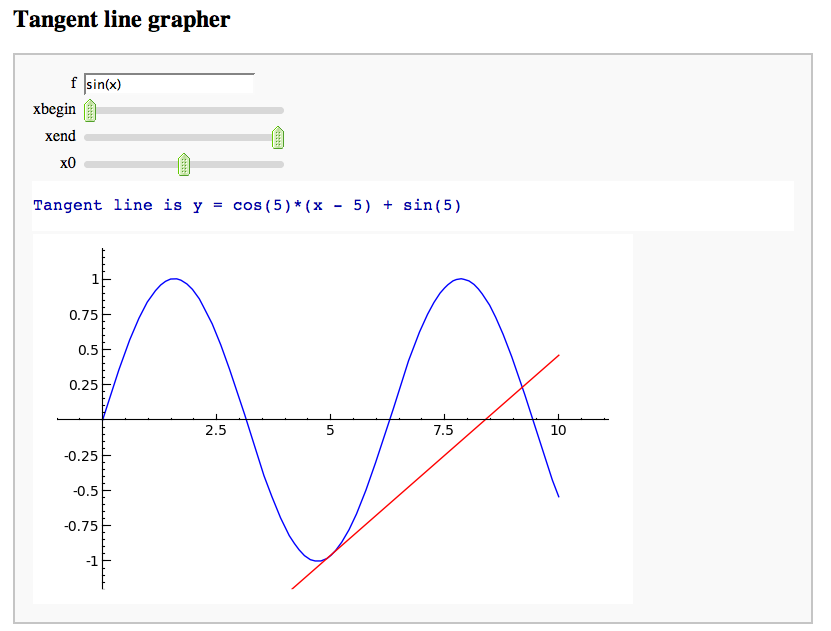
A simple tangent line grapher
by Marshall Hampton
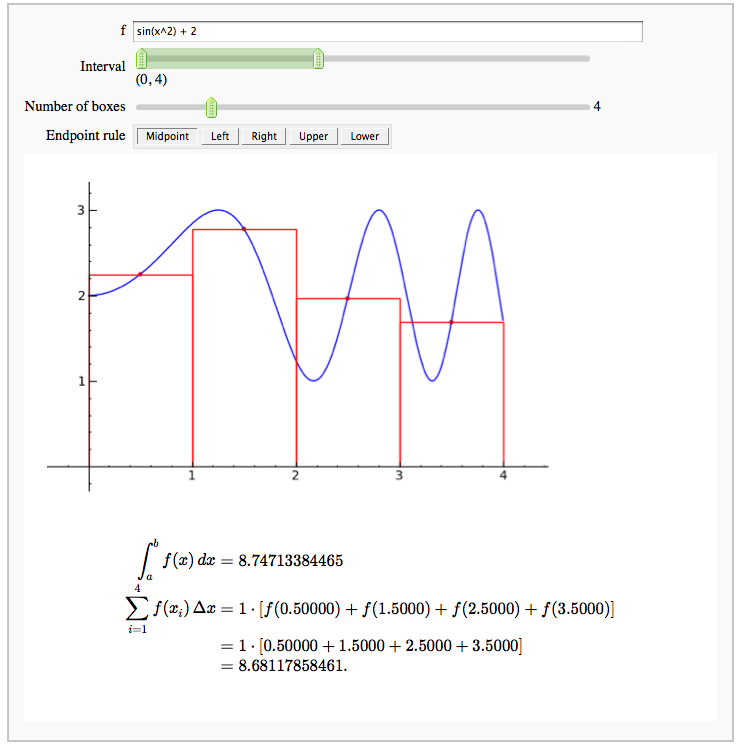
Numerical integrals with the midpoint rule
by Marshall Hampton

Numerical integrals with various rules
by Nick Alexander (based on the work of Marshall Hampton)
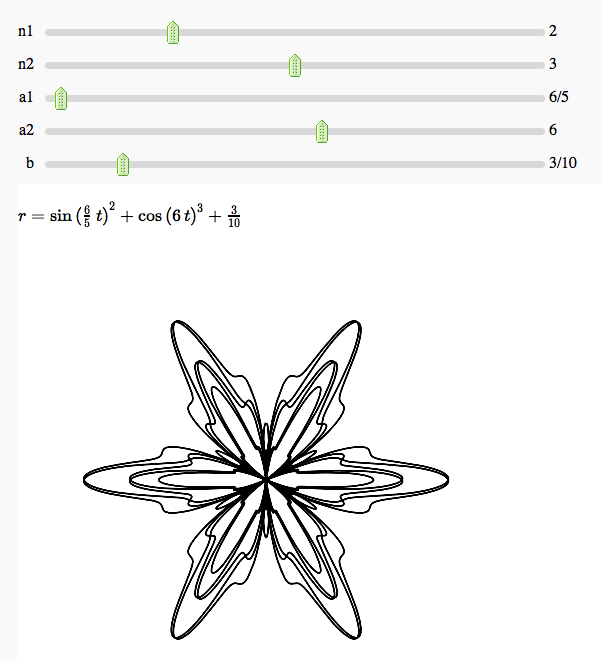
Some polar parametric curves
by Marshall Hampton. This is not very general, but could be modified to show other families of polar curves.
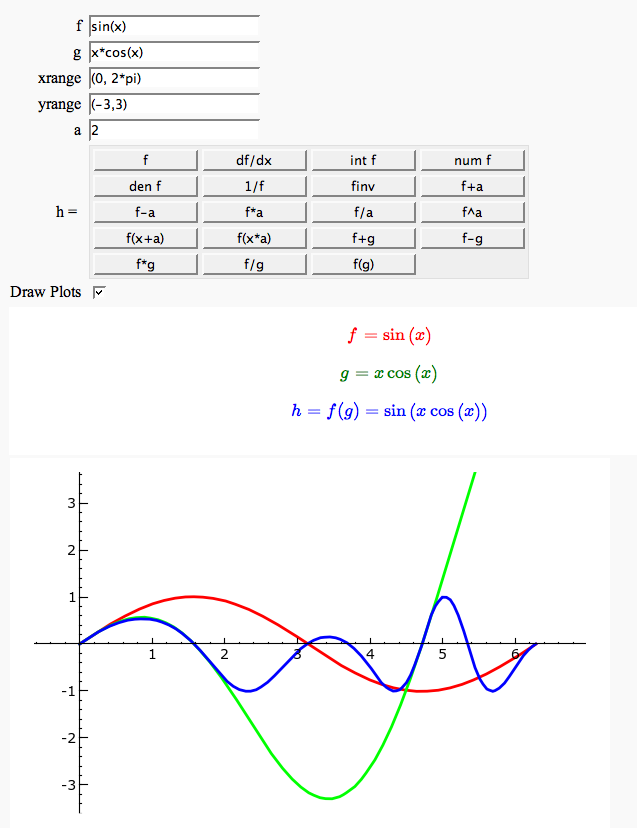
Function tool
Enter symbolic functions f, g, and a, a range, then click the appropriate button to compute and plot some combination of f, g, and a along with f and g. This is inspired by the Matlab funtool GUI.
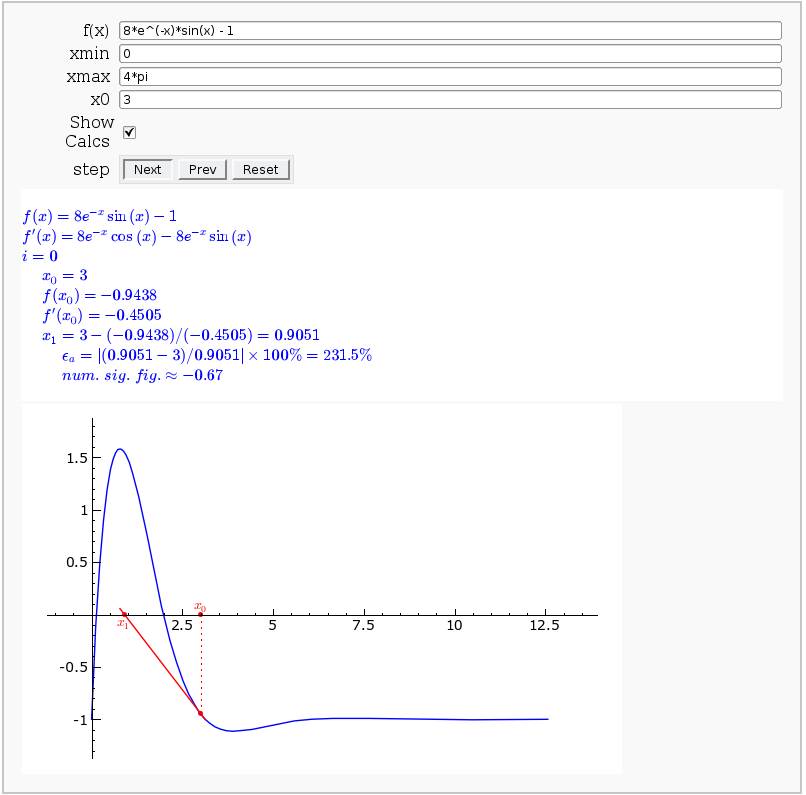
Newton-Raphson Root Finding
by Neal Holtz
This allows user to display the Newton-Raphson procedure one step at a time. It uses the heuristic that, if any of the values of the controls change, then the procedure should be re-started, else it should be continued.
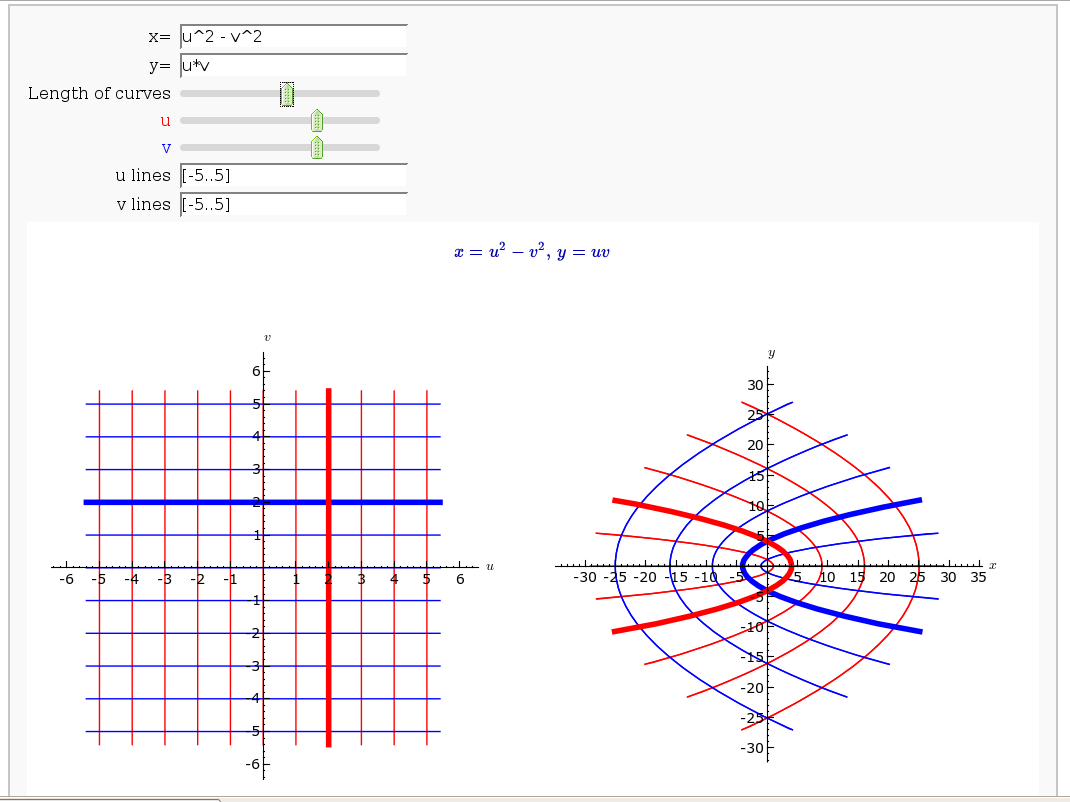
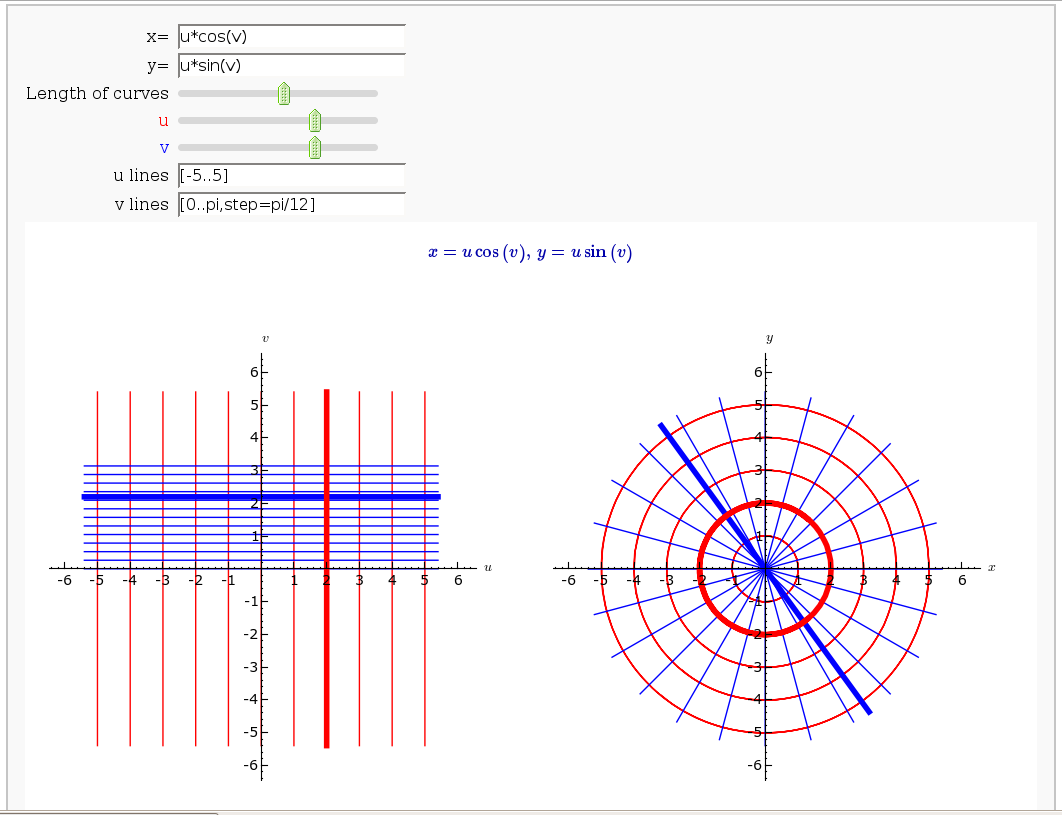
Coordinate Transformations
by Jason Grout
Taylor Series
by Harald Schilly
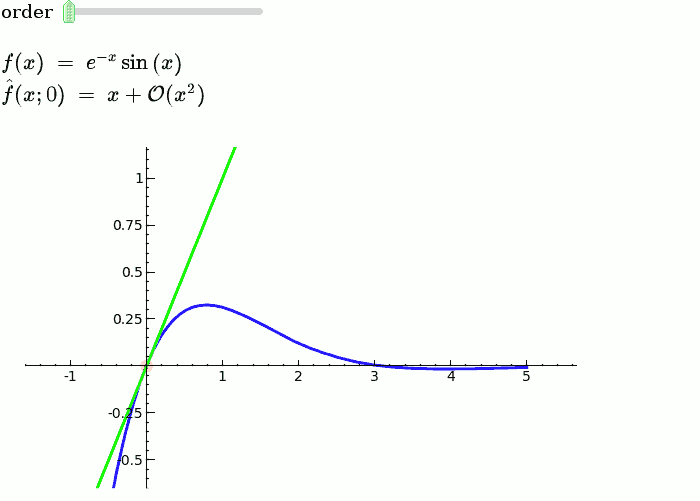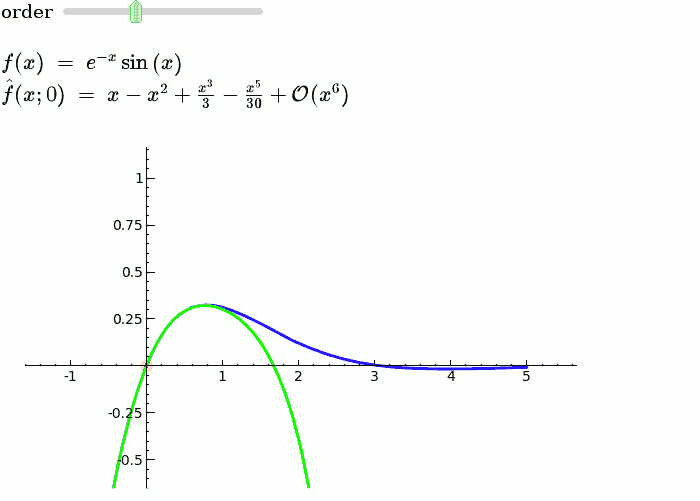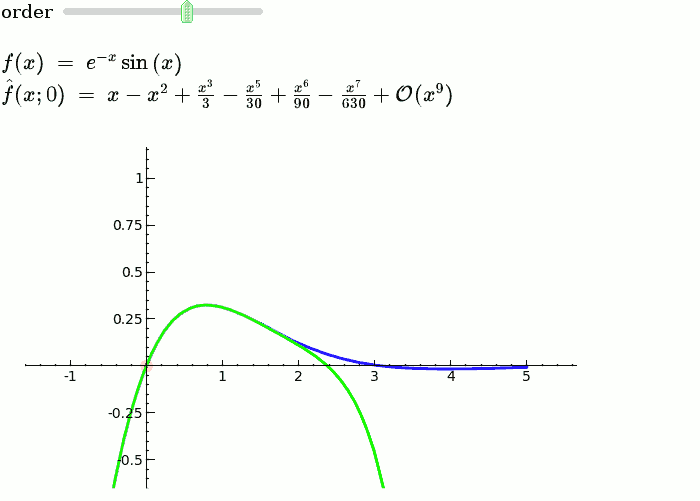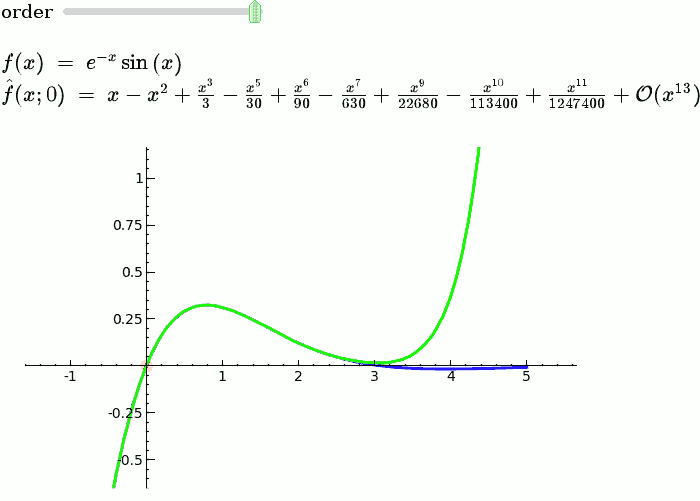
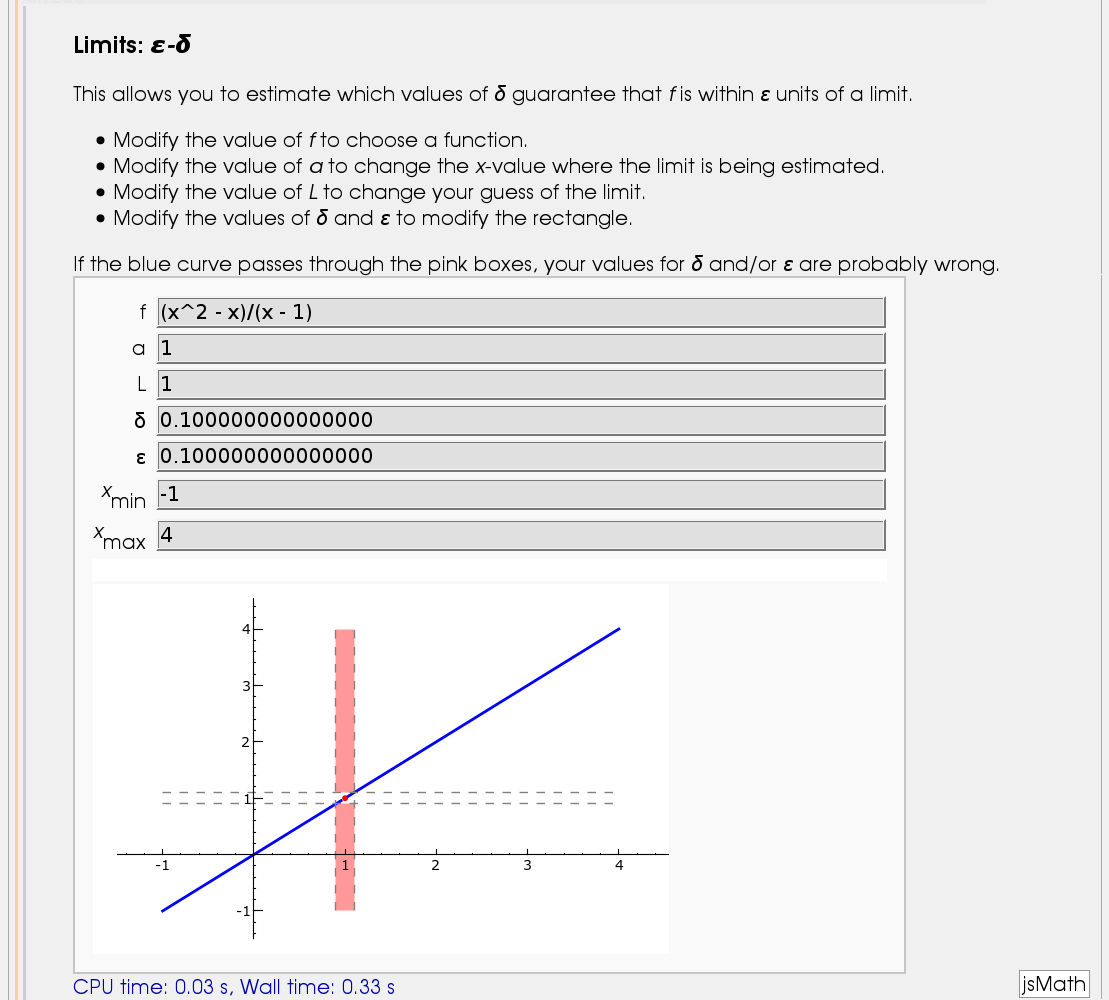
Illustration of the precise definition of a limit
by John Perry
I'll break tradition and put the image first. Apologies if this is Not A Good Thing.
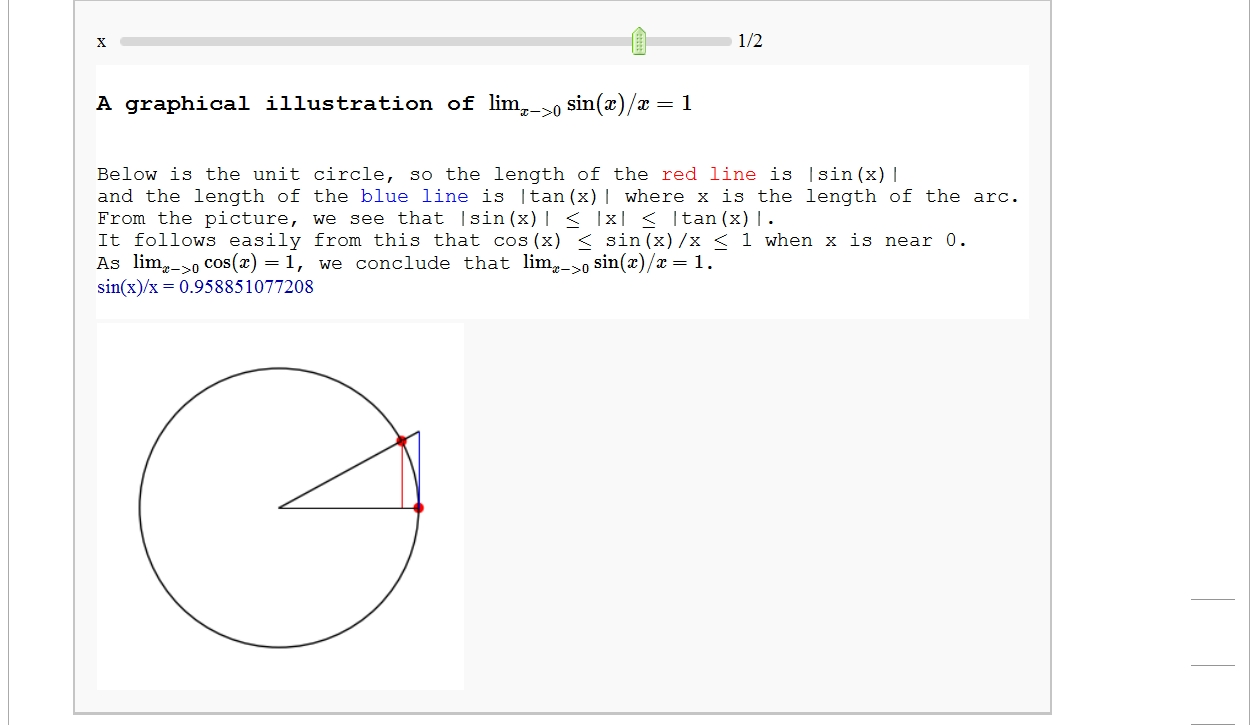
A graphical illustration of sin(x)/x -> 1 as x-> 0
by Wai Yan Pong
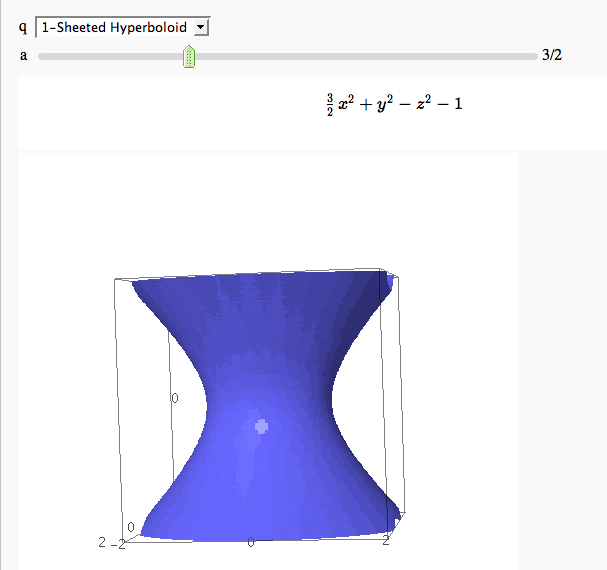
Quadric Surface Plotter
by Marshall Hampton. This is pretty simple, so I encourage people to spruce it up. In particular, it isn't set up to show all possible types of quadrics.
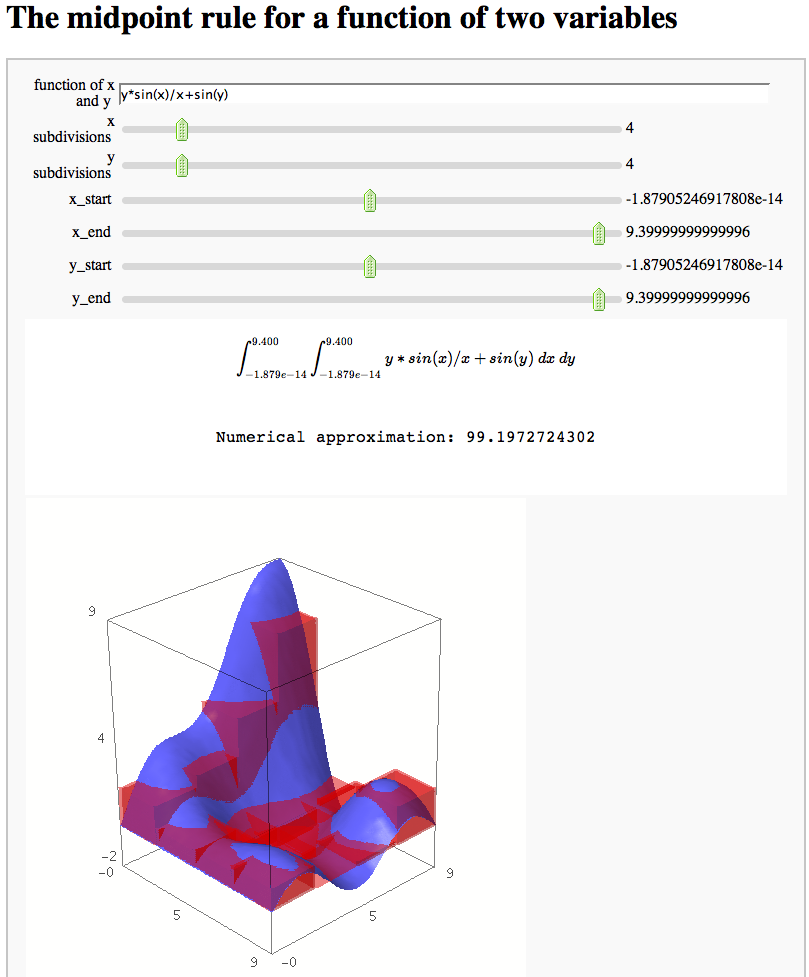
The midpoint rule for numerically integrating a function of two variables
by Marshall Hampton
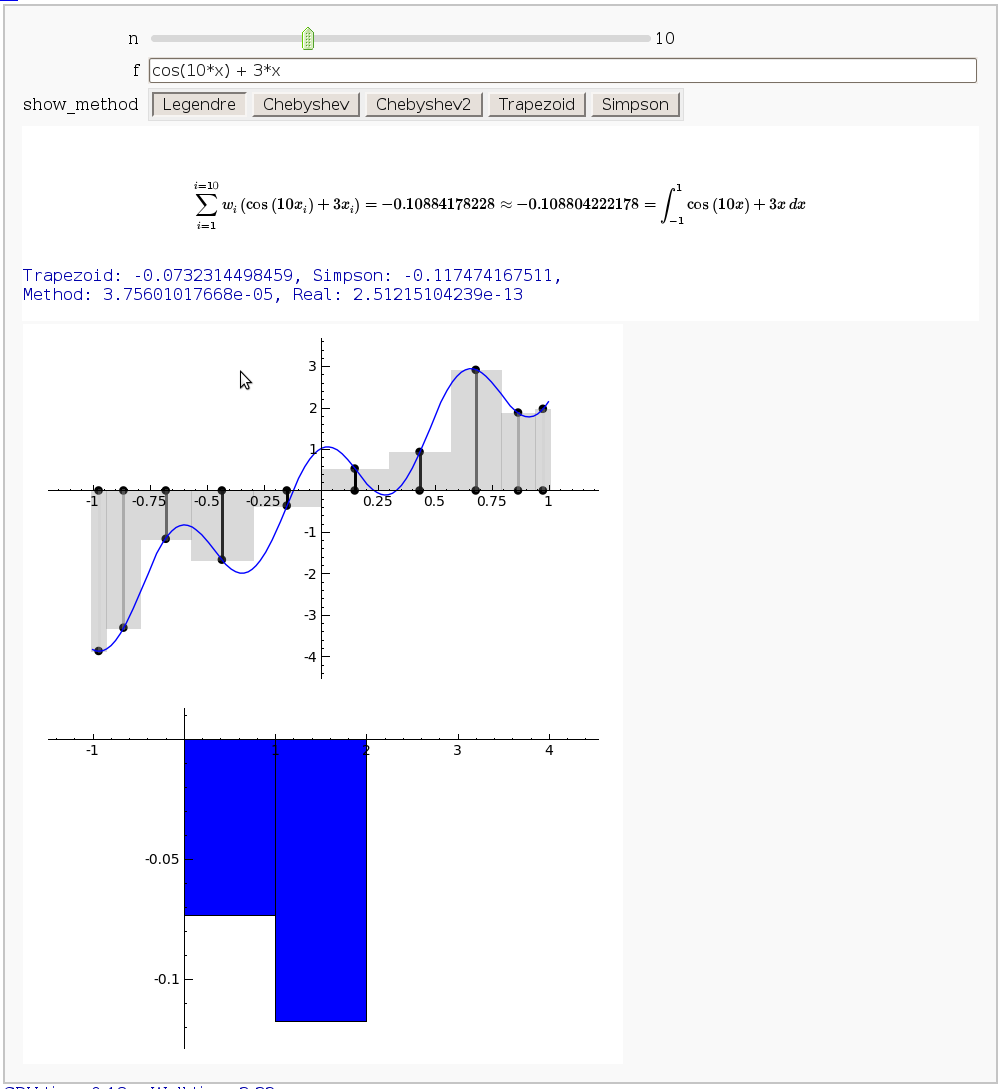
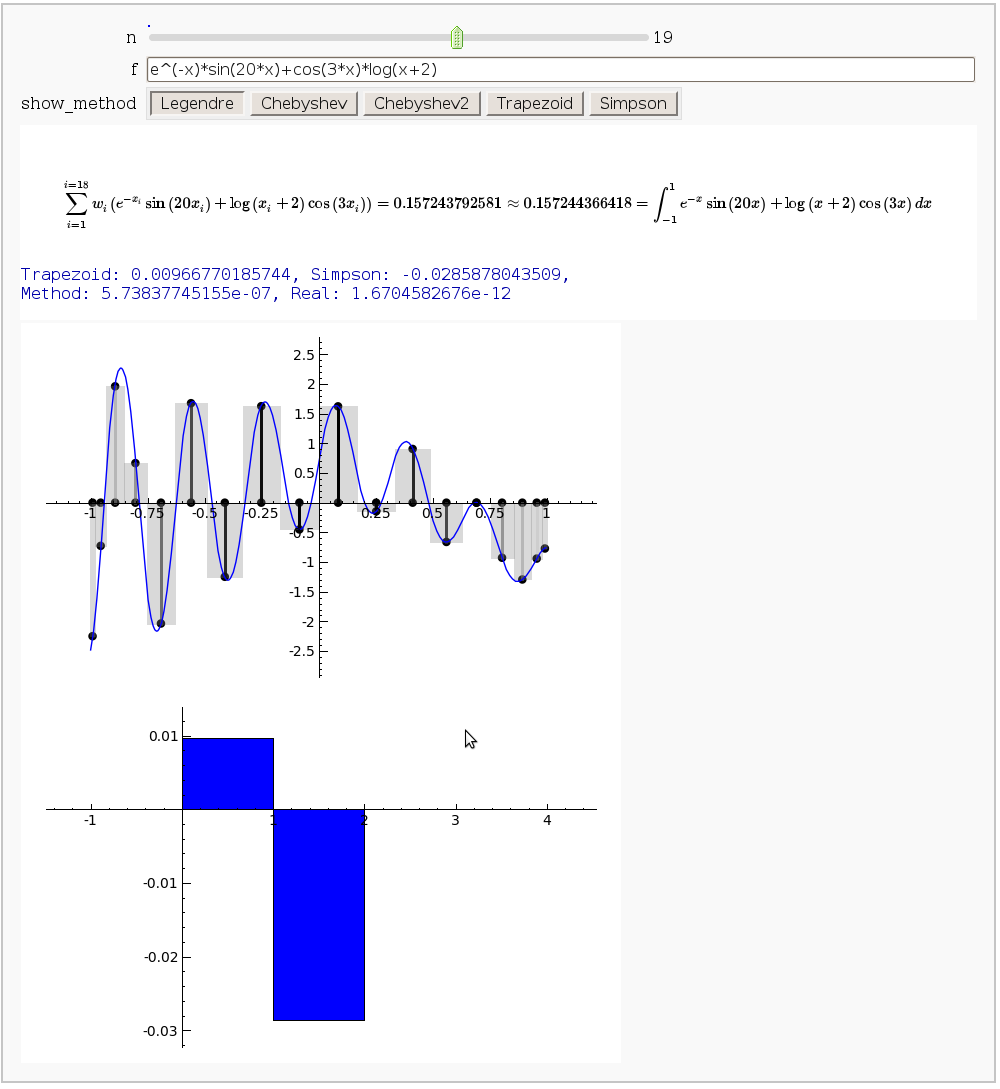
Gaussian (Legendre) quadrature
by Jason Grout
The output shows the points evaluated using Gaussian quadrature (using a weight of 1, so using Legendre polynomials). The vertical bars are shaded to represent the relative weights of the points (darker = more weight). The error in the trapezoid, Simpson, and quadrature methods is both printed out and compared through a bar graph. The "Real" error is the error returned from scipy on the definite integral.
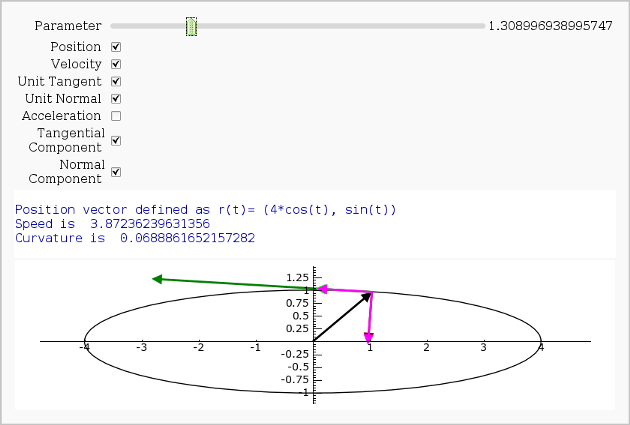
Vector Calculus, 2-D Motion
By Rob Beezer
A fast_float() version is available in a worksheet
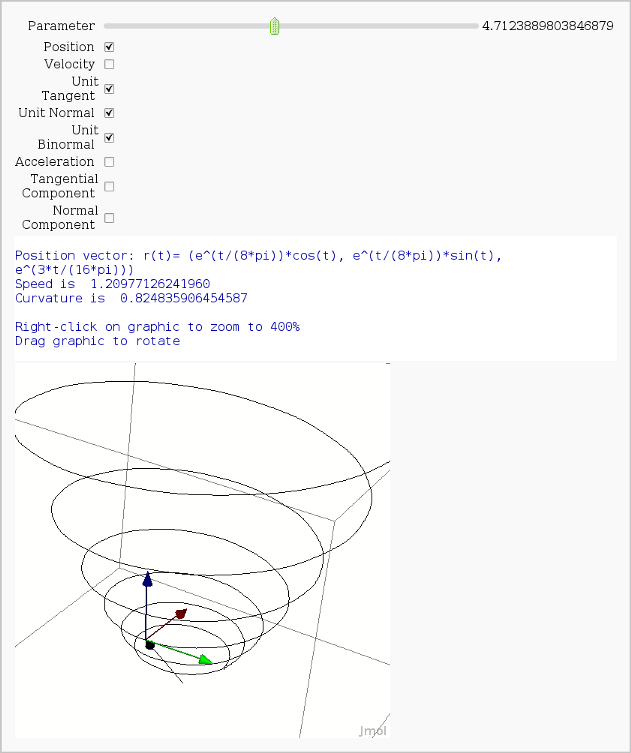
Vector Calculus, 3-D Motion
by Rob Beezer
Available as a worksheet
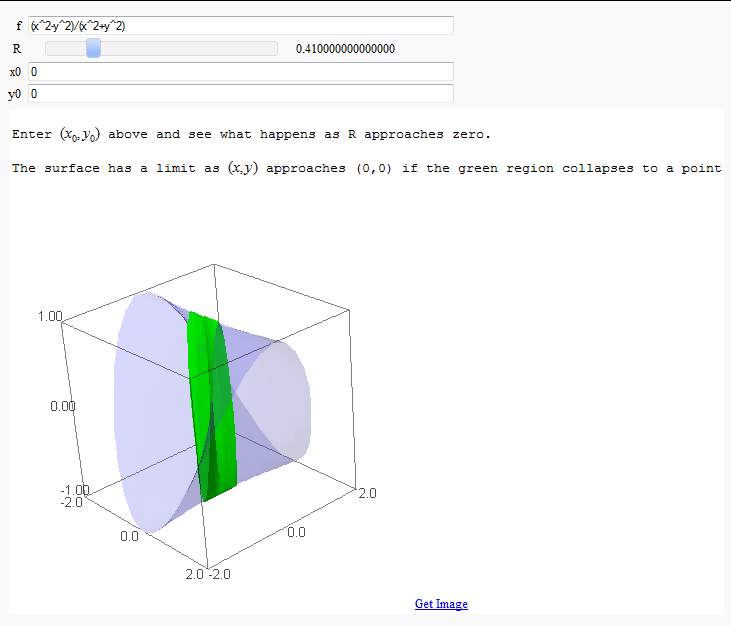
Multivariate Limits by Definition
by John Travis
http://sagenb.mc.edu/home/pub/97/
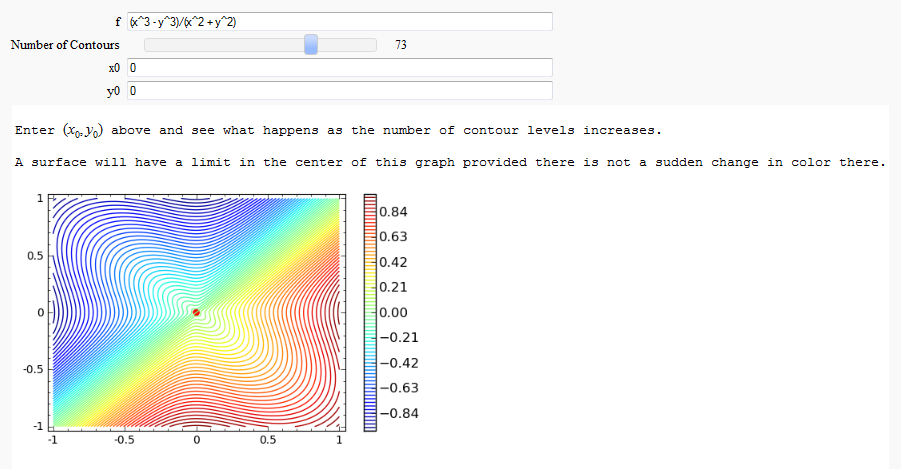
Directional Derivatives
This interact displays graphically a tangent line to a function, illustrating a directional derivative (the slope of the tangent line).
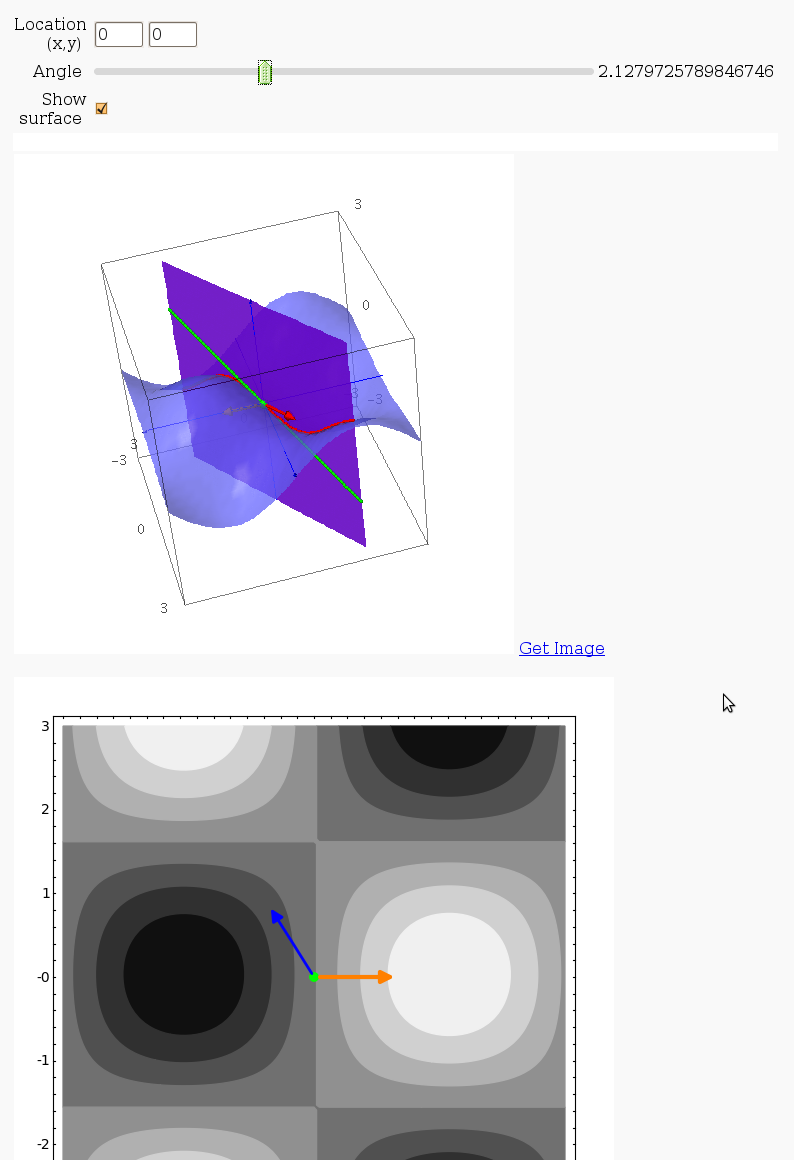
3D graph with points and curves
By Robert Marik
This sagelet is handy when showing local, constrained and absolute maxima and minima in two variables. Available as a worksheet
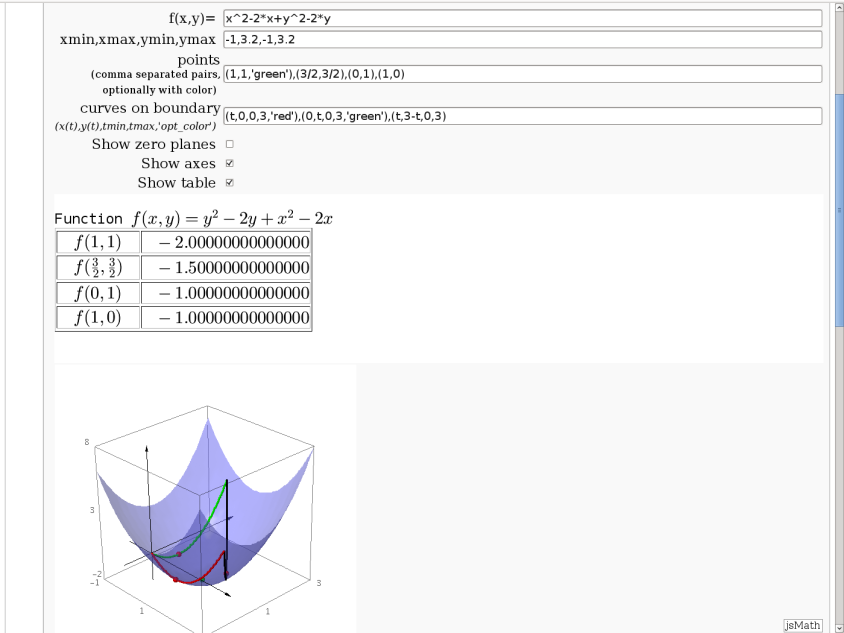
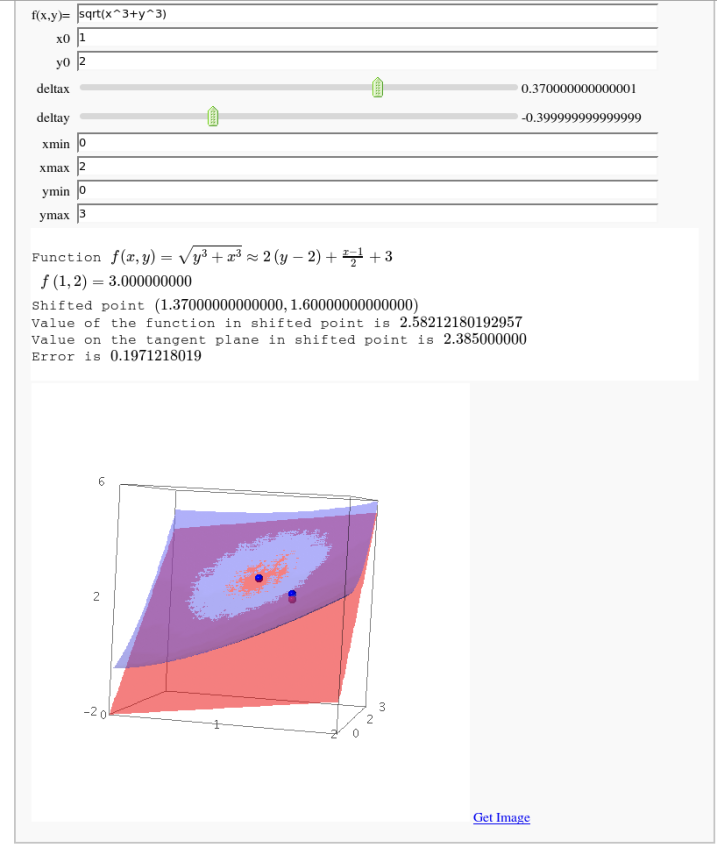
Approximating function in two variables by differential
by Robert Marik
Taylor approximations in two variables
by John Palmieri
This displays the nth order Taylor approximation, for n from 1 to 10, of the function sin(x2 + y2) cos(y) exp(-(x2+y2)/2).
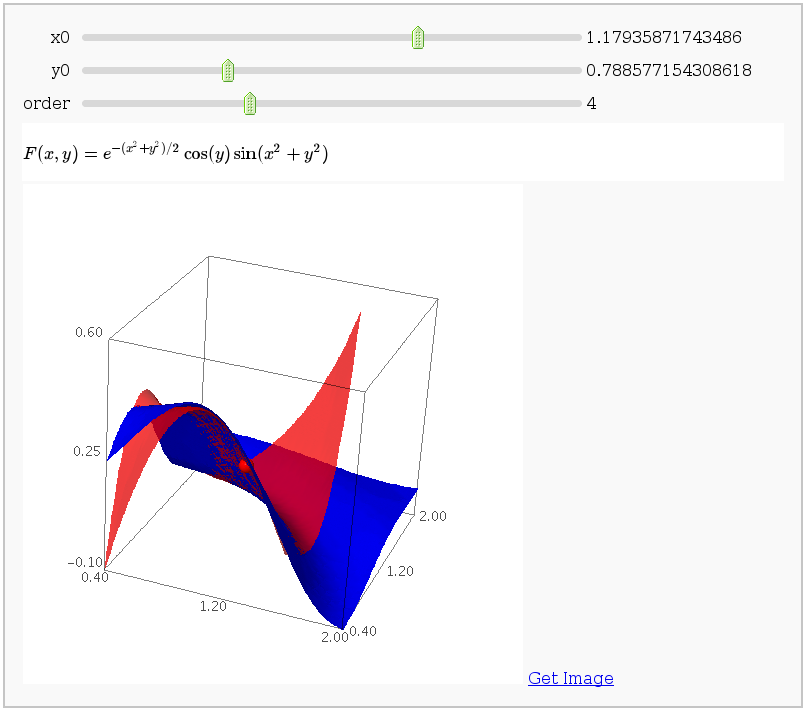
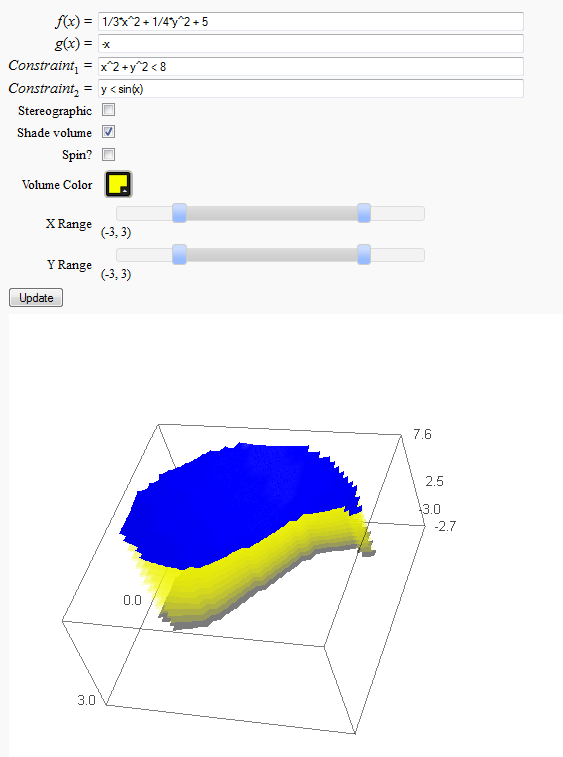
Volumes over non-rectangular domains
by John Travis
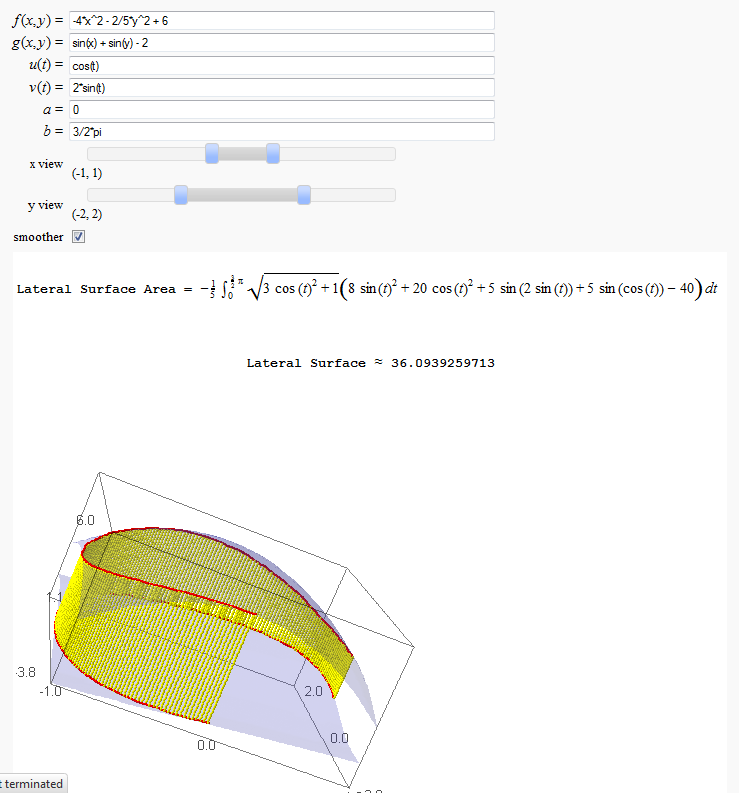
Lateral Surface Area (FIXME in Jupyter)
by John Travis
http://sagenb.mc.edu/home/pub/89/
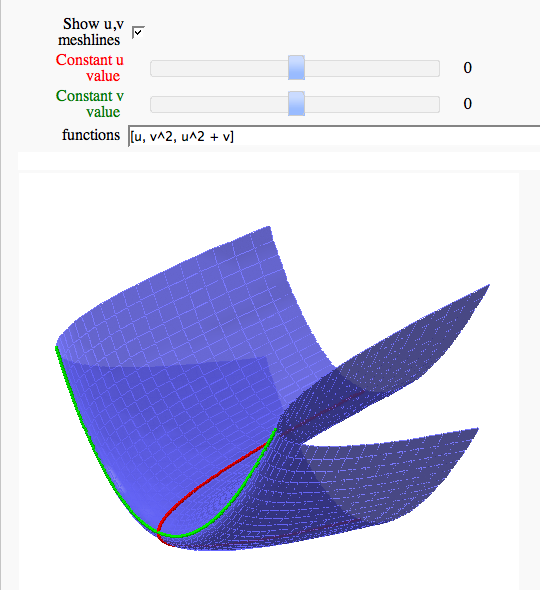
Parametric surface example (FIXME in Jupyter)
by Marshall Hampton
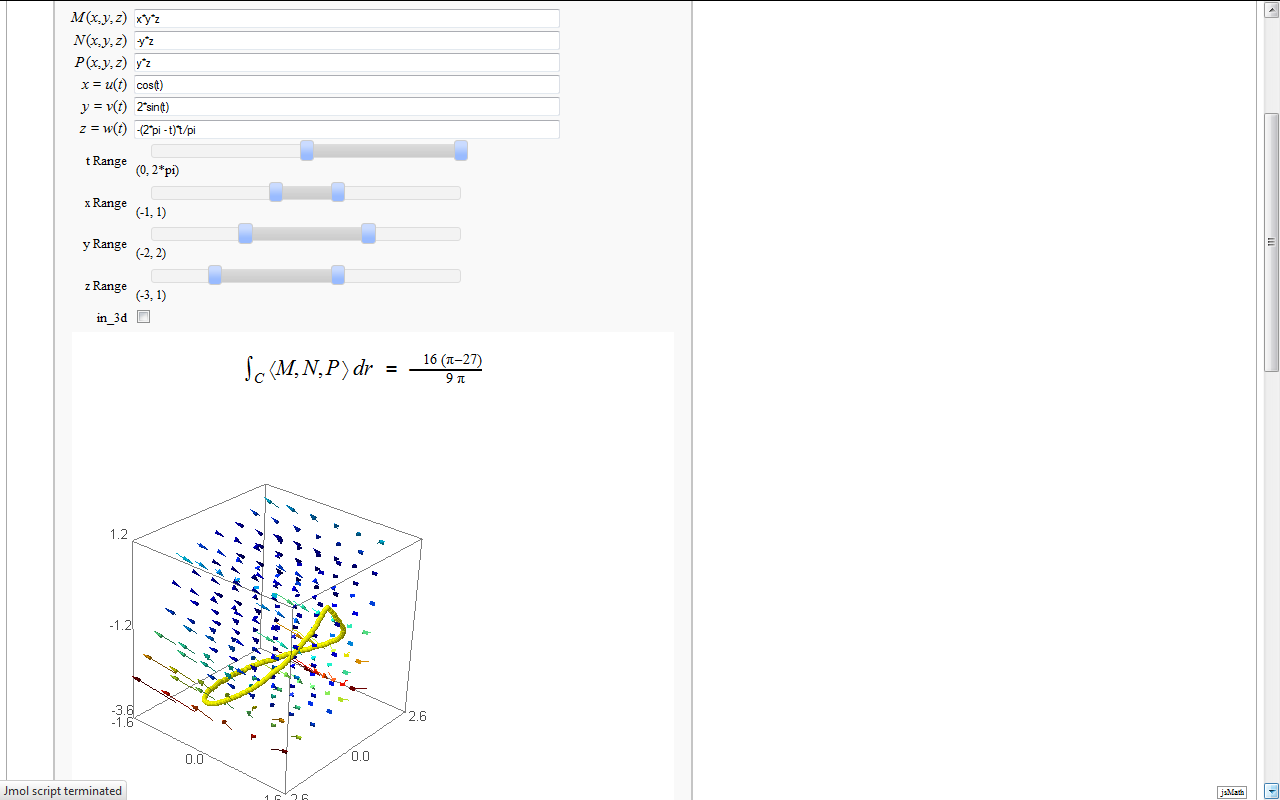
Line Integrals in 3D Vector Field
by John Travis