|
Size: 29376
Comment:
|
Size: 48272
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| = Sage Interactions - Number Theory = goto [[interact|interact main page]] |
|
| Line 5: | Line 2: |
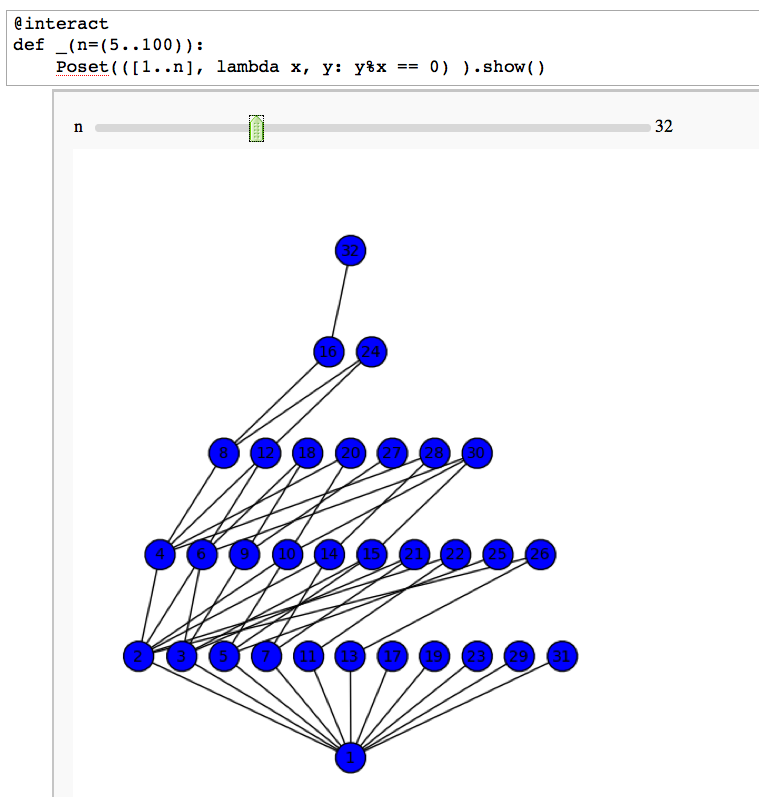
= Integer Factorization = == Divisibility Poset == by William Stein {{{#!sagecell @interact def _(n=(5..100)): Poset(([1..n], lambda x, y: y%x == 0) ).show() }}} {{attachment:divposet.png}} |
|
| Line 8: | Line 18: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 41: | Line 51: |
| g += line([(j*2-len(cur),-i), ((k*2)-len(rows[i-1]),-i+1)], | g += line([(j*2-len(cur),-i), ((k*2)-len(rows[i-1]),-i+1)], |
| Line 55: | Line 65: |
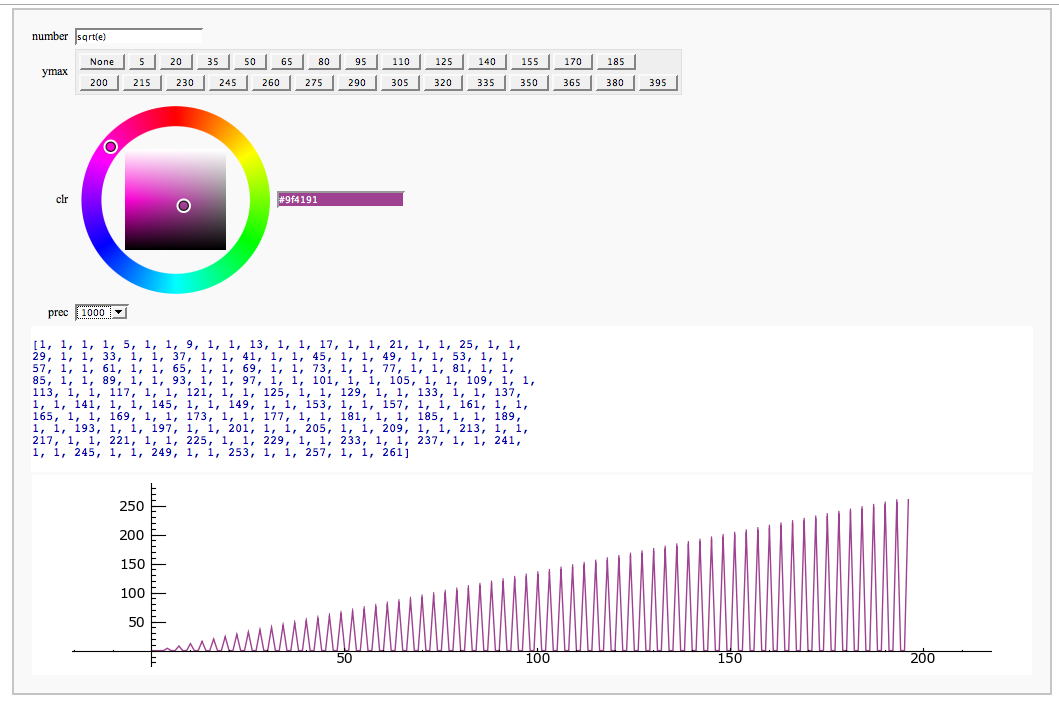
| == Continued Fraction Plotter == by William Stein {{{ @interact def _(number=e, ymax=selector([None,5,20,..,400],nrows=2), clr=Color('purple'), prec=[500,1000,..,5000]): c = list(continued_fraction(RealField(prec)(number))); print c show(line([(i,z) for i, z in enumerate(c)],rgbcolor=clr),ymax=ymax,figsize=[10,2]) }}} {{attachment:contfracplot.png}} |
More complicated demonstration using Mathematica: http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/FactorTrees/ == Factoring an Integer == by Timothy Clemans Sage implementation of the Mathematica demonstration of the same name. http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/FactoringAnInteger/ {{{#!sagecell @interact def _(r=selector(range(0,10000,1000), label='range', buttons=True), n=slider(0,1000,1,2,'n',False)): if not r and n in (0, 1): n = 2 s = '$%d = %s$' % (r + n, factor(r + n)) s = s.replace('*', '\\times') html(s) }}} = Prime Numbers = |
| Line 67: | Line 86: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 75: | Line 94: |
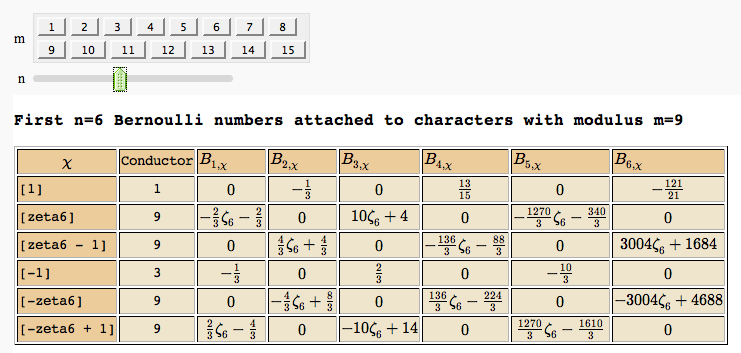
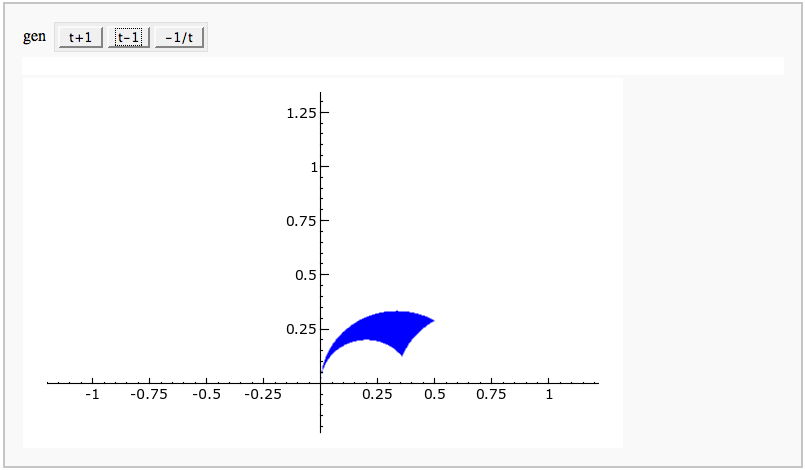
| == Computing Generalized Bernoulli Numbers == by William Stein (Sage-2.10.3) {{{ @interact def _(m=selector([1..15],nrows=2), n=(7,(3..10))): G = DirichletGroup(m) s = "<h3>First n=%s Bernoulli numbers attached to characters with modulus m=%s</h3>"%(n,m) s += '<table border=1>' s += '<tr bgcolor="#edcc9c"><td align=center>$\\chi$</td><td>Conductor</td>' + \ ''.join('<td>$B_{%s,\chi}$</td>'%k for k in [1..n]) + '</tr>' for eps in G.list(): v = ''.join(['<td align=center bgcolor="#efe5cd">$%s$</td>'%latex(eps.bernoulli(k)) for k in [1..n]]) s += '<tr><td bgcolor="#edcc9c">%s</td><td bgcolor="#efe5cd" align=center>%s</td>%s</tr>\n'%( eps, eps.conductor(), v) s += '</table>' html(s) }}} {{attachment:bernoulli.png}} == Fundamental Domains of SL_2(ZZ) == by Robert Miller {{{ L = [[-0.5, 2.0^(x/100.0) - 1 + sqrt(3.0)/2] for x in xrange(1000, -1, -1)] R = [[0.5, 2.0^(x/100.0) - 1 + sqrt(3.0)/2] for x in xrange(1000)] xes = [x/1000.0 for x in xrange(-500,501,1)] M = [[x,abs(sqrt(x^2-1))] for x in xes] fundamental_domain = L+M+R fundamental_domain = [[x-1,y] for x,y in fundamental_domain] @interact def _(gen = selector(['t+1', 't-1', '-1/t'], nrows=1)): global fundamental_domain if gen == 't+1': fundamental_domain = [[x+1,y] for x,y in fundamental_domain] elif gen == 't-1': fundamental_domain = [[x-1,y] for x,y in fundamental_domain] elif gen == '-1/t': new_dom = [] for x,y in fundamental_domain: sq_mod = x^2 + y^2 new_dom.append([(-1)*x/sq_mod, y/sq_mod]) fundamental_domain = new_dom P = polygon(fundamental_domain) P.ymax(1.2); P.ymin(-0.1) P.show() }}} {{attachment:fund_domain.png}} |
== Prime Spiral - Square FIXME == by David Runde {{{#!sagecell @interact def square_prime_spiral(start=1, end=100, size_limit = 10, show_lines=false, invert=false, x_cord=0, y_cord=0, n = 0): """ REFERENCES: Alpern, Dario. "Ulam's Spiral". http://www.alpertron.com.ar/ULAM.HTM Sacks, Robert. http://www.NumberSpiral.com Ventrella, Jeffery. "Prime Numbers are the Holes Behind Complex Composite Patterns". http://www.divisorplot.com Williamson, John. Number Spirals. http://www.dcs.gla.ac.uk/~jhw/spirals/index.html jhw@dcs.gla.ac.uk Weisstein, Eric W. "Prime-Generating Polynomial." From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Prime-GeneratingPolynomial.html """ #Takes an (x,y) coordinate (and the start of the spiral) and gives its corresponding n value def find_n(x,y, start): if x>0 and y>-x and y<=x: return 4*(x-1)^2 + 5*(x-1) + (start+1) + y elif x<=0 and y>=x and y<=-x: return 4*x^2 - x + (start) -y elif y>=0 and -y+1 <= x and y-1 >= x: return 4*y^2 -y + start -x elif y<0 and -x >= y and y<x: return 4*(y+1)^2 -11*(y+1) + (start+7) +x else: print 'NaN' #Takes in an n and the start value of the spiral and gives its (x,y) coordinate def find_xy(num, start): num = num - start +1 bottom = floor(sqrt(num)) top = ceil(sqrt(num)) if bottom^2 < num and num<=bottom^2+bottom+1: if bottom%2 == 0: x=-bottom/2 y=-x-(num-bottom^2)+1 else: x=bottom/2+1/2 y=-x + (num-bottom^2) else: if top%2 == 0: y=top/2 x=-top/2+1+top^2-num else: y=-top/2+1/2 x=top/2 -1/2 - (top^2-num) x = Integer(x) y = Integer(y) return (x,y) if start < 1 or end <=start: print "invalid start or end value" if n > end: print "WARNING: n is larger than the end value" #Changes the entry of a matrix by taking the old matrix and the (x,y) coordinate (in matrix coordinates) and returns the changed matrix def matrix_morph(M, x, y, set): N = copy(M) N[x-1,y] = set M = N return M #These functions return an int based on where the t is located in the spiral def SW_NE(t, x, y, start): if -y<x: return 4*t^2 + 2*t -x+y+start else: return 4*t^2 + 2*t +x-y+start def NW_SE(t, x, y, start): if x<y: return 4*t^2 -x-y+start else: return 4*t^2 + 4*t +x+y+start size = ceil(sqrt(end-start+1)) #Size of the matrix num=copy(start) # Start number (might not be used) x = ceil(size/2) #starting center x of the matrix (in matrix coordinates) y = copy(x) #starting center y of the matrix (in matrix coordinates) if n !=0: x_cord, y_cord = find_xy(n, start) #Overrides the user given x and y coordinates xt = copy(x_cord) yt = copy(y_cord) countx=0 county=0 overcount = 1 if size <= size_limit: M = matrix(ZZ, size+1) # Allows the numbers to be seen in the smaller matricies else: M = matrix(GF(2), size+1) # Restricts the entries to 0 or 1 main_list = set() #print x_cord, y_cord if show_lines: for t in [(-size-1)..size+1]: m= SW_NE(t, xt, yt, start) if m.is_pseudoprime(): main_list.add(m) m= NW_SE(t, xt, yt, start) if m.is_pseudoprime(): main_list.add(m) else: main_list = set(prime_range(end)) #This for loop changes the matrix by spiraling out from the center and changing each entry as it goes. It is faster than the find_xy function above. for num in [start..end]: #print x, "=x y=", y, " num =", num if countx < overcount: if overcount % 2 == 1: x+=1 else: x-=1 countx += 1 elif county < overcount: if overcount % 2 == 1: y+=1 else: y-=1 county += 1 else: overcount += 1 countx=2 county=0 if overcount % 2 == 1: x+=1 else: x-=1 if not invert and num in main_list: if size <= size_limit: M = matrix_morph(M, x, y, num) else: M = matrix_morph(M, x, y, 1) elif invert and num not in main_list: #This does the opposite of the above if statement by changing the matrix only when a number is not in the list of allowable primes if size <= size_limit: M = matrix_morph(M, x, y, num) else: M = matrix_morph(M, x, y, 1) if n != 0: print '(to go from x,y coords to an n, reset by setting n=0)' (x_cord, y_cord) = find_xy(n, start) #print 'if n =', n, 'then (x,y) =', (x_cord, y_cord) print '(x,y) =', (x_cord, y_cord), '<=> n =', find_n(x_cord, y_cord, start) print ' ' print "SW/NE line" if -y_cord<x_cord: print '4*t^2 + 2*t +', -x_cord+y_cord+start else: print '4*t^2 + 2*t +', +x_cord-y_cord+start print "NW/SE line" if x_cord<y_cord: print '4*t^2 +', -x_cord-y_cord+start else: print '4*t^2 + 4*t +', +x_cord+y_cord+start if size <= size_limit: show(M) #Displays the matrix with integer entries else: M.visualize_structure() # Displays the final resulting matrix as a series of pixels (1 <=> pixel on) #matrix_plot(M) }}} {{attachment:SquareSpiral.PNG}} == Prime Spiral - Polar == by David Runde {{{#!sagecell @interact def polar_prime_spiral(start=1, end=2000, show_factors = false, highlight_primes = false, show_curves=true, n = 0): #For more information about the factors in the spiral, visit http://www.dcs.gla.ac.uk/~jhw/spirals/index.html by John Williamson. if start < 1 or end <=start: print "invalid start or end value" if n > end: print "WARNING: n is greater than end value" def f(n): return (sqrt(n)*cos(2*pi*sqrt(n)), sqrt(n)*sin(2*pi*sqrt(n))) list =[] list2=[] if show_factors == false: for i in [start..end]: if i.is_pseudoprime(): list.append(f(i-start+1)) #Primes list else: list2.append(f(i-start+1)) #Composites list P = points(list) R = points(list2, alpha = .1) #Faded Composites else: for i in [start..end]: list.append(disk((f(i-start+1)),0.05*pow(2,len(factor(i))-1), (0,2*pi))) #resizes each of the dots depending of the number of factors of each number if i.is_pseudoprime() and highlight_primes: list2.append(f(i-start+1)) P = plot(list) p_size = 5 #the orange dot size of the prime markers if not highlight_primes: list2 = [(f(n-start+1))] R=points(list2, hue = .1, pointsize = p_size) if n > 0: print 'n =', factor(n) p = 1 #The X which marks the given n W1 = disk((f(n-start+1)), p, (pi/6, 2*pi/6)) W2 = disk((f(n-start+1)), p, (4*pi/6, 5*pi/6)) W3 = disk((f(n-start+1)), p, (7*pi/6, 8*pi/6)) W4 = disk((f(n-start+1)), p, (10*pi/6, 11*pi/6)) Q = plot(W1+W2+W3+W4, alpha = .1) n=n-start+1 #offsets the n for different start values to ensure accurate plotting if show_curves: begin_curve = 0 t = var('t') a=1 b=0 if n > (floor(sqrt(n)))^2 and n <= (floor(sqrt(n)))^2 + floor(sqrt(n)): c = -((floor(sqrt(n)))^2 - n) c2= -((floor(sqrt(n)))^2 + floor(sqrt(n)) - n) else: c = -((ceil(sqrt(n)))^2 - n) c2= -((floor(sqrt(n)))^2 + floor(sqrt(n)) - n) print 'Pink Curve: n^2 +', c print 'Green Curve: n^2 + n +', c2 def g(m): return (a*m^2+b*m+c); def r(m) : return sqrt(g(m)) def theta(m) : return r(m)- m*sqrt(a) S1 = parametric_plot(((r(t))*cos(2*pi*(theta(t))),(r(t))*sin(2*pi*(theta(t)))), begin_curve, ceil(sqrt(end-start)), rgbcolor=hue(0.8), thickness = .2) #Pink Line b=1 c= c2; S2 = parametric_plot(((r(t))*cos(2*pi*(theta(t))),(r(t))*sin(2*pi*(theta(t)))), begin_curve, ceil(sqrt(end-start)), rgbcolor=hue(0.6), thickness = .2) #Green Line show(R+P+S1+S2+Q, aspect_ratio = 1, axes = false) else: show(R+P+Q, aspect_ratio = 1, axes = false) else: show(R+P, aspect_ratio = 1, axes = false) }}} {{attachment:PolarSpiral.PNG}} = Modular Forms = |
| Line 127: | Line 307: |
| {{{ j = 0 @interact def _(N=[1..100], k=selector([2,4,..,12],nrows=1), prec=(3..40), |
{{{#!sagecell @interact def _(N=[1..100], k=selector([2,4,..,12],nrows=1), prec=(3..40), |
| Line 133: | Line 312: |
| print j; global j; j += 1 | |
| Line 150: | Line 328: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 163: | Line 341: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 171: | Line 349: |
| G = Graph(T, multiedges=True, loops=not three_d) | G = DiGraph(T, multiedges=not three_d) if three_d: G.remove_loops() |
| Line 182: | Line 362: |
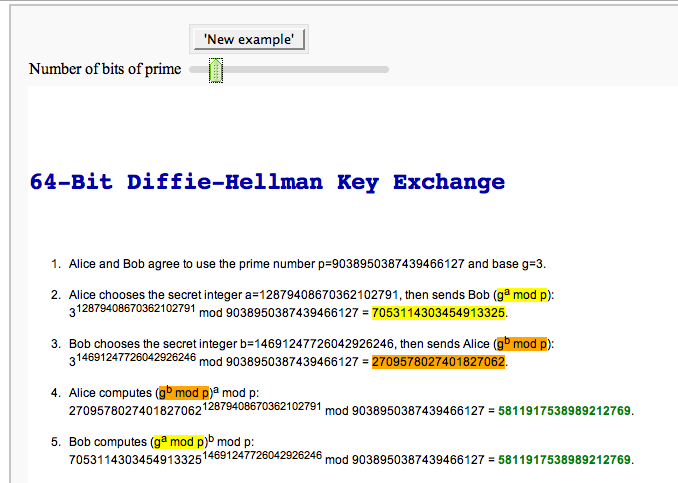
| == Demonstrating the Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange Protocol == by Timothy Clemans (refereed by William Stein) {{{ @interact def diffie_hellman(button=selector(["New example"],label='',buttons=True), bits=("Number of bits of prime", (8,12,..512))): maxp = 2^bits p = random_prime(maxp) k = GF(p) if bits>100: g = k(2) else: g = k.multiplicative_generator() a = ZZ.random_element(10, maxp) b = ZZ.random_element(10, maxp) print """ <html> <style> .gamodp { background:yellow } .gbmodp { background:orange } .dhsame { color:green; font-weight:bold } </style> <h2>%s-Bit Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange</h2> <ol style="color:#000;font:12px Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif"> <li>Alice and Bob agree to use the prime number p=%s and base g=%s.</li> <li>Alice chooses the secret integer a=%s, then sends Bob (<span class="gamodp">g<sup>a</sup> mod p</span>):<br/>%s<sup>%s</sup> mod %s = <span class="gamodp">%s</span>.</li> <li>Bob chooses the secret integer b=%s, then sends Alice (<span class="gbmodp">g<sup>b</sup> mod p</span>):<br/>%s<sup>%s</sup> mod %s = <span class="gbmodp">%s</span>.</li> <li>Alice computes (<span class="gbmodp">g<sup>b</sup> mod p</span>)<sup>a</sup> mod p:<br/>%s<sup>%s</sup> mod %s = <span class="dhsame">%s</span>.</li> <li>Bob computes (<span class="gamodp">g<sup>a</sup> mod p</span>)<sup>b</sup> mod p:<br/>%s<sup>%s</sup> mod %s = <span class="dhsame">%s</span>.</li> </ol></html> """ % (bits, p, g, a, g, a, p, (g^a), b, g, b, p, (g^b), (g^b), a, p, (g^ b)^a, g^a, b, p, (g^a)^b) }}} {{attachment:dh.png}} == Plotting an elliptic curve over a finite field == {{{ E = EllipticCurve('37a') @interact def _(p=slider(prime_range(1000), default=389)): show(E) print "p = %s"%p show(E.change_ring(GF(p)).plot(),xmin=0,ymin=0) }}} {{attachment:ellffplot.png}} == Prime Spiral - Square == by David Runde {{{ @interact def square_prime_spiral(start=1, end=100, size_limit = 10, show_lines=false, invert=false, x_cord=0, y_cord=0, n = 0): """ REFERENCES: Alpern, Dario. "Ulam's Spiral". http://www.alpertron.com.ar/ULAM.HTM Sacks, Robert. http://www.NumberSpiral.com Ventrella, Jeffery. "Prime Numbers are the Holes Behind Complex Composite Patterns". http://www.divisorplot.com Williamson, John. Number Spirals. http://www.dcs.gla.ac.uk/~jhw/spirals/index.html jhw@dcs.gla.ac.uk Weisstein, Eric W. "Prime-Generating Polynomial." From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Prime-GeneratingPolynomial.html """ #Takes an (x,y) coordinate (and the start of the spiral) and gives its corresponding n value def find_n(x,y, start): if x>0 and y>-x and y<=x: return 4*(x-1)^2 + 5*(x-1) + (start+1) + y elif x<=0 and y>=x and y<=-x: return 4*x^2 - x + (start) -y elif y>=0 and -y+1 <= x and y-1 >= x: return 4*y^2 -y + start -x elif y<0 and -x >= y and y<x: return 4*(y+1)^2 -11*(y+1) + (start+7) +x else: print 'NaN' #Takes in an n and the start value of the spiral and gives its (x,y) coordinate def find_xy(num, start): num = num - start +1 bottom = floor(sqrt(num)) top = ceil(sqrt(num)) if bottom^2 < num and num<=bottom^2+bottom+1: if bottom%2 == 0: x=-bottom/2 y=-x-(num-bottom^2)+1 else: x=bottom/2+1/2 y=-x + (num-bottom^2) else: if top%2 == 0: y=top/2 x=-top/2+1+top^2-num else: y=-top/2+1/2 x=top/2 -1/2 - (top^2-num) x = Integer(x) y = Integer(y) return (x,y) if start < 1 or end <=start: print "invalid start or end value" if n > end: print "WARNING: n is larger than the end value" #Changes the entry of a matrix by taking the old matrix and the (x,y) coordinate (in matrix coordinates) and returns the changed matrix def matrix_morph(M, x, y, set): N = M.copy() N[x-1,y] = set M = N return M #These functions return an int based on where the t is located in the spiral def SW_NE(t, x, y, start): if -y<x: return 4*t^2 + 2*t -x+y+start else: return 4*t^2 + 2*t +x-y+start def NW_SE(t, x, y, start): if x<y: return 4*t^2 -x-y+start else: return 4*t^2 + 4*t +x+y+start size = ceil(sqrt(end-start+1)) #Size of the matrix num=copy(start) # Start number (might not be used) x = ceil(size/2) #starting center x of the matrix (in matrix coordinates) y = copy(x) #starting center y of the matrix (in matrix coordinates) if n !=0: x_cord, y_cord = find_xy(n, start) #Overrides the user given x and y coordinates xt = copy(x_cord) yt = copy(y_cord) countx=0 county=0 overcount = 1 if size <= size_limit: M = matrix(ZZ, size+1) # Allows the numbers to be seen in the smaller matricies else: M = matrix(GF(2), size+1) # Restricts the entries to 0 or 1 main_list = set() #print x_cord, y_cord if show_lines: for t in [(-size-1)..size+1]: m= SW_NE(t, xt, yt, start) if m.is_pseudoprime(): main_list.add(m) m= NW_SE(t, xt, yt, start) if m.is_pseudoprime(): main_list.add(m) else: main_list = set(prime_range(end)) #This for loop changes the matrix by spiraling out from the center and changing each entry as it goes. It is faster than the find_xy function above. for num in [start..end]: #print x, "=x y=", y, " num =", num if countx < overcount: if overcount % 2 == 1: x+=1 else: x-=1 countx += 1 elif county < overcount: if overcount % 2 == 1: y+=1 else: y-=1 county += 1 else: overcount += 1 countx=2 county=0 if overcount % 2 == 1: x+=1 else: x-=1 if not invert and num in main_list: if size <= size_limit: M = matrix_morph(M, x, y, num) else: M = matrix_morph(M, x, y, 1) elif invert and num not in main_list: #This does the opposite of the above if statement by changing the matrix only when a number is not in the list of allowable primes if size <= size_limit: M = matrix_morph(M, x, y, num) else: M = matrix_morph(M, x, y, 1) if n != 0: print '(to go from x,y coords to an n, reset by setting n=0)' (x_cord, y_cord) = find_xy(n, start) #print 'if n =', n, 'then (x,y) =', (x_cord, y_cord) print '(x,y) =', (x_cord, y_cord), '<=> n =', find_n(x_cord, y_cord, start) print ' ' print "SW/NE line" if -y_cord<x_cord: print '4*t^2 + 2*t +', -x_cord+y_cord+start else: print '4*t^2 + 2*t +', +x_cord-y_cord+start print "NW/SE line" if x_cord<y_cord: print '4*t^2 +', -x_cord-y_cord+start else: print '4*t^2 + 4*t +', +x_cord+y_cord+start if size <= size_limit: show(M) #Displays the matrix with integer entries else: M.visualize_structure() # Displays the final resulting matrix as a series of pixels (1 <=> pixel on) #matrix_plot(M) }}} {{attachment:SquareSpiral.PNG}} == Prime Spiral - Polar == by David Runde {{{ @interact def polar_prime_spiral(start=1, end=2000, show_factors = false, highlight_primes = false, show_curves=true, n = 0): #For more information about the factors in the spiral, visit http://www.dcs.gla.ac.uk/~jhw/spirals/index.html by John Williamson. if start < 1 or end <=start: print "invalid start or end value" if n > end: print "WARNING: n is greater than end value" def f(n): return (sqrt(n)*cos(2*pi*sqrt(n)), sqrt(n)*sin(2*pi*sqrt(n))) list =[] list2=[] if show_factors == false: for i in [start..end]: if i.is_pseudoprime(): list.append(f(i-start+1)) #Primes list else: list2.append(f(i-start+1)) #Composites list P = points(list) R = points(list2, alpha = .1) #Faded Composites else: for i in [start..end]: list.append(disk((f(i-start+1)),0.05*pow(2,len(factor(i))-1), (0,2*pi))) #resizes each of the dots depending of the number of factors of each number if i.is_pseudoprime() and highlight_primes: list2.append(f(i-start+1)) P = plot(list) p_size = 5 #the orange dot size of the prime markers if not highlight_primes: list2 = [(f(n-start+1))] R=points(list2, hue = .1, pointsize = p_size) if n > 0: print 'n =', factor(n) p = 1 #The X which marks the given n W1 = disk((f(n-start+1)), p, (pi/6, 2*pi/6)) W2 = disk((f(n-start+1)), p, (4*pi/6, 5*pi/6)) W3 = disk((f(n-start+1)), p, (7*pi/6, 8*pi/6)) W4 = disk((f(n-start+1)), p, (10*pi/6, 11*pi/6)) Q = plot(W1+W2+W3+W4, alpha = .1) n=n-start+1 #offsets the n for different start values to ensure accurate plotting if show_curves: begin_curve = 0 t = var('t') a=1 b=0 if n > (floor(sqrt(n)))^2 and n <= (floor(sqrt(n)))^2 + floor(sqrt(n)): c = -((floor(sqrt(n)))^2 - n) c2= -((floor(sqrt(n)))^2 + floor(sqrt(n)) - n) else: c = -((ceil(sqrt(n)))^2 - n) c2= -((floor(sqrt(n)))^2 + floor(sqrt(n)) - n) print 'Pink Curve: n^2 +', c print 'Green Curve: n^2 + n +', c2 def g(m): return (a*m^2+b*m+c); def r(m) : return sqrt(g(m)) def theta(m) : return r(m)- m*sqrt(a) S1 = parametric_plot(((r(t))*cos(2*pi*(theta(t))),(r(t))*sin(2*pi*(theta(t)))), begin_curve, ceil(sqrt(end-start)), rgbcolor=hue(0.8), thickness = .2) #Pink Line b=1 c= c2; S2 = parametric_plot(((r(t))*cos(2*pi*(theta(t))),(r(t))*sin(2*pi*(theta(t)))), begin_curve, ceil(sqrt(end-start)), rgbcolor=hue(0.6), thickness = .2) #Green Line show(R+P+S1+S2+Q, aspect_ratio = 1, axes = false) else: show(R+P+Q, aspect_ratio = 1, axes = false) else: show(R+P, aspect_ratio = 1, axes = false) }}} {{attachment:PolarSpiral.PNG}} == Quadratic Residue Table == |
= Modular Arithmetic = == Quadratic Residue Table FIXME == |
| Line 448: | Line 366: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 499: | Line 417: |
| == Cubic Residue Table == | == Cubic Residue Table FIXME == |
| Line 501: | Line 419: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 519: | Line 437: |
| if Mod(a,3)!=0 and Mod(b,3)==0: return True else: return False |
return Mod(a,3)!=0 and Mod(b,3)==0 |
| Line 557: | Line 472: |
| MP += line([(i,0),(i,r)], rgbcolor='black') | MP += line([(i,0),(i,r)], rgbcolor='black') |
| Line 581: | Line 496: |
| = Cyclotomic Fields = |
|
| Line 583: | Line 500: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 632: | Line 549: |
| S = circle((0,0),1,rgbcolor='yellow') \ + line([e_pt,e_gs_pt], rgbcolor='red', thickness=4) \ + line([f_pt,f_gs_pt], rgbcolor='blue', thickness=3) \ + line([ef_pt,ef_gs_pt], rgbcolor='purple',thickness=2) \ + point(e_pt,pointsize=50, rgbcolor='red') \ + point(f_pt,pointsize=50, rgbcolor='blue') \ + point(ef_pt,pointsize=50,rgbcolor='purple') \ + point(f_gs_pt,pointsize=75, rgbcolor='black') \ + point(e_gs_pt,pointsize=75, rgbcolor='black') \ + point(ef_gs_pt,pointsize=75, rgbcolor='black') \ + point(js_pt,pointsize=100,rgbcolor='green') |
S = circle((0,0),1,rgbcolor='yellow') S += line([e_pt,e_gs_pt], rgbcolor='red', thickness=4) S += line([f_pt,f_gs_pt], rgbcolor='blue', thickness=3) S += line([ef_pt,ef_gs_pt], rgbcolor='purple',thickness=2) S += point(e_pt,pointsize=50, rgbcolor='red') S += point(f_pt,pointsize=50, rgbcolor='blue') S += point(ef_pt,pointsize=50,rgbcolor='purple') S += point(f_gs_pt,pointsize=75, rgbcolor='black') S += point(e_gs_pt,pointsize=75, rgbcolor='black') S += point(ef_gs_pt,pointsize=75, rgbcolor='black') S += point(js_pt,pointsize=100,rgbcolor='green') |
| Line 644: | Line 561: |
| S += text('$J(%s,%s) = %s$'%(latex2(e),latex2(f),latex(js)), \ | S += text('$J(%s,%s) = %s$'%(latex2(e),latex2(f),latex(js)), |
| Line 663: | Line 580: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 712: | Line 629: |
| S = circle((0,0),1,rgbcolor='yellow') \ + line([e_pt,e_gs_pt], rgbcolor='red', thickness=4) \ + line([f_pt,f_gs_pt], rgbcolor='blue', thickness=3) \ + line([ef_pt,ef_gs_pt], rgbcolor='purple',thickness=2) \ + point(e_pt,pointsize=50, rgbcolor='red') \ + point(f_pt,pointsize=50, rgbcolor='blue') \ + point(ef_pt,pointsize=50,rgbcolor='purple') \ + point(f_gs_pt,pointsize=75, rgbcolor='black') \ + point(e_gs_pt,pointsize=75, rgbcolor='black') \ + point(ef_gs_pt,pointsize=75, rgbcolor='black') \ + point(js_pt,pointsize=100,rgbcolor='green') |
S = circle((0,0),1,rgbcolor='yellow') S += line([e_pt,e_gs_pt], rgbcolor='red', thickness=4) S += line([f_pt,f_gs_pt], rgbcolor='blue', thickness=3) S += line([ef_pt,ef_gs_pt], rgbcolor='purple',thickness=2) S += point(e_pt,pointsize=50, rgbcolor='red') S += point(f_pt,pointsize=50, rgbcolor='blue') S += point(ef_pt,pointsize=50,rgbcolor='purple') S += point(f_gs_pt,pointsize=75, rgbcolor='black') S += point(e_gs_pt,pointsize=75, rgbcolor='black') S += point(ef_gs_pt,pointsize=75, rgbcolor='black') S += point(js_pt,pointsize=100,rgbcolor='green') |
| Line 724: | Line 641: |
| S += text('$J(%s,%s) = %s$'%(latex2(e),latex2(f),latex(js)), \ | S += text('$J(%s,%s) = %s$'%(latex2(e),latex2(f),latex(js)), |
| Line 736: | Line 653: |
| ga[i].save('j%d.PNG'%i,figsize=4,aspect_ratio=1, \ | ga[i].save('j%d.png'%i,figsize=4,aspect_ratio=1, |
| Line 742: | Line 659: |
| html('<table bgcolor=lightgrey cellpadding=2>') | s='<table bgcolor=lightgrey cellpadding=2>' |
| Line 744: | Line 661: |
| html('<tr><td align="center"><img src="cell://j%d.PNG"></td>'%(2*i)) html('<td align="center"><img src="cell://j%d.PNG"></td></tr>'%(2*i+1)) html('</table>') }}} |
s+='<tr><td align="center"><img src="cell://j%d.png"></td>'%(2*i) s+='<td align="center"><img src="cell://j%d.png"></td></tr>'%(2*i+1) s+='</table>' html(s)}}} |
| Line 750: | Line 667: |
= Elliptic Curves = |
|
| Line 753: | Line 672: |
| {{{ | {{{#!sagecell |
| Line 759: | Line 678: |
| else: | else: |
| Line 766: | Line 685: |
def line_from_curve_points(E,P,Q,style='-',rgb=(1,0,0),length=25): """ P,Q two points on an elliptic curve. Output is a graphic representation of the straight line intersecting with P,Q. """ # The function tangent to P=Q on E if P == Q: if P[2]==0: return line([(1,-length),(1,length)],linestyle=style,rgbcolor=rgb) else: # Compute slope of the curve E in P l=-(3*P[0]^2 + 2*E.a2()*P[0] + E.a4() - E.a1()*P[1])/((-2)*P[1] - E.a1()*P[0] - E.a3()) f(x) = l * (x - P[0]) + P[1] return plot(f(x),-length,length,linestyle=style,rgbcolor=rgb) # Trivial case of P != R where P=O or R=O then we get the vertical line from the other point elif P[2] == 0: return line([(Q[0],-length),(Q[0],length)],linestyle=style,rgbcolor=rgb) elif Q[2] == 0: return line([(P[0],-length),(P[0],length)],linestyle=style,rgbcolor=rgb) # Non trivial case where P != R else: # Case where x_1 = x_2 return vertical line evaluated in Q if P[0] == Q[0]: return line([(P[0],-length),(P[0],length)],linestyle=style,rgbcolor=rgb) #Case where x_1 != x_2 return line trough P,R evaluated in Q" l=(Q[1]-P[1])/(Q[0]-P[0]) f(x) = l * (x - P[0]) + P[1] return plot(f(x),-length,length,linestyle=style,rgbcolor=rgb) |
|
| Line 768: | Line 718: |
| curve = E.plot(rgbcolor = (0,0,1),xmin=25,xmax=25,plot_points=300) | curve = E.plot(rgbcolor = (0,0,1),xmin=-5,xmax=5,plot_points=300) |
| Line 794: | Line 744: |
def line_from_curve_points(E,P,Q,style='-',rgb=(1,0,0),length=25): """ P,Q two points on an elliptic curve. Output is a graphic representation of the straight line intersecting with P,Q. """ # The function tangent to P=Q on E if P == Q: if P[2]==0: return line([(1,-length),(1,length)],linestyle=style,rgbcolor=rgb) |
}}} {{attachment:PointAddEllipticCurve.png}} == Plotting an elliptic curve over a finite field == {{{#!sagecell E = EllipticCurve('37a') @interact def _(p=slider(prime_range(1000), default=389)): show(E) print "p = %s"%p show(E.change_ring(GF(p)).plot(),xmin=0,ymin=0) }}} {{attachment:ellffplot.png}} = Cryptography = == The Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange Protocol == by Timothy Clemans and William Stein {{{#!sagecell @interact def diffie_hellman(bits=slider(8, 513, 4, 8, 'Number of bits', False), button=selector(["Show new example"],label='',buttons=True)): maxp = 2 ^ bits p = random_prime(maxp) k = GF(p) if bits > 100: g = k(2) else: g = k.multiplicative_generator() a = ZZ.random_element(10, maxp) b = ZZ.random_element(10, maxp) html(""" <style> .gamodp, .gbmodp { color:#000; padding:5px } .gamodp { background:#846FD8 } .gbmodp { background:#FFFC73 } .dhsame { color:#000; font-weight:bold } </style> <h2 style="color:#000;font-family:Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif">%s-Bit Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange</h2> <ol style="color:#000;font-family:Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif"> <li>Alice and Bob agree to use the prime number p = %s and base g = %s.</li> <li>Alice chooses the secret integer a = %s, then sends Bob (<span class="gamodp">g<sup>a</sup> mod p</span>):<br/>%s<sup>%s</sup> mod %s = <span class="gamodp">%s</span>.</li> <li>Bob chooses the secret integer b=%s, then sends Alice (<span class="gbmodp">g<sup>b</sup> mod p</span>):<br/>%s<sup>%s</sup> mod %s = <span class="gbmodp">%s</span>.</li> <li>Alice computes (<span class="gbmodp">g<sup>b</sup> mod p</span>)<sup>a</sup> mod p:<br/>%s<sup>%s</sup> mod %s = <span class="dhsame">%s</span>.</li> <li>Bob computes (<span class="gamodp">g<sup>a</sup> mod p</span>)<sup>b</sup> mod p:<br/>%s<sup>%s</sup> mod %s = <span class="dhsame">%s</span>.</li> </ol> """ % (bits, p, g, a, g, a, p, (g^a), b, g, b, p, (g^b), (g^b), a, p, (g^ b)^a, g^a, b, p, (g^a)^b)) }}} {{attachment:dh.png}} = Other = == Continued Fraction Plotter == by William Stein {{{#!sagecell @interact def _(number=e, ymax=selector([5,20,..,400],nrows=2), clr=Color('purple'), prec=[500,1000,..,5000]): c = list(continued_fraction(RealField(prec)(number))); print c show(line([(i,z) for i, z in enumerate(c)],rgbcolor=clr),ymax=ymax,figsize=[10,2]) }}} {{attachment:contfracplot.png}} == Computing Generalized Bernoulli Numbers == by William Stein (Sage-2.10.3) {{{#!sagecell @interact def _(m=selector([1..15],nrows=2), n=(7,(3..10))): G = DirichletGroup(m) s = "<h3>First n=%s Bernoulli numbers attached to characters with modulus m=%s</h3>"%(n,m) s += '<table border=1>' s += '<tr bgcolor="#edcc9c"><td align=center>$\\chi$</td><td>Conductor</td>' + \ ''.join('<td>$B_{%s,\chi}$</td>'%k for k in [1..n]) + '</tr>' for eps in G.list(): v = ''.join(['<td align=center bgcolor="#efe5cd">$%s$</td>'%latex(eps.bernoulli(k)) for k in [1..n]]) s += '<tr><td bgcolor="#edcc9c">%s</td><td bgcolor="#efe5cd" align=center>%s</td>%s</tr>\n'%( eps, eps.conductor(), v) s += '</table>' html(s) }}} {{attachment:bernoulli.png}} == Fundamental Domains of SL_2(ZZ) == by Robert Miller {{{#!sagecell L = [[-0.5, 2.0^(x/100.0) - 1 + sqrt(3.0)/2] for x in xrange(1000, -1, -1)] R = [[0.5, 2.0^(x/100.0) - 1 + sqrt(3.0)/2] for x in xrange(1000)] xes = [x/1000.0 for x in xrange(-500,501,1)] M = [[x,abs(sqrt(x^2-1))] for x in xes] fundamental_domain = L+M+R fundamental_domain = [[x-1,y] for x,y in fundamental_domain] @interact def _(gen = selector(['t+1', 't-1', '-1/t'], buttons=True,nrows=1)): global fundamental_domain if gen == 't+1': fundamental_domain = [[x+1,y] for x,y in fundamental_domain] elif gen == 't-1': fundamental_domain = [[x-1,y] for x,y in fundamental_domain] elif gen == '-1/t': new_dom = [] for x,y in fundamental_domain: sq_mod = x^2 + y^2 new_dom.append([(-1)*x/sq_mod, y/sq_mod]) fundamental_domain = new_dom P = polygon(fundamental_domain) P.ymax(1.2); P.ymin(-0.1) P.show() }}} {{attachment:fund_domain.png}} = Multiple Zeta Values or Euler-Zagier numbers = by Akhilesh P. == Computing Multiple Zeta values (Euler-Zagier numbers) == === Word Input === {{{#!sagecell R=RealField(10) @interact def _( weight=(5,(2..20))): n=weight a=[0 for i in range(n-1)] a.append(1) @interact def _(v=('word', input_grid(1, n, default=[a], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x)))), accuracy=(100..100000)): D=accuracy a=[v[i] for i in range(len(v))] DD=int(3.321928*D)+int(R(log(3.321928*D))/R(log(10)))+4 RIF=RealIntervalField(DD) def Li(word): n=int(DD*log(10)/log(2))+1 B=[] L=[] S=[] count=-1 k=len(word) for i in range(k): B.append(RIF('0')) L.append(RIF('0')) if(word[i]==1 and i<k-1): S.append(RIF('0')) count=count+1 T=RIF('1') for m in range(n): T=T/2 B[k-1]=RIF('1')/(m+1) j=count for i in range(k-2,-1,-1): if(word[i]==0): B[i]=B[i+1]/(m+1) elif(word[i]==1): B[i]=S[j]/(m+1) S[j]=S[j]+B[i+1] j=j-1 L[i]=T*B[i]+L[i] L[k-1]=T*B[k-1]+L[k-1] return(L) def dual(a): b=list() b=a b=b[::-1] for i in range(len(b)): b[i]=1-b[i] return(b) def zeta(a): b=dual(a) l1=Li(a)+[1] l2=Li(b)+[1] Z=RIF('0') for i in range(len(l1)): Z=Z+l1[i]*l2[len(a)-i] return(Z) print zeta(a) }}} {{attachment:akhi1.png}} === Composition Input === {{{#!sagecell R=RealField(10) @interact def _( Depth=(5,(2..20))): n=Depth a=[2] a=a+[1 for i in range(n-1)] @interact def _(v=('Composition', input_grid(1, n, default=[a], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x)))), accuracy=(100..100000)): D=accuracy a=[v[i] for i in range(len(v))] def comptobin(a): word=[] for i in range(len(a)): word=word+[0]*(a[i]-1)+[1] return(word) a=comptobin(a) DD=int(3.321928*D)+int(R(log(3.321928*D))/R(log(10)))+4 RIF=RealIntervalField(DD) def Li(word): n=int(DD*log(10)/log(2))+1 B=[] L=[] S=[] count=-1 k=len(word) for i in range(k): B.append(RIF('0')) L.append(RIF('0')) if(word[i]==1 and i<k-1): S.append(RIF('0')) count=count+1 T=RIF('1') for m in range(n): T=T/2 B[k-1]=RIF('1')/(m+1) j=count for i in range(k-2,-1,-1): if(word[i]==0): B[i]=B[i+1]/(m+1) elif(word[i]==1): B[i]=S[j]/(m+1) S[j]=S[j]+B[i+1] j=j-1 L[i]=T*B[i]+L[i] L[k-1]=T*B[k-1]+L[k-1] return(L) def dual(a): b=list() b=a b=b[::-1] for i in range(len(b)): b[i]=1-b[i] return(b) def zeta(a): b=dual(a) l1=Li(a)+[1] l2=Li(b)+[1] Z=RIF('0') for i in range(len(l1)): Z=Z+l1[i]*l2[len(a)-i] return(Z) print zeta(a) }}} {{attachment:akhi5.png}} == Program to Compute Integer Relation between Multiple Zeta Values (Euler-Zagier numbers) == {{{#!sagecell from mpmath import * print "Enter the number of composition" @interact def _( n=(5,(2..20))): a=[] for i in range(n): a.append([i+2,1]) print "In each box Enter composition as an array" @interact def _(v=('Compositions', input_box( default=a, to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x)))), accuracy=(100..100000)): D=accuracy R=RealField(10) a=v def comptobin(a): word=[] for i in range(len(a)): word=word+[0]*(a[i]-1)+[1] return(word) DD=int(D)+int(R(log(3.321928*D))/R(log(10)))+4 RIF=RealIntervalField(DD) mp.dps=DD def Li(word): n=int(DD*log(10)/log(2))+1 B=[] L=[] S=[] count=-1 k=len(word) for i in range(k): B.append(mpf('0')) L.append(mpf('0')) if(word[i]==1 and i<k-1): S.append(mpf('0')) count=count+1 T=mpf('1') for m in range(n): T=T/2 B[k-1]=mpf('1')/(m+1) j=count for i in range(k-2,-1,-1): if(word[i]==0): B[i]=B[i+1]/(m+1) elif(word[i]==1): B[i]=S[j]/(m+1) S[j]=S[j]+B[i+1] j=j-1 L[i]=T*B[i]+L[i] L[k-1]=T*B[k-1]+L[k-1] return(L) def dual(a): b=list() b=a b=b[::-1] for i in range(len(b)): b[i]=1-b[i] return(b) def zeta(a): b=dual(a) l1=Li(a)+[1] l2=Li(b)+[1] Z=mpf('0') for i in range(len(l1)): Z=Z+l1[i]*l2[len(a)-i] return(Z) zet=[] for i in range(n): zet.append((zeta(comptobin(a[i])))) print "zeta(",a[i],")=",zet[i] u=pslq(zet,tol=10**-D,maxcoeff=100,maxsteps=10000) print "the Intger Relation between the above zeta values given by the vector" print u }}} {{attachment:akhi10.png}} == Word to composition == {{{#!sagecell @interact def _( weight=(7,(2..30))): n=weight a=[0 for i in range(n-1)] a.append(1) @interact def _(v=('word', input_grid(1, n, default=[a], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x))))): a=[v[i] for i in range(len(v))] def bintocomp(a): b=[] count=1 for j in range(len(a)): if(a[j]==0): count=count+1 |
| Line 805: | Line 1094: |
| # Compute slope of the curve E in P l=-(3*P[0]^2 + 2*E.a2()*P[0] + E.a4() - E.a1()*P[1])/((-2)*P[1] - E.a1()*P[0] - E.a3()) f(x) = l * (x - P[0]) + P[1] return plot(f(x),-length,length,linestyle=style,rgbcolor=rgb) # Trivial case of P != R where P=O or R=O then we get the vertical line from the other point elif P[2] == 0: return line([(Q[0],-length),(Q[0],length)],linestyle=style,rgbcolor=rgb) elif Q[2] == 0: return line([(P[0],-length),(P[0],length)],linestyle=style,rgbcolor=rgb) # Non trivial case where P != R else: # Case where x_1 = x_2 return vertical line evaluated in Q if P[0] == Q[0]: return line([(P[0],-length),(P[0],length)],linestyle=style,rgbcolor=rgb) #Case where x_1 != x_2 return line trough P,R evaluated in Q" l=(Q[1]-P[1])/(Q[0]-P[0]) f(x) = l * (x - P[0]) + P[1] return plot(f(x),-length,length,linestyle=style,rgbcolor=rgb) }}} {{attachment:PointAddEllipticCurve.png}} |
b.append(count) count=1 return(b) print "Composition is ",bintocomp(a) }}} {{attachment:akhi2.png}} == Composition to Word == {{{#!sagecell @interact def _( Depth=(7,(1..30))): n=Depth a=[] a.append(2) a=a+[1 for i in range(1,n)] @interact def _(v=('composition', input_grid(1, n, default=[a], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x))))): a=[v[i] for i in range(len(v))] def comptobin(a): word=[] for i in range(len(a)): word=word+[0]*(a[i]-1)+[1] return(word) print "Word is ",comptobin(a) }}} {{attachment:akhi3.png}} == Dual of a Word == {{{#!sagecell @interact def _( weight=(7,(2..30))): n=weight a=[0 for i in range(n-1)] a.append(1) @interact def _(v=('word', input_grid(1, n, default=[a], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x))))): a=[v[i] for i in range(len(v))] def dual(a): b=list() b=a b=b[::-1] for i in range(len(b)): b[i]=1-b[i] return(b) print "Dual word is ",dual(a) }}} {{attachment:akhi4.png}} == Shuffle product of two Words == {{{#!sagecell @interact def _( w1=(2,(2..20)), w2=(2,(2..20))): a=[0] b=[0 for i in range(w2-1)] a=a+[1 for i in range(1,w1)] b=b+[1] import itertools #this program gives the list of all binary words of weight n and depth k @interact def _(v1=('word1', input_grid(1, w1, default=[a], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x)))), v2=('word2', input_grid(1, w2, default=[b], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x))))): a=[v1[i] for i in range(len(v1))] b=[v2[i] for i in range(len(v2))] def kbits(n, k): result = [] for bits in itertools.combinations(range(n), k): s = ['0'] * n for bit in bits: s[bit] = '1' result.append(''.join(s)) return result def sort(a,l,m): b=[] n=len(a) for i in range(n): b.append(a[i]) for j in range(l-1,-1,-1): k=0 for t in range(m+1): for i in range(n): if(a[i][j]== t): b[k]=a[i] k=k+1 for i in range(n): a[i]=b[i] return(a) def count(a): n=len(a) b=[] b.append(a[0]) m=[] m.append(1) c=0 for i in range(1,n): if(a[i]==a[i-1]): m[c]=m[c]+1 else: b.append(a[i]) m.append(1) c=c+1 return(b,m) def shuffle(a,b): r=len(a) s=len(b) # Generating an array of strings containing all combinations of weight r+s and depth s M=kbits(r+s,s) n=len(M) a1= [] for i in range(n): a1.append(list(M[i])) # The zeroes are replaced by the entries of a and the ones by the entries of b a2= [] for i in range(n): a2.append([]) count0=0 count1=0 for j in range(s+r): if(a1[i][j]=='0'): a2[i].append(a[count0]) count0=count0+1 if(a1[i][j]=='1'): a2[i].append(b[count1]) count1=count1+1 # Reordering in lexicographic order the entries of a2: this is done by first reordering them according to the last digit, then the next to last digit, etc a3=sort(a2,r+s,max(a+b+[0])) # Getting the same list without repetitions and with multiplicities a4=count(a3) return(a4) c=shuffle(a,b) for i in range(len(c[0])-1): print c[1][i],"*",c[0][i] ,"+ ", print c[1][len(c[0])-1],"*",c[0][len(c[0])-1] }}} {{attachment:akhi6.png}} == Shuffle Regularization at 0 == {{{#!sagecell @interact def _( w=(2,(2..20))): a=[0] a=a+[1 for i in range(1,w)] import itertools #this program gives the list of all binary words of weight n and depth k @interact def _(v=('word', input_grid(1, w, default=[a], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x))))): a=[v[i] for i in range(len(v))] def kbits(n, k): result = [] for bits in itertools.combinations(range(n), k): s = ['0'] * n for bit in bits: s[bit] = '1' result.append(''.join(s)) return result def sort(a,l,m): b=[] n=len(a) for i in range(n): b.append(a[i]) for j in range(l-1,-1,-1): k=0 for t in range(m+1): for i in range(n): if(a[i][j]== t): b[k]=a[i] k=k+1 for i in range(n): a[i]=b[i] return(a) def sort1(a,l,m): b=[] b.append([]) b.append([]) n=len(a[0]) for i in range(n): b[0].append(a[0][i]) b[1].append(a[1][i]) for j in range(l-1,-1,-1): k=0 for t in range(m+1): for i in range(n): if(a[0][i][j]== t): b[0][k]=a[0][i] b[1][k]=a[1][i] k=k+1 for i in range(n): a[0][i]=b[0][i] a[1][i]=b[1][i] return(a) def count(a): n=len(a) b=[] b.append(a[0]) m=[] m.append(1) c=0 for i in range(1,n): if(a[i]==a[i-1]): m[c]=m[c]+1 else: b.append(a[i]) m.append(1) c=c+1 return(b,m) def count1(a): n=len(a[0]) b=[] b.append([]) b.append([]) b[0].append(a[0][0]) b[1].append(a[1][0]) c=0 for i in range(1,n): if(a[0][i]==a[0][i-1]): b[1][c]=b[1][c]+a[1][i] else: b[0].append(a[0][i]) b[1].append(a[1][i]) c=c+1 return(b) def shuffle(a,b): r=len(a) s=len(b) # Generating an array of strings containing all combinations of weight r+s and depth s M=kbits(r+s,s) n=len(M) a1= [] for i in range(n): a1.append(list(M[i])) # The zeroes are replaced by the entries of a and the ones by the entries of b a2= [] for i in range(n): a2.append([]) count0=0 count1=0 for j in range(s+r): if(a1[i][j]=='0'): a2[i].append(a[count0]) count0=count0+1 if(a1[i][j]=='1'): a2[i].append(b[count1]) count1=count1+1 # Reordering in lexicographic order the entries of a2: this is done by first reordering them according to the last digit, then the next to last digit, etc a3=sort(a2,r+s,max(a+b+[0])) # Getting the same list without repetitions and with multiplicities a4=count(a3) return(a4) def Regshuf0(a): r=[] r.append([]) r.append([]) t=0 c=1 for i in range(len(a)+1): if(t==0): b=shuffle(a[:len(a)-i],a[len(a)-i:]) for j in range(len(b[0])): r[0].append(b[0][j]) r[1].append(b[1][j]*c) c=-c if(i<len(a)): if(a[len(a)-1-i]==1): t=1 r=sort1(r,len(a),max(a+[0])) r=count1(r) rg=[] rg.append([]) rg.append([]) for i in range(len(r[0])): if(r[1][i] is not 0): rg[0].append(r[0][i]) rg[1].append(r[1][i]) return(rg) c=Regshuf0(a) for i in range(len(c[0])-1): if(c[1][i] != 0): print c[1][i],"*",c[0][i] ,"+ ", if(c[1][len(c[0])-1] != 0): print c[1][len(c[0])-1],"*",c[0][len(c[0])-1] }}} {{attachment:akhi7.png}} == Shuffle Regularization at 1 == {{{#!sagecell @interact def _( w=(2,(2..20))): a=[0] a=a+[1 for i in range(1,w)] import itertools #this program gives the list of all binary words of weight n and depth k @interact def _(v=('word', input_grid(1, w, default=[a], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x))))): a=[v[i] for i in range(len(v))] def kbits(n, k): result = [] for bits in itertools.combinations(range(n), k): s = ['0'] * n for bit in bits: s[bit] = '1' result.append(''.join(s)) return result def sort(a,l,m): b=[] n=len(a) for i in range(n): b.append(a[i]) for j in range(l-1,-1,-1): k=0 for t in range(m+1): for i in range(n): if(a[i][j]== t): b[k]=a[i] k=k+1 for i in range(n): a[i]=b[i] return(a) def sort1(a,l,m): b=[] b.append([]) b.append([]) n=len(a[0]) for i in range(n): b[0].append(a[0][i]) b[1].append(a[1][i]) for j in range(l-1,-1,-1): k=0 for t in range(m+1): for i in range(n): if(a[0][i][j]== t): b[0][k]=a[0][i] b[1][k]=a[1][i] k=k+1 for i in range(n): a[0][i]=b[0][i] a[1][i]=b[1][i] return(a) def count(a): n=len(a) b=[] b.append(a[0]) m=[] m.append(1) c=0 for i in range(1,n): if(a[i]==a[i-1]): m[c]=m[c]+1 else: b.append(a[i]) m.append(1) c=c+1 return(b,m) def count1(a): n=len(a[0]) b=[] b.append([]) b.append([]) b[0].append(a[0][0]) b[1].append(a[1][0]) c=0 for i in range(1,n): if(a[0][i]==a[0][i-1]): b[1][c]=b[1][c]+a[1][i] else: b[0].append(a[0][i]) b[1].append(a[1][i]) c=c+1 return(b) def shuffle(a,b): r=len(a) s=len(b) # Generating an array of strings containing all combinations of weight r+s and depth s M=kbits(r+s,s) n=len(M) a1= [] for i in range(n): a1.append(list(M[i])) # The zeroes are replaced by the entries of a and the ones by the entries of b a2= [] for i in range(n): a2.append([]) count0=0 count1=0 for j in range(s+r): if(a1[i][j]=='0'): a2[i].append(a[count0]) count0=count0+1 if(a1[i][j]=='1'): a2[i].append(b[count1]) count1=count1+1 # Reordering in lexicographic order the entries of a2: this is done by first reordering them according to the last digit, then the next to last digit, etc a3=sort(a2,r+s,max(a+b+[0])) # Getting the same list without repetitions and with multiplicities a4=count(a3) return(a4) def Regshuf1(a): r=[] r.append([]) r.append([]) t=0 c=1 for i in range(len(a)+1): if(t==0): b=shuffle(a[:i],a[i:]) for j in range(len(b[0])): r[0].append(b[0][j]) r[1].append(b[1][j]*c) c=-c if(i<len(a)): if(a[i]==0): t=1 r=sort1(r,len(a),max(a+[0])) r=count1(r) rg=[] rg.append([]) rg.append([]) for i in range(len(r[0])): if(r[1][i] is not 0): rg[0].append(r[0][i]) rg[1].append(r[1][i]) return(rg) c=Regshuf1(a) for i in range(len(c[0])-1): if(c[1][i] != 0): print c[1][i],"*",c[0][i] ,"+ ", if(c[1][len(c[0])-1] != 0): print c[1][len(c[0])-1],"*",c[0][len(c[0])-1] }}} {{attachment:akhi8.png}} |
Contents
- Integer Factorization
- Prime Numbers
- Modular Forms
- Modular Arithmetic
- Cyclotomic Fields
- Elliptic Curves
- Cryptography
- Other
- Multiple Zeta Values or Euler-Zagier numbers
Integer Factorization
Divisibility Poset
by William Stein
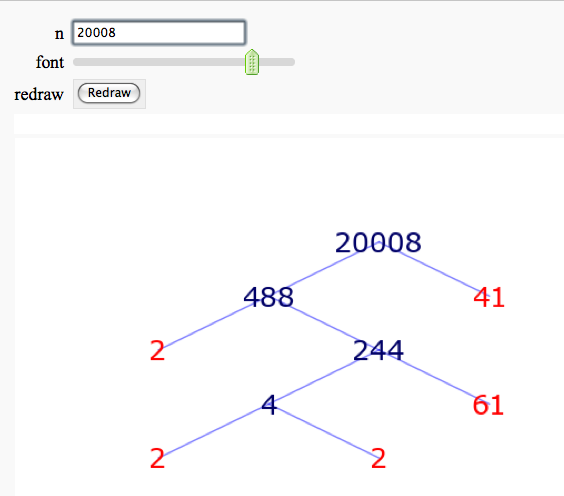
Factor Trees
by William Stein
More complicated demonstration using Mathematica: http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/FactorTrees/
Factoring an Integer
by Timothy Clemans
Sage implementation of the Mathematica demonstration of the same name. http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/FactoringAnInteger/
Prime Numbers
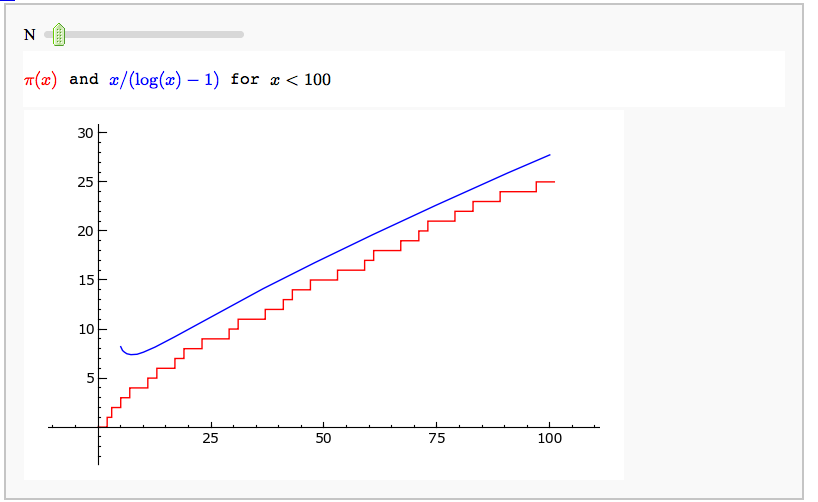
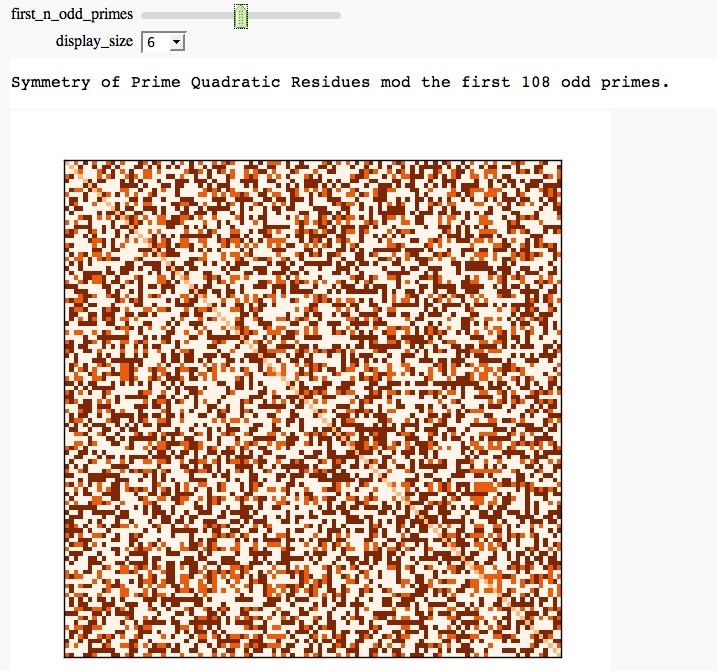
Illustrating the prime number theorem
by William Stein
Prime Spiral - Square FIXME
by David Runde
Prime Spiral - Polar
by David Runde
Modular Forms
Computing modular forms
by William Stein
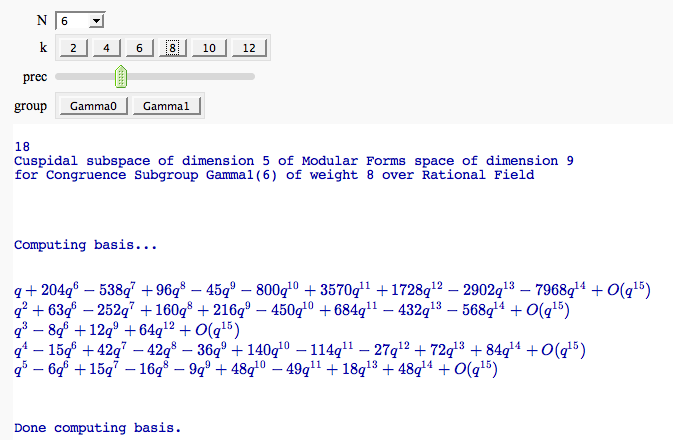
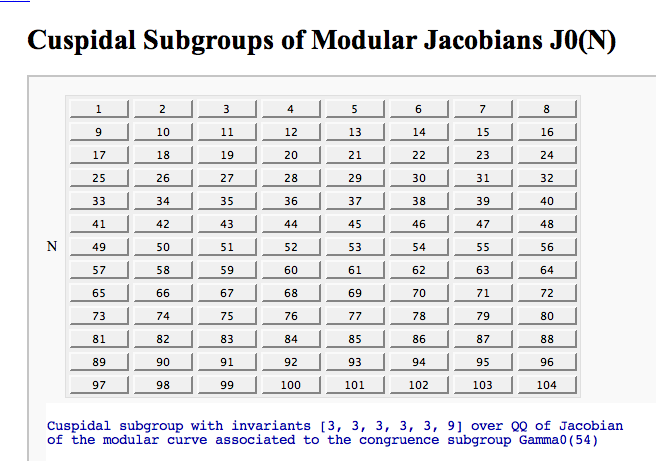
Computing the cuspidal subgroup
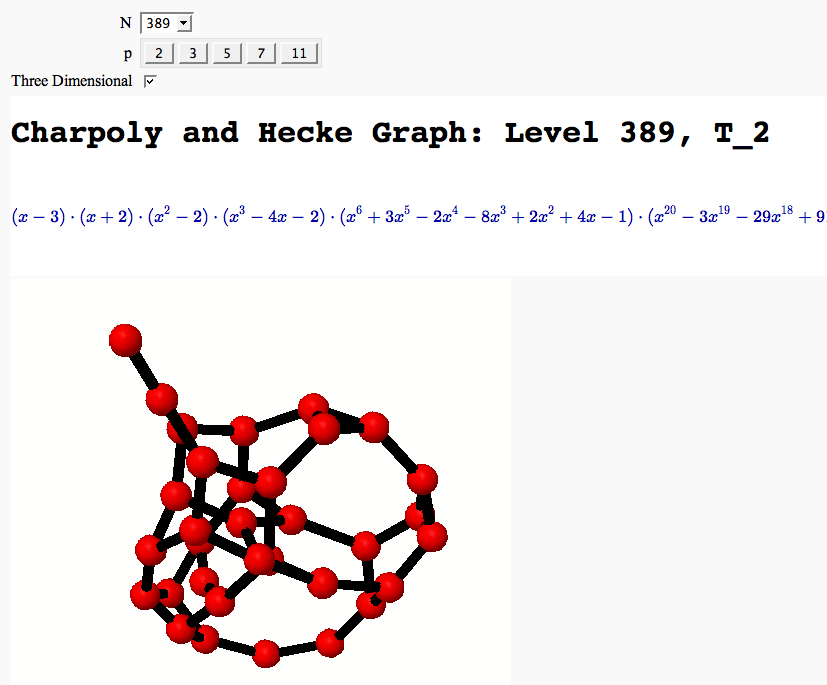
by William Stein
A Charpoly and Hecke Operator Graph
by William Stein
Modular Arithmetic
Quadratic Residue Table FIXME
by Emily Kirkman

Cubic Residue Table FIXME
by Emily Kirkman

Cyclotomic Fields
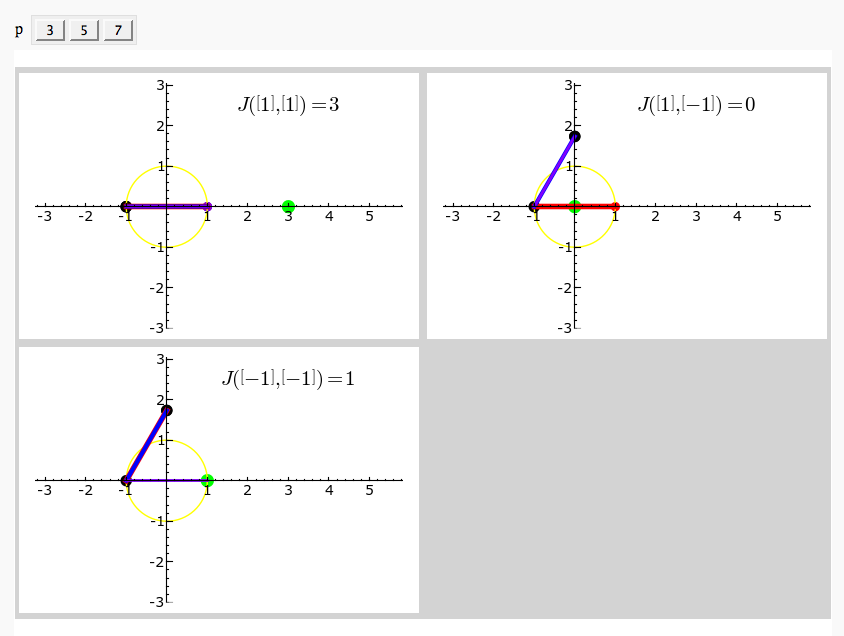
Gauss and Jacobi Sums in Complex Plane
by Emily Kirkman
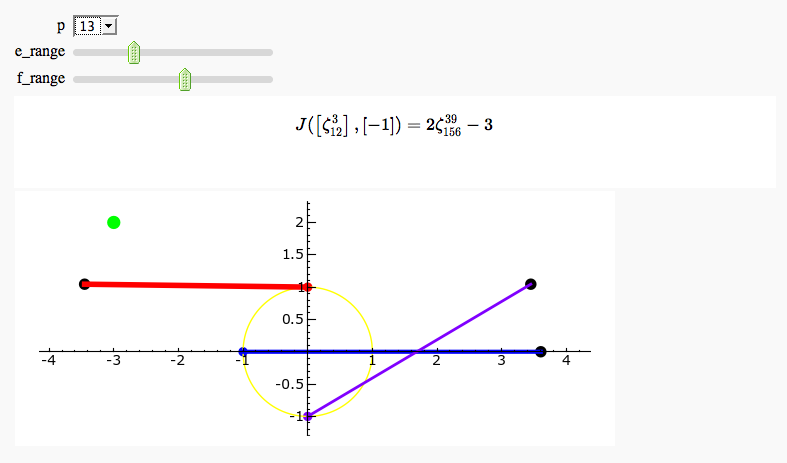
Exhaustive Jacobi Plotter
by Emily Kirkman
Elliptic Curves
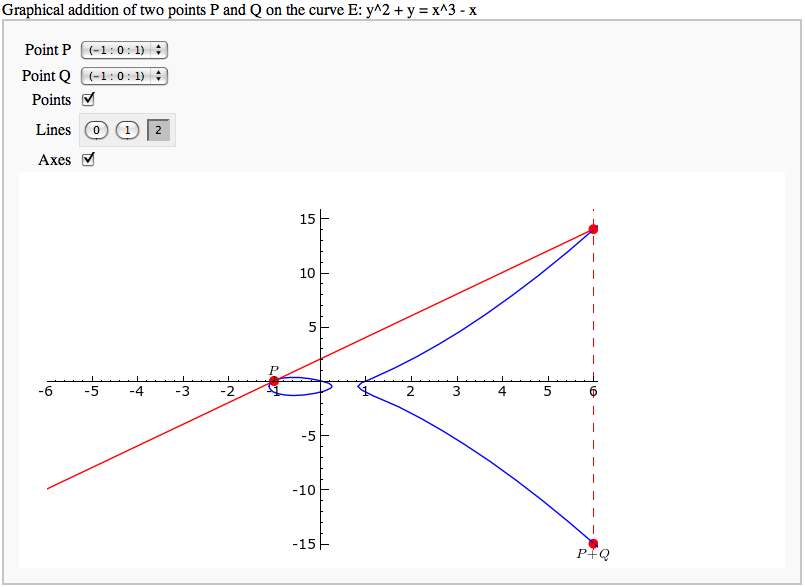
Adding points on an elliptic curve
by David Møller Hansen
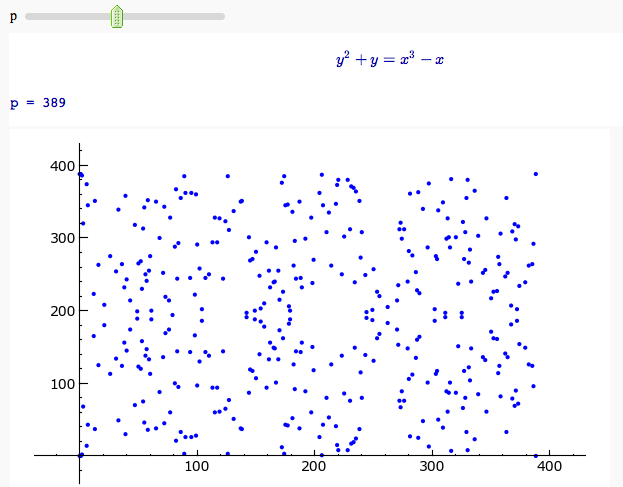
Plotting an elliptic curve over a finite field
Cryptography
The Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange Protocol
by Timothy Clemans and William Stein
Other
Continued Fraction Plotter
by William Stein
Computing Generalized Bernoulli Numbers
by William Stein (Sage-2.10.3)
Fundamental Domains of SL_2(ZZ)
by Robert Miller
Multiple Zeta Values or Euler-Zagier numbers
by Akhilesh P.
Computing Multiple Zeta values (Euler-Zagier numbers)
Word Input
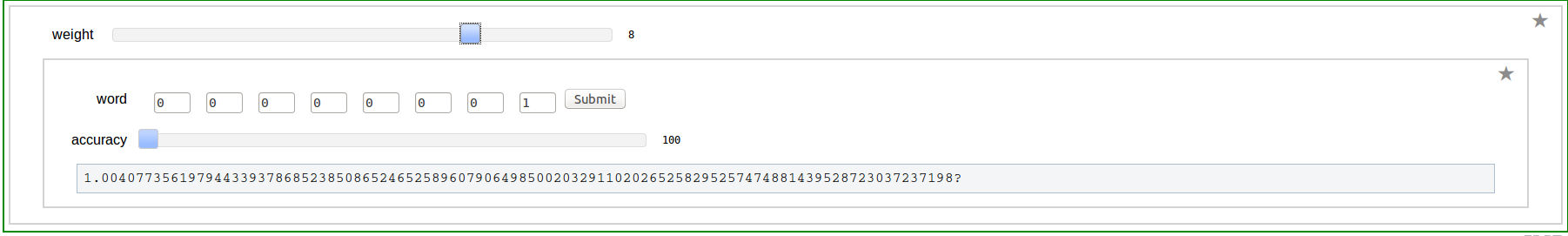
Composition Input
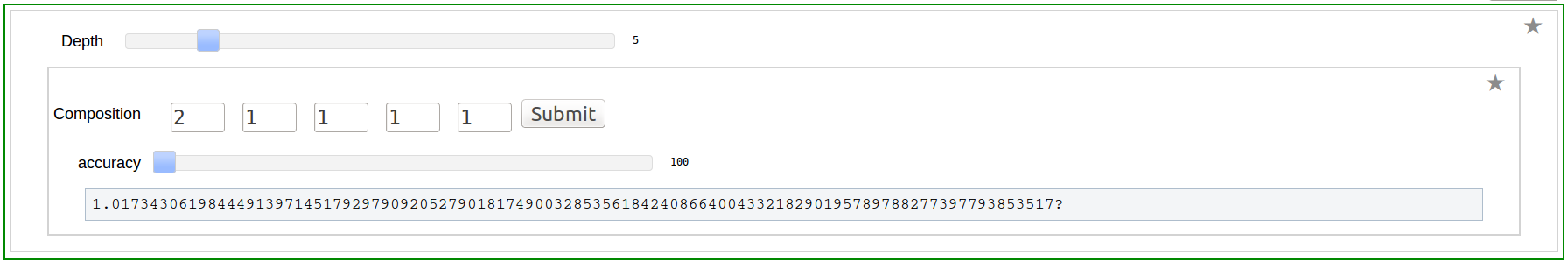
Program to Compute Integer Relation between Multiple Zeta Values (Euler-Zagier numbers)
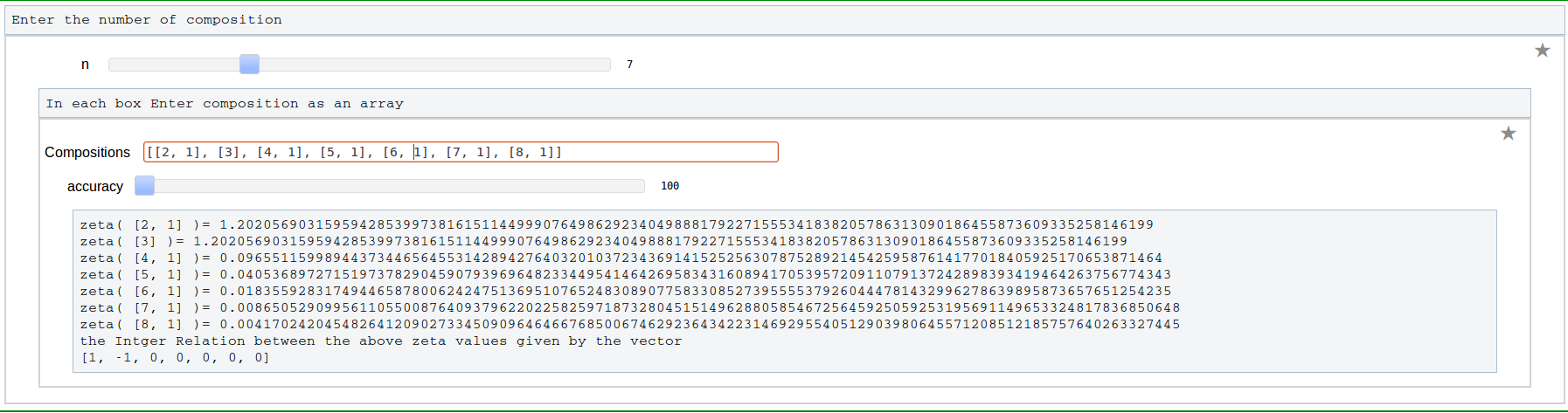
Word to composition
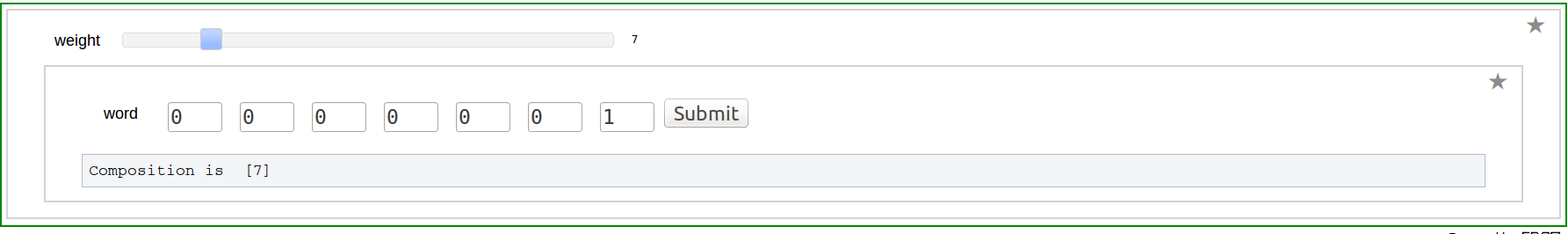
Composition to Word
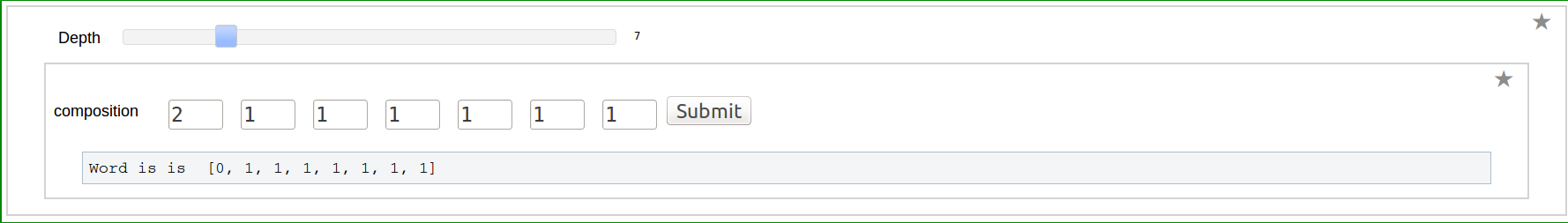
Dual of a Word
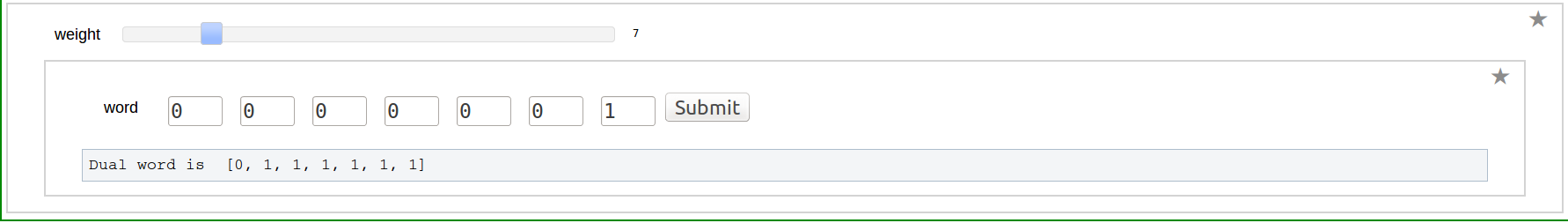
Shuffle product of two Words
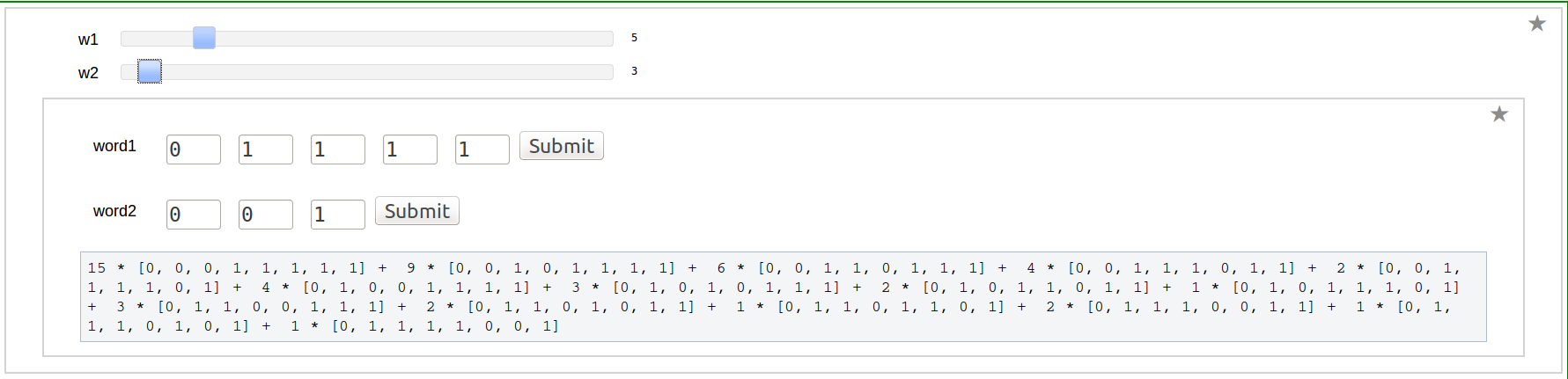
Shuffle Regularization at 0
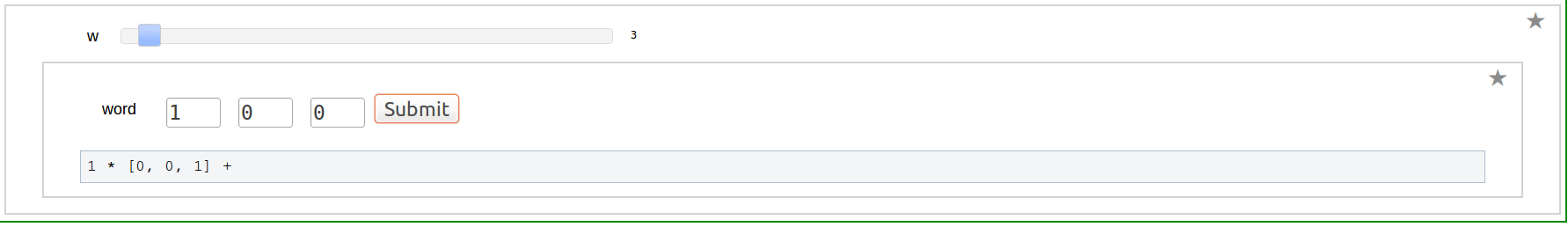
Shuffle Regularization at 1