|
Size: 35452
Comment:
|
Size: 48272
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 872: | Line 872: |
| = Multiple Zeta Values = | = Multiple Zeta Values or Euler-Zagier numbers = |
| Line 874: | Line 874: |
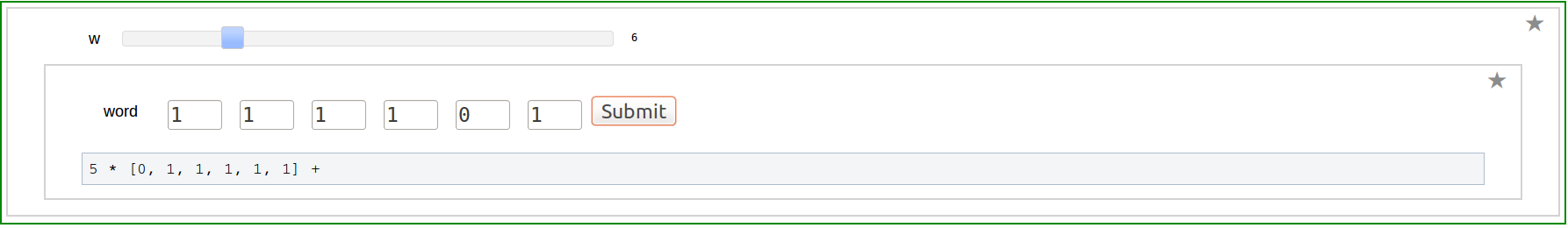
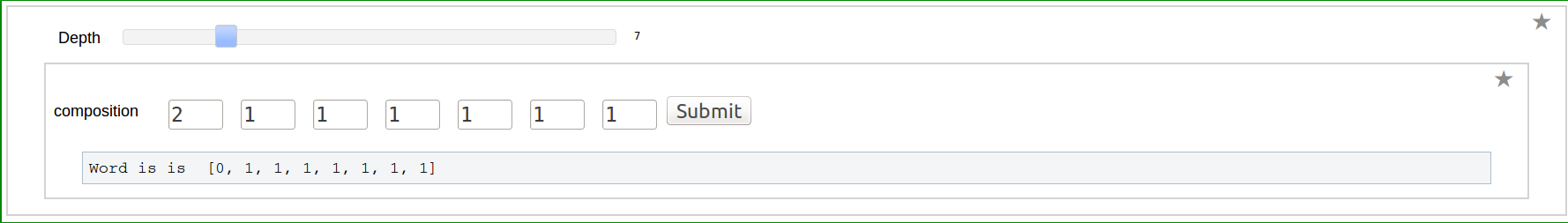
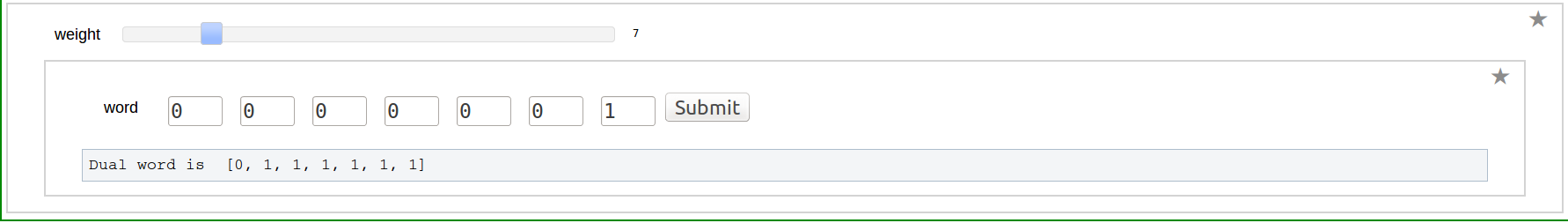
| == Word to composition == {{{#!sagecell @interact def _( weight=(7,(2..30))): n=weight a=[0 for i in range(n-1)] a.append(1) @interact def _(v=('word', input_grid(1, n, default=[a], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x))))): a=[v[i] for i in range(len(v))] def bintocomp(a): b=[] count=1 for j in range(len(a)): if(a[j]==0): count=count+1 else: b.append(count) count=1 return(b) print "Composition is ",bintocomp(a) }}} {{attachment:akhi2.png}} == Composition to Word == {{{#!sagecell @interact def _( Depth=(7,(1..30))): n=Depth a=[] a.append(2) a=a+[1 for i in range(1,n)] @interact def _(v=('composition', input_grid(1, n, default=[a], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x))))): a=[v[i] for i in range(len(v))] def comptobin(a): word=[] for i in range(len(a)): word=word+[0]*(a[i]-1)+[1] return(word) print "Word is ",comptobin(a) }}} {{attachment:akhi3.png}} == Dual of a Word == {{{#!sagecell @interact def _( weight=(7,(2..30))): n=weight a=[0 for i in range(n-1)] a.append(1) @interact def _(v=('word', input_grid(1, n, default=[a], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x))))): a=[v[i] for i in range(len(v))] def dual(a): b=list() b=a b=b[::-1] for i in range(len(b)): b[i]=1-b[i] return(b) print "Dual word is ",dual(a) }}} {{attachment:akhi2.png}} == Computing Multiple Zeta values == |
== Computing Multiple Zeta values (Euler-Zagier numbers) == |
| Line 1071: | Line 1002: |
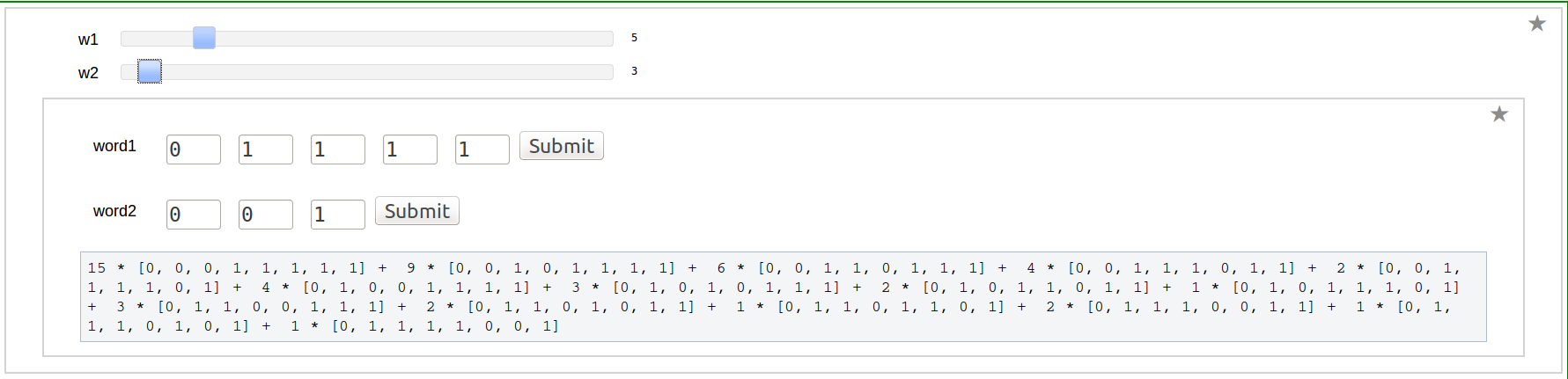
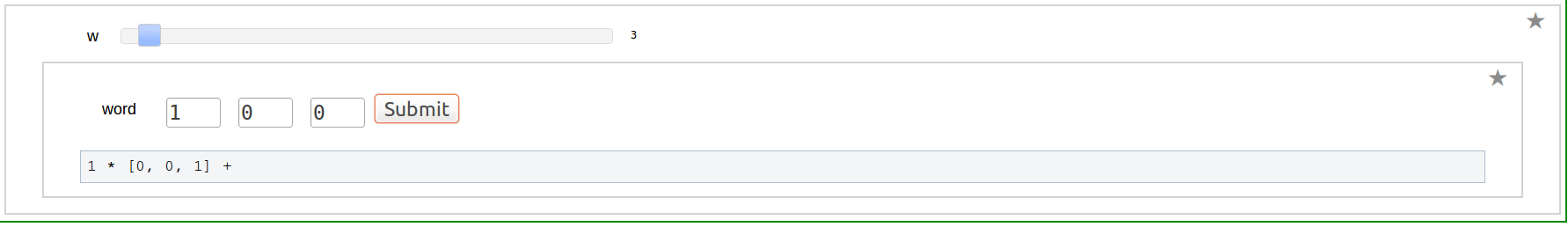
| == Program to Compute Integer Relation between Multiple Zeta Values (Euler-Zagier numbers) == {{{#!sagecell from mpmath import * print "Enter the number of composition" @interact def _( n=(5,(2..20))): a=[] for i in range(n): a.append([i+2,1]) print "In each box Enter composition as an array" @interact def _(v=('Compositions', input_box( default=a, to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x)))), accuracy=(100..100000)): D=accuracy R=RealField(10) a=v def comptobin(a): word=[] for i in range(len(a)): word=word+[0]*(a[i]-1)+[1] return(word) DD=int(D)+int(R(log(3.321928*D))/R(log(10)))+4 RIF=RealIntervalField(DD) mp.dps=DD def Li(word): n=int(DD*log(10)/log(2))+1 B=[] L=[] S=[] count=-1 k=len(word) for i in range(k): B.append(mpf('0')) L.append(mpf('0')) if(word[i]==1 and i<k-1): S.append(mpf('0')) count=count+1 T=mpf('1') for m in range(n): T=T/2 B[k-1]=mpf('1')/(m+1) j=count for i in range(k-2,-1,-1): if(word[i]==0): B[i]=B[i+1]/(m+1) elif(word[i]==1): B[i]=S[j]/(m+1) S[j]=S[j]+B[i+1] j=j-1 L[i]=T*B[i]+L[i] L[k-1]=T*B[k-1]+L[k-1] return(L) def dual(a): b=list() b=a b=b[::-1] for i in range(len(b)): b[i]=1-b[i] return(b) def zeta(a): b=dual(a) l1=Li(a)+[1] l2=Li(b)+[1] Z=mpf('0') for i in range(len(l1)): Z=Z+l1[i]*l2[len(a)-i] return(Z) zet=[] for i in range(n): zet.append((zeta(comptobin(a[i])))) print "zeta(",a[i],")=",zet[i] u=pslq(zet,tol=10**-D,maxcoeff=100,maxsteps=10000) print "the Intger Relation between the above zeta values given by the vector" print u }}} {{attachment:akhi10.png}} == Word to composition == {{{#!sagecell @interact def _( weight=(7,(2..30))): n=weight a=[0 for i in range(n-1)] a.append(1) @interact def _(v=('word', input_grid(1, n, default=[a], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x))))): a=[v[i] for i in range(len(v))] def bintocomp(a): b=[] count=1 for j in range(len(a)): if(a[j]==0): count=count+1 else: b.append(count) count=1 return(b) print "Composition is ",bintocomp(a) }}} {{attachment:akhi2.png}} == Composition to Word == {{{#!sagecell @interact def _( Depth=(7,(1..30))): n=Depth a=[] a.append(2) a=a+[1 for i in range(1,n)] @interact def _(v=('composition', input_grid(1, n, default=[a], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x))))): a=[v[i] for i in range(len(v))] def comptobin(a): word=[] for i in range(len(a)): word=word+[0]*(a[i]-1)+[1] return(word) print "Word is ",comptobin(a) }}} {{attachment:akhi3.png}} == Dual of a Word == {{{#!sagecell @interact def _( weight=(7,(2..30))): n=weight a=[0 for i in range(n-1)] a.append(1) @interact def _(v=('word', input_grid(1, n, default=[a], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x))))): a=[v[i] for i in range(len(v))] def dual(a): b=list() b=a b=b[::-1] for i in range(len(b)): b[i]=1-b[i] return(b) print "Dual word is ",dual(a) }}} {{attachment:akhi4.png}} == Shuffle product of two Words == {{{#!sagecell @interact def _( w1=(2,(2..20)), w2=(2,(2..20))): a=[0] b=[0 for i in range(w2-1)] a=a+[1 for i in range(1,w1)] b=b+[1] import itertools #this program gives the list of all binary words of weight n and depth k @interact def _(v1=('word1', input_grid(1, w1, default=[a], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x)))), v2=('word2', input_grid(1, w2, default=[b], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x))))): a=[v1[i] for i in range(len(v1))] b=[v2[i] for i in range(len(v2))] def kbits(n, k): result = [] for bits in itertools.combinations(range(n), k): s = ['0'] * n for bit in bits: s[bit] = '1' result.append(''.join(s)) return result def sort(a,l,m): b=[] n=len(a) for i in range(n): b.append(a[i]) for j in range(l-1,-1,-1): k=0 for t in range(m+1): for i in range(n): if(a[i][j]== t): b[k]=a[i] k=k+1 for i in range(n): a[i]=b[i] return(a) def count(a): n=len(a) b=[] b.append(a[0]) m=[] m.append(1) c=0 for i in range(1,n): if(a[i]==a[i-1]): m[c]=m[c]+1 else: b.append(a[i]) m.append(1) c=c+1 return(b,m) def shuffle(a,b): r=len(a) s=len(b) # Generating an array of strings containing all combinations of weight r+s and depth s M=kbits(r+s,s) n=len(M) a1= [] for i in range(n): a1.append(list(M[i])) # The zeroes are replaced by the entries of a and the ones by the entries of b a2= [] for i in range(n): a2.append([]) count0=0 count1=0 for j in range(s+r): if(a1[i][j]=='0'): a2[i].append(a[count0]) count0=count0+1 if(a1[i][j]=='1'): a2[i].append(b[count1]) count1=count1+1 # Reordering in lexicographic order the entries of a2: this is done by first reordering them according to the last digit, then the next to last digit, etc a3=sort(a2,r+s,max(a+b+[0])) # Getting the same list without repetitions and with multiplicities a4=count(a3) return(a4) c=shuffle(a,b) for i in range(len(c[0])-1): print c[1][i],"*",c[0][i] ,"+ ", print c[1][len(c[0])-1],"*",c[0][len(c[0])-1] }}} {{attachment:akhi6.png}} == Shuffle Regularization at 0 == {{{#!sagecell @interact def _( w=(2,(2..20))): a=[0] a=a+[1 for i in range(1,w)] import itertools #this program gives the list of all binary words of weight n and depth k @interact def _(v=('word', input_grid(1, w, default=[a], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x))))): a=[v[i] for i in range(len(v))] def kbits(n, k): result = [] for bits in itertools.combinations(range(n), k): s = ['0'] * n for bit in bits: s[bit] = '1' result.append(''.join(s)) return result def sort(a,l,m): b=[] n=len(a) for i in range(n): b.append(a[i]) for j in range(l-1,-1,-1): k=0 for t in range(m+1): for i in range(n): if(a[i][j]== t): b[k]=a[i] k=k+1 for i in range(n): a[i]=b[i] return(a) def sort1(a,l,m): b=[] b.append([]) b.append([]) n=len(a[0]) for i in range(n): b[0].append(a[0][i]) b[1].append(a[1][i]) for j in range(l-1,-1,-1): k=0 for t in range(m+1): for i in range(n): if(a[0][i][j]== t): b[0][k]=a[0][i] b[1][k]=a[1][i] k=k+1 for i in range(n): a[0][i]=b[0][i] a[1][i]=b[1][i] return(a) def count(a): n=len(a) b=[] b.append(a[0]) m=[] m.append(1) c=0 for i in range(1,n): if(a[i]==a[i-1]): m[c]=m[c]+1 else: b.append(a[i]) m.append(1) c=c+1 return(b,m) def count1(a): n=len(a[0]) b=[] b.append([]) b.append([]) b[0].append(a[0][0]) b[1].append(a[1][0]) c=0 for i in range(1,n): if(a[0][i]==a[0][i-1]): b[1][c]=b[1][c]+a[1][i] else: b[0].append(a[0][i]) b[1].append(a[1][i]) c=c+1 return(b) def shuffle(a,b): r=len(a) s=len(b) # Generating an array of strings containing all combinations of weight r+s and depth s M=kbits(r+s,s) n=len(M) a1= [] for i in range(n): a1.append(list(M[i])) # The zeroes are replaced by the entries of a and the ones by the entries of b a2= [] for i in range(n): a2.append([]) count0=0 count1=0 for j in range(s+r): if(a1[i][j]=='0'): a2[i].append(a[count0]) count0=count0+1 if(a1[i][j]=='1'): a2[i].append(b[count1]) count1=count1+1 # Reordering in lexicographic order the entries of a2: this is done by first reordering them according to the last digit, then the next to last digit, etc a3=sort(a2,r+s,max(a+b+[0])) # Getting the same list without repetitions and with multiplicities a4=count(a3) return(a4) def Regshuf0(a): r=[] r.append([]) r.append([]) t=0 c=1 for i in range(len(a)+1): if(t==0): b=shuffle(a[:len(a)-i],a[len(a)-i:]) for j in range(len(b[0])): r[0].append(b[0][j]) r[1].append(b[1][j]*c) c=-c if(i<len(a)): if(a[len(a)-1-i]==1): t=1 r=sort1(r,len(a),max(a+[0])) r=count1(r) rg=[] rg.append([]) rg.append([]) for i in range(len(r[0])): if(r[1][i] is not 0): rg[0].append(r[0][i]) rg[1].append(r[1][i]) return(rg) c=Regshuf0(a) for i in range(len(c[0])-1): if(c[1][i] != 0): print c[1][i],"*",c[0][i] ,"+ ", if(c[1][len(c[0])-1] != 0): print c[1][len(c[0])-1],"*",c[0][len(c[0])-1] }}} {{attachment:akhi7.png}} == Shuffle Regularization at 1 == {{{#!sagecell @interact def _( w=(2,(2..20))): a=[0] a=a+[1 for i in range(1,w)] import itertools #this program gives the list of all binary words of weight n and depth k @interact def _(v=('word', input_grid(1, w, default=[a], to_value=lambda x: vector(flatten(x))))): a=[v[i] for i in range(len(v))] def kbits(n, k): result = [] for bits in itertools.combinations(range(n), k): s = ['0'] * n for bit in bits: s[bit] = '1' result.append(''.join(s)) return result def sort(a,l,m): b=[] n=len(a) for i in range(n): b.append(a[i]) for j in range(l-1,-1,-1): k=0 for t in range(m+1): for i in range(n): if(a[i][j]== t): b[k]=a[i] k=k+1 for i in range(n): a[i]=b[i] return(a) def sort1(a,l,m): b=[] b.append([]) b.append([]) n=len(a[0]) for i in range(n): b[0].append(a[0][i]) b[1].append(a[1][i]) for j in range(l-1,-1,-1): k=0 for t in range(m+1): for i in range(n): if(a[0][i][j]== t): b[0][k]=a[0][i] b[1][k]=a[1][i] k=k+1 for i in range(n): a[0][i]=b[0][i] a[1][i]=b[1][i] return(a) def count(a): n=len(a) b=[] b.append(a[0]) m=[] m.append(1) c=0 for i in range(1,n): if(a[i]==a[i-1]): m[c]=m[c]+1 else: b.append(a[i]) m.append(1) c=c+1 return(b,m) def count1(a): n=len(a[0]) b=[] b.append([]) b.append([]) b[0].append(a[0][0]) b[1].append(a[1][0]) c=0 for i in range(1,n): if(a[0][i]==a[0][i-1]): b[1][c]=b[1][c]+a[1][i] else: b[0].append(a[0][i]) b[1].append(a[1][i]) c=c+1 return(b) def shuffle(a,b): r=len(a) s=len(b) # Generating an array of strings containing all combinations of weight r+s and depth s M=kbits(r+s,s) n=len(M) a1= [] for i in range(n): a1.append(list(M[i])) # The zeroes are replaced by the entries of a and the ones by the entries of b a2= [] for i in range(n): a2.append([]) count0=0 count1=0 for j in range(s+r): if(a1[i][j]=='0'): a2[i].append(a[count0]) count0=count0+1 if(a1[i][j]=='1'): a2[i].append(b[count1]) count1=count1+1 # Reordering in lexicographic order the entries of a2: this is done by first reordering them according to the last digit, then the next to last digit, etc a3=sort(a2,r+s,max(a+b+[0])) # Getting the same list without repetitions and with multiplicities a4=count(a3) return(a4) def Regshuf1(a): r=[] r.append([]) r.append([]) t=0 c=1 for i in range(len(a)+1): if(t==0): b=shuffle(a[:i],a[i:]) for j in range(len(b[0])): r[0].append(b[0][j]) r[1].append(b[1][j]*c) c=-c if(i<len(a)): if(a[i]==0): t=1 r=sort1(r,len(a),max(a+[0])) r=count1(r) rg=[] rg.append([]) rg.append([]) for i in range(len(r[0])): if(r[1][i] is not 0): rg[0].append(r[0][i]) rg[1].append(r[1][i]) return(rg) c=Regshuf1(a) for i in range(len(c[0])-1): if(c[1][i] != 0): print c[1][i],"*",c[0][i] ,"+ ", if(c[1][len(c[0])-1] != 0): print c[1][len(c[0])-1],"*",c[0][len(c[0])-1] }}} {{attachment:akhi8.png}} |
Contents
- Integer Factorization
- Prime Numbers
- Modular Forms
- Modular Arithmetic
- Cyclotomic Fields
- Elliptic Curves
- Cryptography
- Other
- Multiple Zeta Values or Euler-Zagier numbers
Integer Factorization
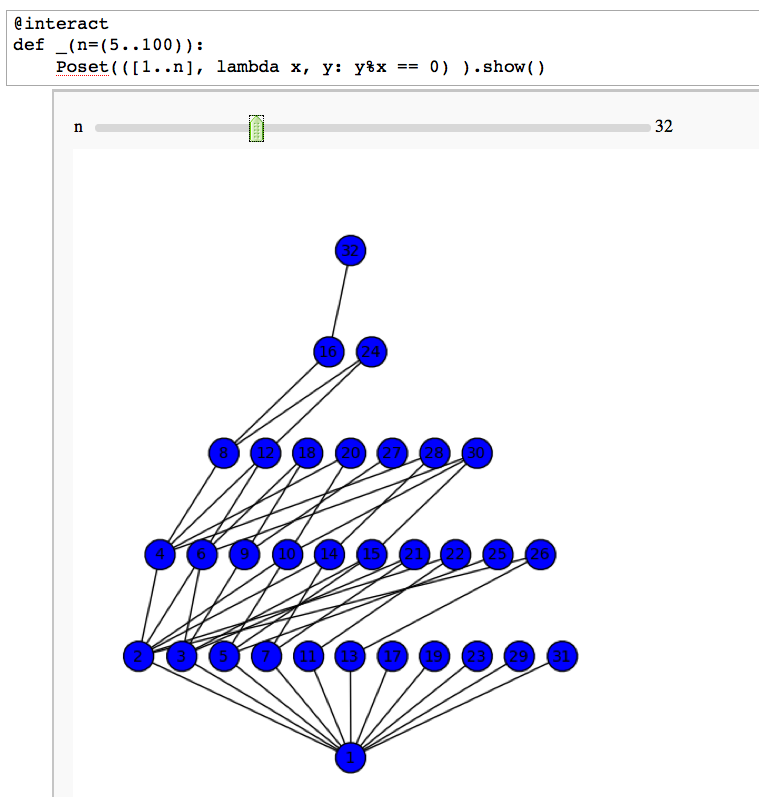
Divisibility Poset
by William Stein
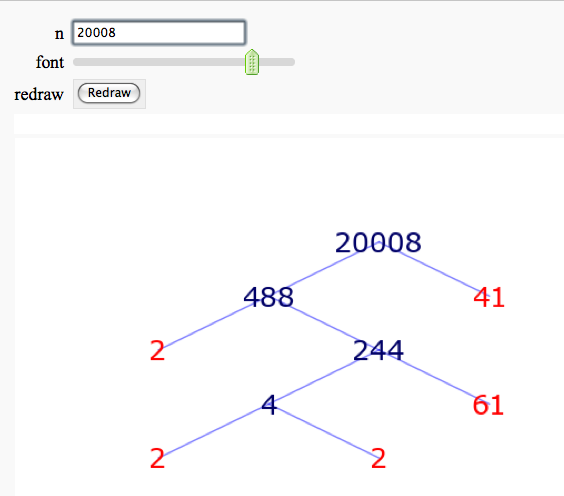
Factor Trees
by William Stein
More complicated demonstration using Mathematica: http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/FactorTrees/
Factoring an Integer
by Timothy Clemans
Sage implementation of the Mathematica demonstration of the same name. http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/FactoringAnInteger/
Prime Numbers
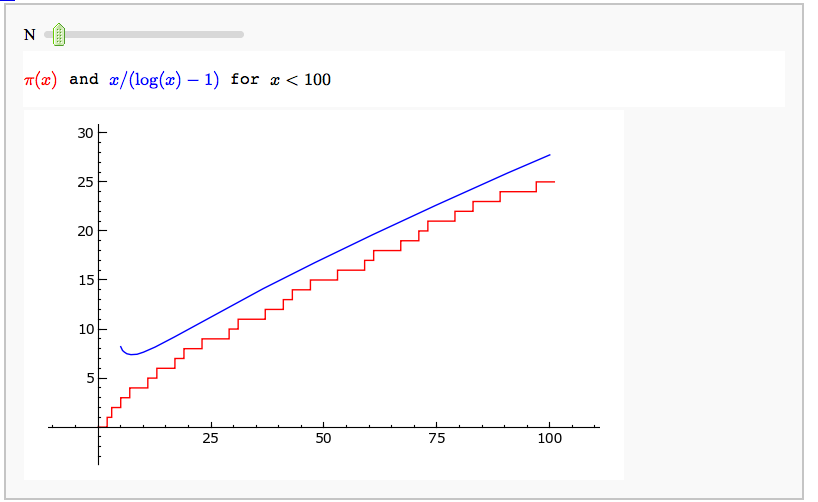
Illustrating the prime number theorem
by William Stein
Prime Spiral - Square FIXME
by David Runde
Prime Spiral - Polar
by David Runde
Modular Forms
Computing modular forms
by William Stein
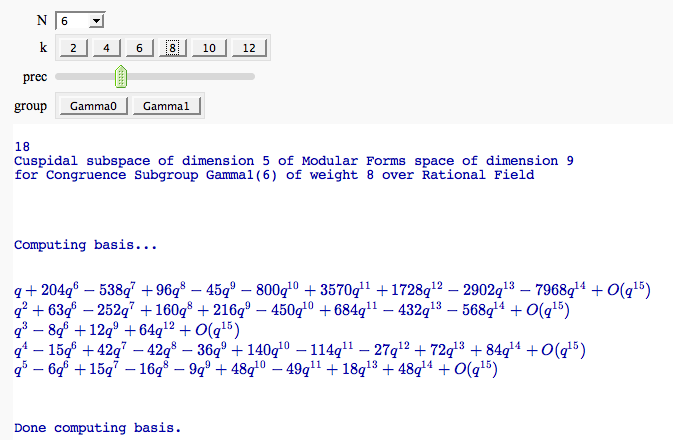
Computing the cuspidal subgroup
by William Stein
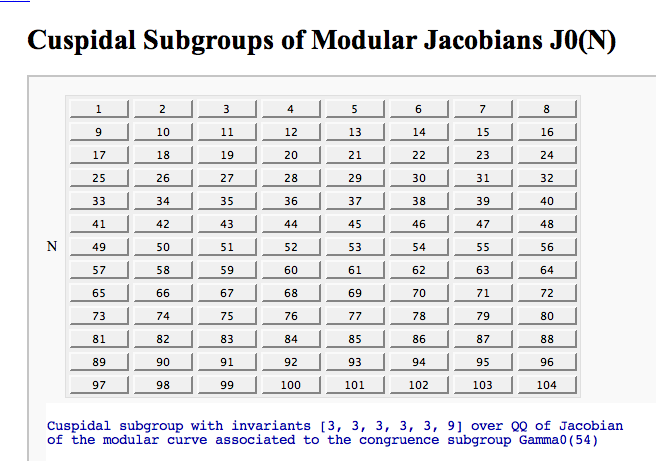
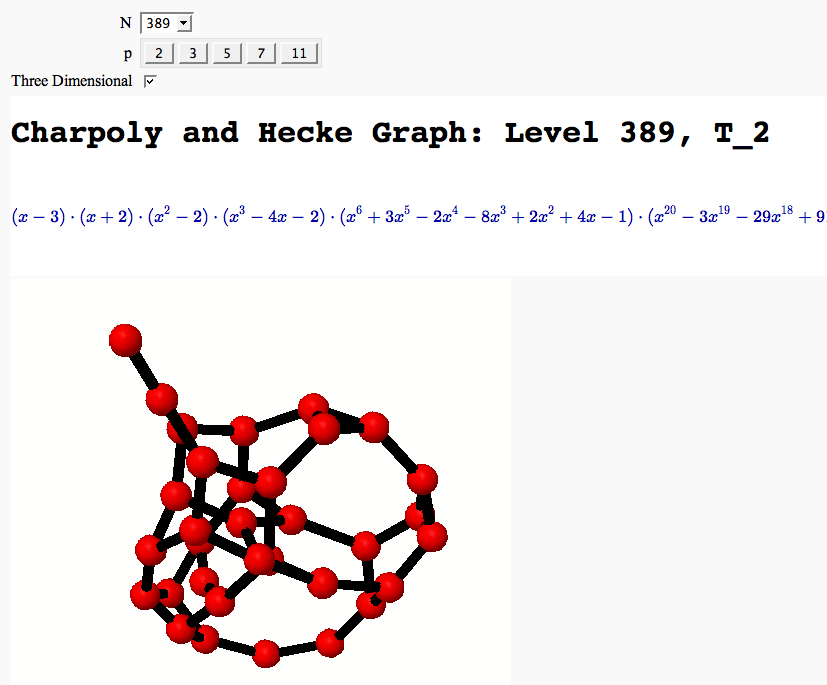
A Charpoly and Hecke Operator Graph
by William Stein
Modular Arithmetic
Quadratic Residue Table FIXME
by Emily Kirkman

Cubic Residue Table FIXME
by Emily Kirkman

Cyclotomic Fields
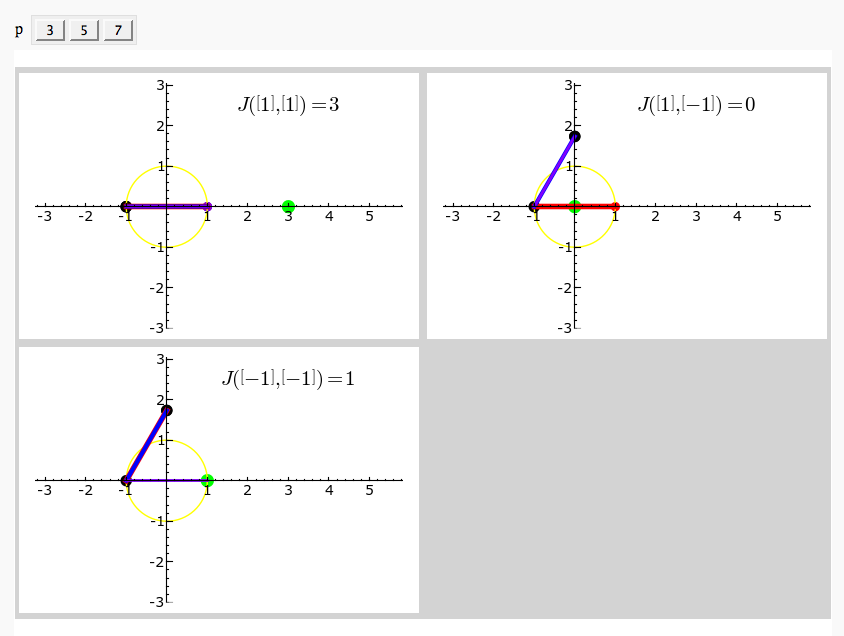
Gauss and Jacobi Sums in Complex Plane
by Emily Kirkman
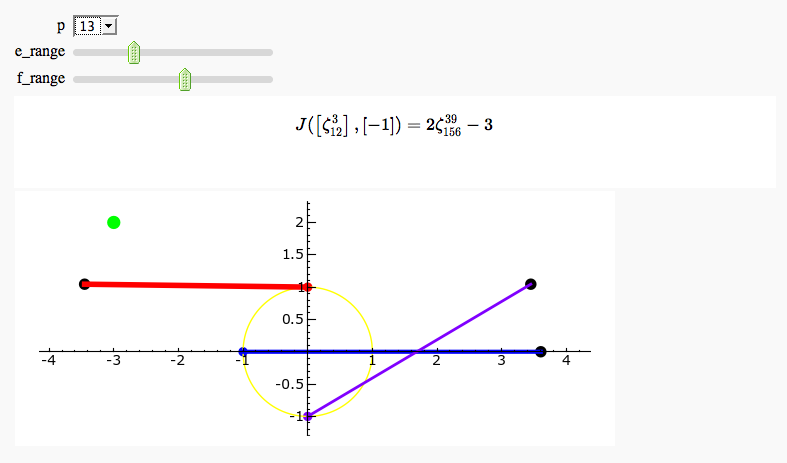
Exhaustive Jacobi Plotter
by Emily Kirkman
Elliptic Curves
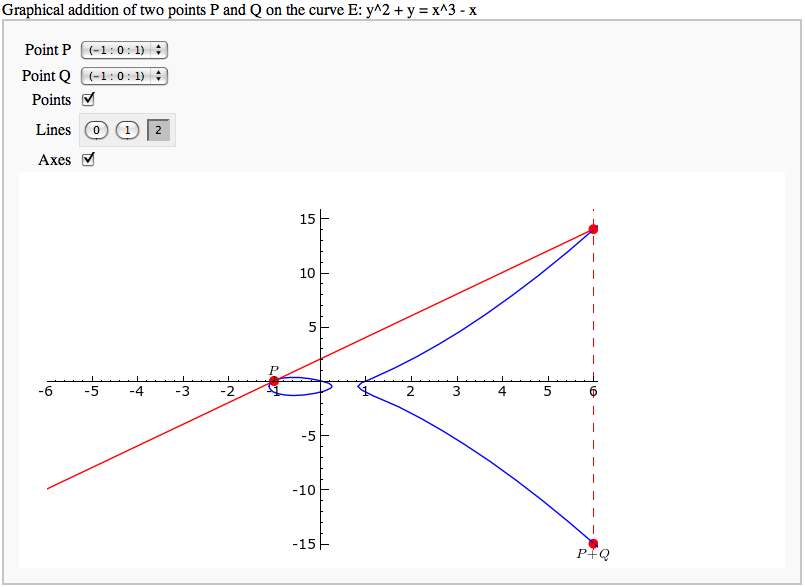
Adding points on an elliptic curve
by David Møller Hansen
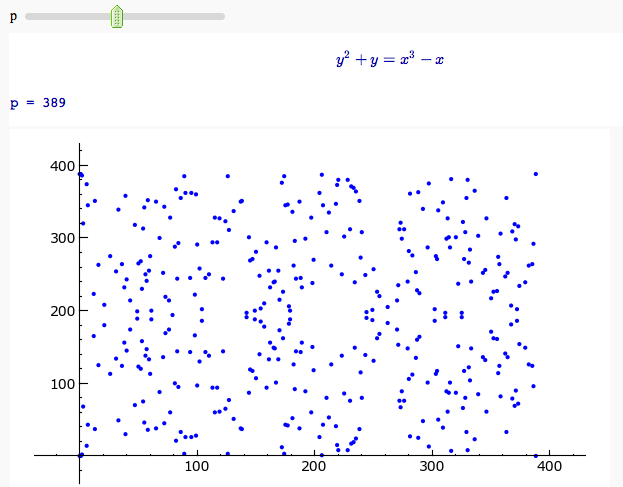
Plotting an elliptic curve over a finite field
Cryptography
The Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange Protocol
by Timothy Clemans and William Stein
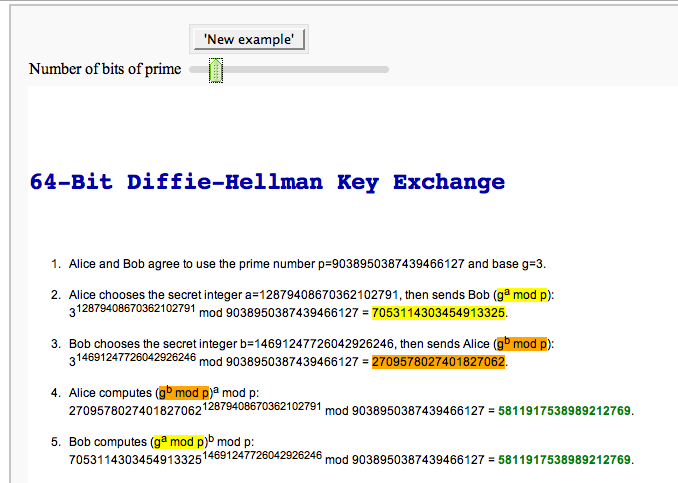
Other
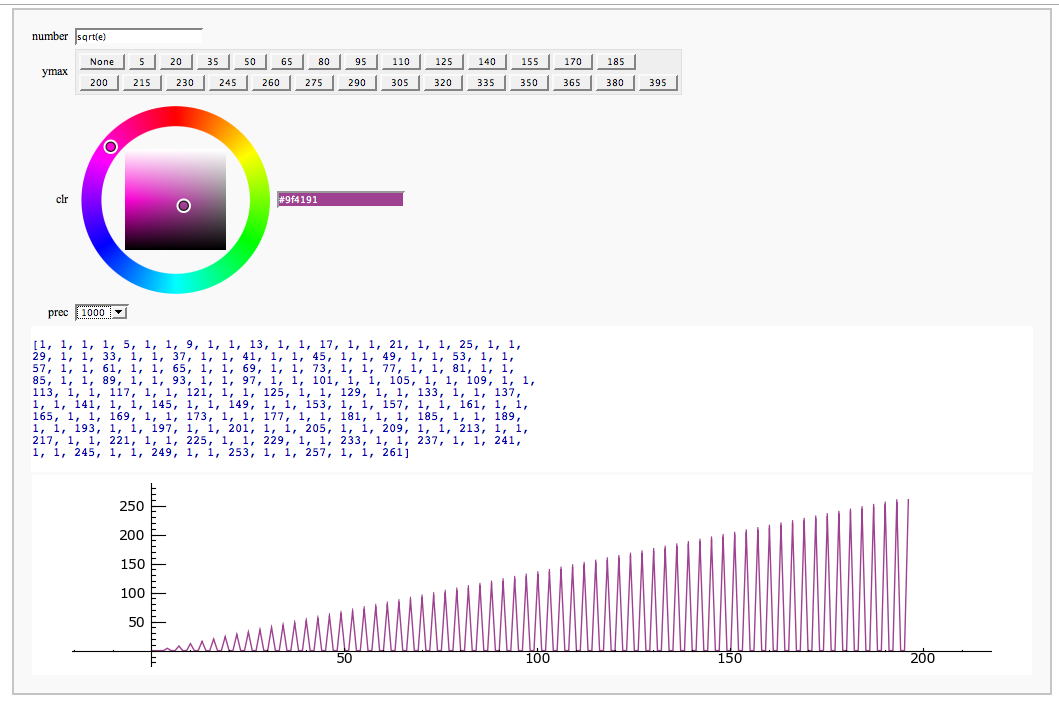
Continued Fraction Plotter
by William Stein
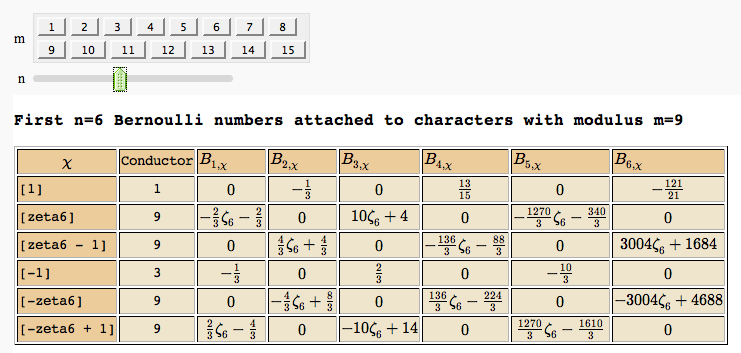
Computing Generalized Bernoulli Numbers
by William Stein (Sage-2.10.3)
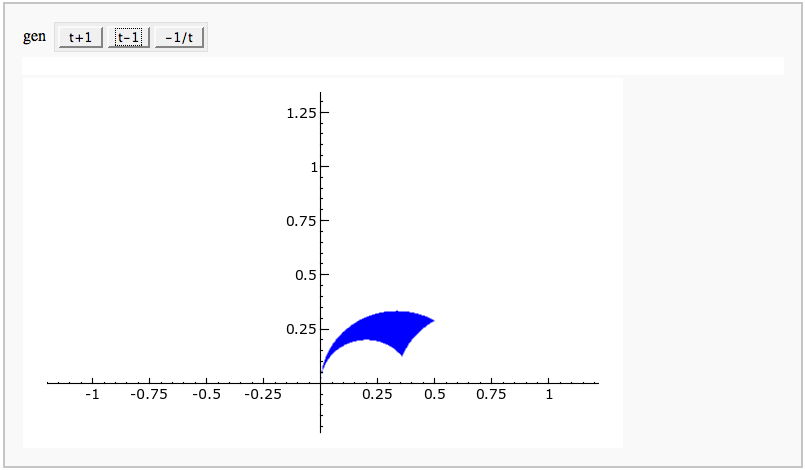
Fundamental Domains of SL_2(ZZ)
by Robert Miller
Multiple Zeta Values or Euler-Zagier numbers
by Akhilesh P.
Computing Multiple Zeta values (Euler-Zagier numbers)
Word Input
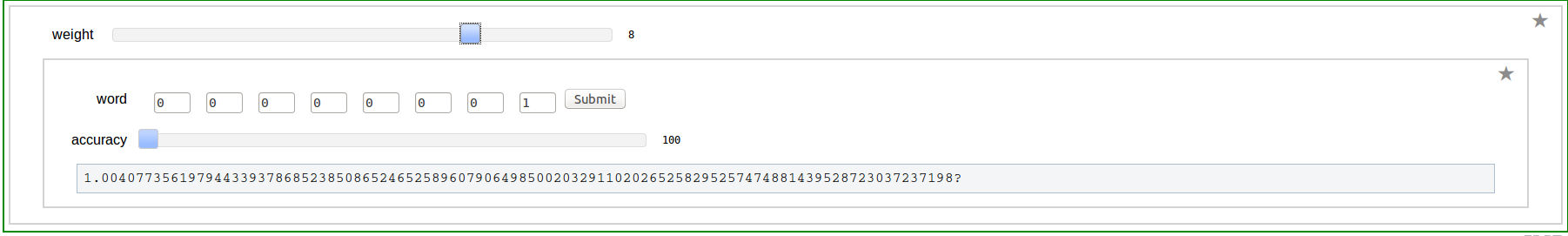
Composition Input
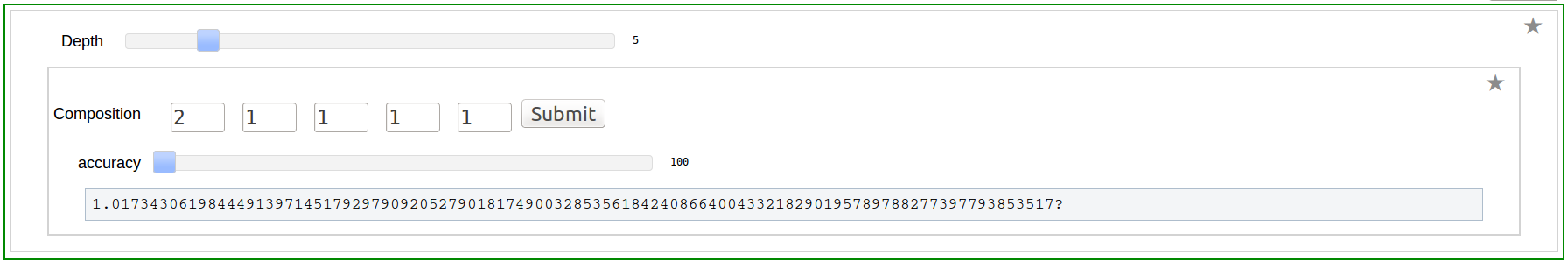
Program to Compute Integer Relation between Multiple Zeta Values (Euler-Zagier numbers)
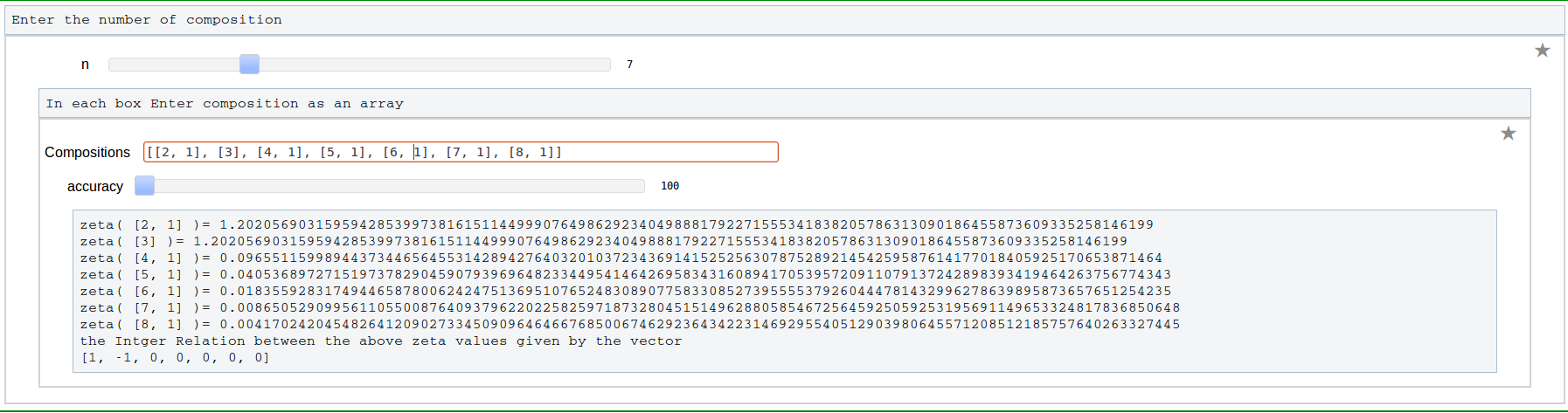
Word to composition
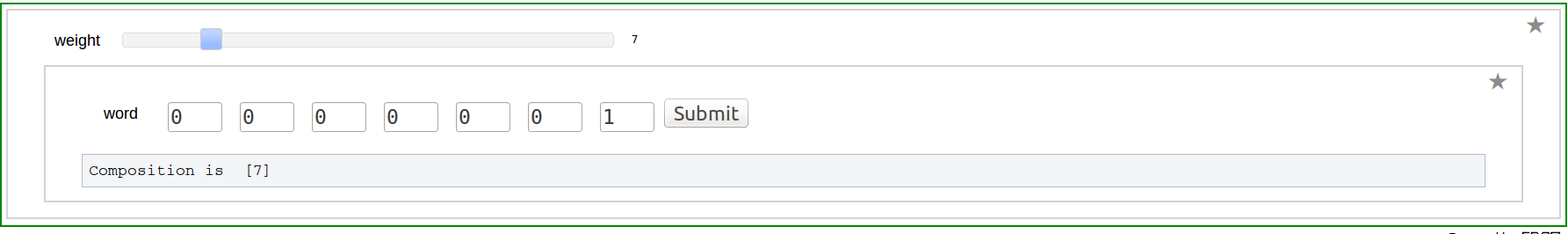
Composition to Word
Dual of a Word
Shuffle product of two Words
Shuffle Regularization at 0
Shuffle Regularization at 1